Abstract
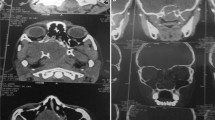
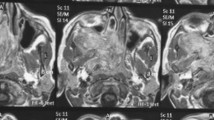
Juvenile angiofibroma is a rare, highly vascular, histologically benign but locally invasive tumour, affecting predominantly male adolescents. To describe our experience in diagnosis of angiofibroma and treatment by combined endoscopic and transpalatal route. We analysed a case series of 50 patients of nasopharyngeal angiofibroma in Fisch stages I and II who presented at our institute during a period of four years 2011–2014, their clinical presentation, their treatment by combined transpalatal and endoscopic approach, intraoperative and post operative course, complications and tumour recurrence. Patients were aged 8–26 years. All patients were treated surgically by combined approach endoscopic and transpalatal. The mean operation time was 90 min, and the mean bleeding volume was 300 ml. Only 8 % patients came with recurrence and only 10 % came with palatal perforation (fistula formation). With gratifying results we advocate this novel technique for the treatment of early to intermediate JNA.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wormald PJ, Hasselt A (2003) Endoscopic removal of juvenile angiofibroma. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 129:684–691. doi:10.1016/S0194-5998(03)01580-8
Sinha V, Ninama M, Prajapati B, Gupta D, More Y, Bhat V, Singh SN (2009) Juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofi broma—our experience at a referral hospital. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 61(Suppl 1):17–21
Chmielik LP, Frackiewicz M, Krajewski R et al (2009) Perioperative problems and treatment of a teenager with a juvenile angiofibroma refusing blood transfusion. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 73:689–692
Baser B, Kothari S, Kinger A (2011) Endoscopic approach to fisch stage II to III-b juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 63(1):1–4
Andrews JC, Fisch U, Valavanis A, Aeppli U, Makek MS (1989) The surgical management of extensive nasopharyngeal angiofibromas with the infratemporal fossa approach. Laryngoscope 99:429–437
Wiatrak BJ, Koopmann CF, Turrisi AT (1993) Radiation therapy as an alternative to surgery in the management of intracranial juvenile nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 51(28):51–61
Panda N, Gupta G, Sharma S, Gupta A (2012) Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma-changing trends in the management. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 64(3):233–239
Ardehali MM, Samimi SH, Bakhshaee M (2014) An effective technique for endoscopic resection of advanced stage angiofibroma. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol 26(74):25–30
Mendonça CA, de Jesus EPF, Santos ACG, Barreto VMP, Santos RC Jr (2013) Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma: Our experience and literature review. Int Arch Otorhinolaryngol 17(1):14–19
Desarda KK, Bora MP (1998) Importance of pre-operative embolization in the surgery of nasopharyngeal angiofibroma. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 50(1):36–39
Ghosh B, Saha S, Chandra S, Nandi TK, Bera SP (2003) Juvenile nasopharvngeal angiofibroma—three years experience. Indian J Otolarvngol Head Neck Surg 55(4):228–233
Sinha A, Gupta S (2000) Nasopharyngeal angiofibroma : staging and management—a review of the case series report. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 52(4):366–370
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
None.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed Consent
Full written consent was taken from the patients regarding the nature of the treatment and further use of his photographs and details for the publishing.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gupta, R., Agarwal, S.P. Juvenile Nasopharyngeal Angiofibroma: Combined Approach for Excision, Transpalatal and Endoscopic; A New Perspective. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 70, 125–129 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-016-1027-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-016-1027-8