Abstract
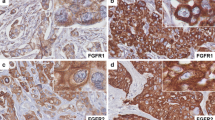
Invasive breast carcinomas are heterogeneous and exhibit distinct molecular features and biological behavior. Understanding the underlying molecular events that promote breast cancer progression is necessary to improve treatment and prognostication. TGF-β receptor III (TBR3) is a member of the TGF-β signaling pathway, with functions in cell proliferation and migration in malignancies, including breast cancer. Recent studies propose that TBR3 may function as a tumor suppressor and that its loss may correlate with disease progression. However, there are limited data on the expression of TBR3 in breast cancer in relationship to tumor type, hormonal receptor status and HER-2/neu, and patient outcome. In this study, we investigated the expression of TBR3 in a cohort of 205 primary invasive breast carcinomas in tissue microarrays (TMAs), with comprehensive clinical, pathological and follow- up information. Sections were stained for TBR3 and evaluated for intensity of reactivity based on a 4-tiered scoring system (1 to 4; TBR3 low = scores 1–2; TBR3 high = scores 3–4). Of the 205 invasive carcinomas, 123 were luminal type (95 type A, 28 type B), 8 were HER-2 type, and 62 were triple negative (TN). TBR3 was high in 112 (55 %) and low in 93 (45 %) cases. Low TBR3 was associated with higher histological grade and worse disease free and overall survival, all features of biologically aggressive breast carcinomas. TBR3 was significantly associated with the subtype of breast cancer, as low TBR3 was detected in 95 % of TN compared to 22 % of luminal tumors (p < 0.0001). We discovered a significant association between low TBR3 protein expression, TN breast cancer phenotype, and disease progression. These data suggest that TBR3 loss might be linked to the development of TN breast cancers and pave the way to investigating whether restoring TBR3 function may be a therapeutic strategy against TN breast carcinomas.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andres JL, Stanley K, Cheifetz S, Massague J (1989) Membrane-anchored and soluble forms of betaglycan, a polymorphic proteoglycan that binds transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol 109:3137–45
Bandyopadhyay A, Zhu Y, Malik SN, Kreisberg J, Brattain MG, Sprague EA, Luo J, López-Casillas F, Sun LZ (2002) Extracellular domain of TGFβ type III receptor inhibits angiogenesis and tumor growth in human cancer cells. Oncogene 21:3541–51
Bieche I, Khodja A, Lidereau R (1999) Deletion mapping of chromosomal region 1p32-pter in primary breast cancer. Gene Chromosome Cancer 24:255–263
Borg A, Zhang QX, Olsson H, Wenngren E (1992) Chromosome 1 alterations in breast cancer: allelic loss on 1p and 1q is related to lymphogenic metastases and poor prognosis. Gene Chromosome Cancer 5:311–320
Dalal BI, Keown PA, Greenberg AH (1993) Immunocytochemical localization of secreted transforming growth factor-beta 1 to the advancing edges of primary tumors and to lymph node metastases of human mammary carcinoma. Am J Pathol 143:381–389
Diaz LK, Cryns VL, Symmans WF, Sneige N (2007) Triple negative breast carcinoma and the basal phenotype: from expression profiling to clinical practice. Adv Anat Pathol 14(6):419–30
Dong M, How T, Kirkbride KC, Gordon KJ, Lee JD, Hempel PK, Moeller BJ, Marks JR, Blobe GC (2007) The type III TGFβ receptor suppresses breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest 117:206–17
Gatza CE, Oh SY, Blobe GC (2010) Roles for the type III TGFβ receptor in human cancer. Cell Signal 22:1163–74
Ghellal A, Li C, Hayes M, Byrne G, Bundred N, Kumar S (2000) Prognostic significance of TGF beta 1 and TGF beta 3 in human breast carcinoma. Anticancer Res 20:4413–4418
Gordon K, Dong M, Chislock E, Fields T, Blobe G (2008) Loss of type III transforming growth factor β receptor expression increases motility and invasiveness associated with epithelial to mesenchymal transition during pancreatic cancer progression. Carcinogenesis 29(2):252–62
Gorsch SM, Memoli VA, Stukel TA, Gold LI, Arrick BA (1992) Immunohistochemical staining for transforming growth factor beta 1 associates with disease progression in human breast cancer. Cancer Res 52:6949–6952
Hanks BA, Holtzhausen A, Evans KS, Jamieson R, Gimpel P, Campbell OM, Hector-Greene M, Sun L, Tewari A, George A, Starr M, Nixon A, Augustine C, Beasley G, Tyler DS, Osada T, Morse MA, Ling L, Lyerly HK (2013) Blobe GCl. Type III TGF-β receptor downregulation generates an immunotolerant tumor microenvironment. J Clin Invest 123(9):3925–40
Kim MJ, Ro JY, Ahn SH, Kim HH, Kim SB, Gong G (2006) Clinicopathologic significance of the basal-like subtype of breast cancer: a comparison with hormone receptor and Her2/neu-overexpressing phenotypes. Hum Pathol 37(9):1217–26
Kittaneh M, Montero AJ, Glück S (2013) Molecular profiling for breast cancer: a comprehensive review. Biomark Cancer 5:61–70
Lopez-Casillas F, Payne H, Andres J, Massague J (1994) Betaglycan can act as a dual modulator of TGF-beta access to signaling receptors: mapping of ligand binding and GAG attachment sites. J Cell Biol 124(4):557–68
Mythreye K, Blobe GC (2009) The type III TGFβ receptor regulates epithelial and cancer cell migration through β-arrestin2-mediated activation of Cdc42. PNAS 20:8221–6
Pal A, Huang W, Toy KA, Kleer CG (2012) CCN6 knockdown disrupts acinar organization of breast cells in three-dimensional cultures through up-regulation of type III TGF-β receptor. Neoplasia 14(11):1067–74
Parker JS, Mullins M, Cheang MC, Leung S, Voduc D, Vickery T, Davies S, Fauron C, He X, Hu Z, Quackenbush JF, Stijleman IJ, Palazzo J, Marron JS, Nobel AB, Mardis E, Nielsen TO, Ellis MJ, Perou CM, Bernard PS (2009) Supervised risk predictor of breast cancer based on intrinsic subtypes. J Clin Oncol 27(8):1160–7
Ragnarsson G, Eiriksdottir G, Johannsdottir JT, Jonasson JG, Egilsson V, Ingvarsson S (1999) Loss of heterozygosity at chromosome 1p in different solid human tumours: association with survival. Br J Cancer 79:1468–1474
Rakha EA, Reis-Filho JS, Ellis IO (2008a) Basal-like breast cancer: a critical review. J Clin Oncol 26(15):2568–81
Rakha EA, El-Sayed ME, Lee AH, Elston CW, Grainge MJ, Hodi Z, Blamey RW, Ellis IO (2008b) Prognostic significance of Nottingham histologic grade in invasive breast carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 26(19):3153–8
Rivenbark AG, O’Connor SM, Coleman WB (2013) Molecular and cellular heterogeneity in breast cancer: challenges for personalized medicine. Am J Pathol 183(4):1113–24
Walker RA, Dearing SJ (1992) Transforming growth factor beta 1 in ductal carcinoma in situ and invasive carcinomas of the breast. Eur J Cancer 28:641–644
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by NIH grants R01 CA107469, R01 CA125577 and U01CA154224 (to CGK), the University of Michigan’s Cancer Center Support Grant (5 P30 CA46592).
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pang, J.C., Virani, N.K., Kidwell, K.M. et al. Characterization of type III TGF-β receptor expression in invasive breast carcinomas: a potential new marker and target for triple negative breast cancer. J. Cell Commun. Signal. 8, 211–218 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-014-0240-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12079-014-0240-z