Abstract
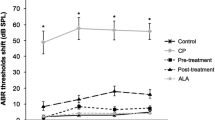
This experimental study was designed to investigate the protective effects of molsidomine (MOL) on against cisplatin-induced ototoxicity (CIO). To examine this effect, distortion product otoacoustic emissions (DPOAEs) measurements and serum levels of oxidative and antioxidant status [including malondialdehyde (MDA), superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT), glutathione (GSH), glutathione peroxidase (GPX), total oxidant status (TOS), total antioxidant status (TAS), and oxidative stress index (OSI)] were evaluated. Thirty-two female wistar albino rats were divided into four groups including; control (Group K), cisplatin (Group C), cisplatin plus MOL group (Group CM), and MOL group (Group M). DPOAEs measurements between 0.9961 and 8.0003 Hz as DP-gram and input/output (I/O) functions were performed in the same (left) ear of all rats on days 0, 1st, 5th and 12th. Prior to death, the last DPOAEs measurements and blood samples were taken. In the C group, statistically significant DPOAE amplitude reductions were detected at 2.5195, 3.1758, 3.9961, 5.0391, 6.3516 and 8.0039 Hz frequencies (p < 0.05) between 0th and 1st, 0th and 5th and 0th and 12th days’ measurements (p < 0.05). Serum level of MDA, TAC and OSI levels were significantly higher in the C group versus K group (p < 0.05). In the CM group, there were no significant differences at all frequencies between 0th and other days’ measurements (p > 0.05) and the serum levels of all biochemical parameters were shifted toward normal values, similar to the K group (p < 0.05). No significant differences were detected in the either M or K group’s measurements. According to these results, cisplatin-related ototoxicity has been significantly prevented by MOL.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rybak LP, Whitworth CA (2005) Ototoxicity: therapeutic opportunities. Drug Discovery Today 10:1313–1321
Rybak LP, Mukherjea D, Jajoo S, Ramkumar V (2009) Cisplatin ototoxicity and protection: clinical and experimental studies. Tohoku J Exp Med 219:177–186
Altintas R, Parlakpinar H, Beytur A, Vardi N, Polat A, Sagir M, Odabas GP (2012) Protective effect of dexpanthenol on ischemia-reperfusion-induced renal injury in rats. Kidney Blood Press Res 36:220–230
Yumusakhuylu AC, Yazici M, Sari M, Binnetoglu A, Kosemihal E, Akdas F, Sirvanci S, Yuksel M, Uneri C, Tutkun A (2012) Protective role of resveratrol against cisplatin induced ototoxicity in guinea pigs. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76:404–408
Ravi R, Somani SM, Rybak LP (1995) Mechanism of cisplatin ototoxicity: antioxidant system. Pharmacol Toxicol 76:386–394
Erdem T, Bayindir T, Filiz A, Iraz M, Selimoglu E (2012) The effect of resveratrol on the prevention of cisplatin ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 269:2185–2188
Celebi S, Gurdal MM, Ozkul MH, Yasar H, Balikci HH (2013) The effect of intratympanic vitamin C administration on cisplatin-induced ototoxicity. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270:1293–1297
Kalcioglu MT, Kizilay A, Gulec M, Karatas E, Iraz M, Akyol O, Egri M, Ozturan O (2005) The protective effect of erdosteine against ototoxicity induced by cisplatin in rats. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 262:856–863
Kizilay A, Kalcioglu MT, Ozerol E, Iraz M, Gulec M, Akyol O, Ozturan O (2004) Caffeic acid phenethyl ester ameliorated ototoxicity induced by cisplatin in rats. J Chemother 16:381–387
Kelles M, Tan M, Kalcioglu MT, Toplu Y, Bulam N (2013) The protective effect of Chrysin against cisplatin induced ototoxicity in rats. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. doi:10.1007/s12070-013-0695-x
Gruetter CA, Barry BK, McNamara DB et al (1979) Relaxation of bovine coronary artery and activation of coronary arterial guanylate cyclase by nitric oxide, nitroprusside and a carcinogenic nitrosoamine. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res 5:211–224
Bentli R, Parlakpinar H, Polat A, Samdanci E, Sarihan ME, Sagir M (2013) Molsidomine prevents cisplatin-induced hepatotoxicity. Arch Med Res 4:521–528
Disli OM, Sarihan E, Colak MC, Vardi N, Polat A, Yagmur J, Tamtekin B, Parlakpinar H (2013) Effects of molsidomine on doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Eur Surg Res 51:79–90. doi:10.1159/000354807
Uchiyama M, Mihara M (1978) Determination of malonaldehyde precursor in tissues by tiobarbituric acid test. Anal Biochem 34:271–278
Sun Y, Oberley L, Li Y (1988) A simple method for clinical assay of superoxide dismutase. Clin Chem 34:497–500
Aebi H (1974) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methods of enzymatic analysis. Academic Press, New York, pp 673–677
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–170
Ellman GL (1959) Tissue sulfhydryl groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 82:70–77
Erel O (2004) A novel automated direct measurement method for total antioxidant capacitiy using a new generation, more stable ABTS radical cation. Clin Biochem 37:277–285
Erel O (2005) A new automated colorimetric method for measuring total oxidant status. Clin Biochem 38:1103–1111
Aycicek A, Erel O, Kocyigit A (2005) Decreased total antioxidant capacity and increased oxidative stress in passive smoker infants and their mothers. Pediatr Int 47:635–639
McKeage MJ (1995) Comparative adverse effects of platinum drugs. Drug Saf 13:228–244
Kukovetz WR, Holzmann S (1986) Cyclic GMP as the mediator of molsidomine-induced vasodilatation. Eur J Pharmacol 122:109–130
Johnson G 3rd, Tsao PS, Lefer AM (1991) Cardioprotective effects of authentic nitric oxide in myocardial ischemia with reperfusion. Crit Care Med 19:244–252
Chander V, Chopra K (2005) Renal protective effect of molsidomine and l-arginine in ischemia–reperfusion induced injury in rats. J Surg Res 128:132–139
Rodriguez-Peña A, Garcia-Criado FJ, Eleno N et al (2004) Intrarenal administration of molsidomine, a molecule releasing nitric oxide, reduces renal ischemia–reperfusion injury in rats. Am J Transplant 4:1605–1613
Disli OM, Sarihan E, Colak MC, Vardi N, Polat A, Yagmur J, Tamtekin B, Parlakpinar H (2013) Effects of molsidomine against doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in rats. Eur Surg Res 51:79–90
Lopez-Gonzalez MA, Guerrero JM, Rojas F, Delgado F (2000) Ototoxicity caused by cisplatin is ameliorated by melatonin and other antioxidants. J Pineal Res 28:73–80
Ozturan O, Jerger J, Lew H, Lynch GR (1996) Monitoring of cisplatin ototoxicity by distortion-product otoacoustic emissions. Auris Nasus Larynx 23:147–151
Rybak LP, Whitworth CA, Mukherjea D, Ramkuvar V (2007) Mechanisms of cisplatin-induced ototoxicity and prevention. Hear Res 226:157–167
Conflict of interest
None declared.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Toplu, Y., Parlakpinar, H., Sapmaz, E. et al. The Protective Role of Molsidomine on the Cisplatin-Induced Ototoxicity. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 66, 314–319 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-014-0718-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-014-0718-2