Abstract:
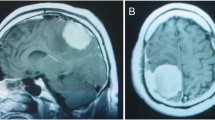
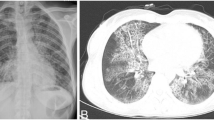
Fungus cerebri is a relatively rare disease. The various reasons attributed to such pathology are, long standing mastoiditis, previous temporal lobe fracture, spontaneous herniation and most important common cause is post operative to mastoidectomy. The diagnosis is mainly clinical and supplemented by imaging studies. The commonly herniated part is the temporal lobe, but cerebellar herniation are also reported Different surgical modalities are used in managing this condition. Surgical approaches in the treatment of brain herniation into the mastoid or middle ear are, neurosurgical, otosurgical and combined. A case of fungus cerebri complicating mastoidectomy is presented and the pathogenesis is discussed






Similar content being viewed by others
References:
Gluckman J (1975) Fungus cerebri: an unusual complication of mastoidectomy. S Afr Med J 49(46):1933–1934
Jackson CG, Pappas DG Jr, Manolidis S, Glasscock ME, Von Doersten PG, Carl R Hampf CR et al (1997) Brain herniation into the middle ear and mastoid: concepts in diagnosis and surgical management. Am J Otolaryngol 18:198–206
Ramalingam KK, RaviRamalingam, Sreenivasa Murthy TM, Chandrakala GR, UttamAgarwal (2007) An unusual case of brain fungus. Orissa J Otolaryngol Head & Neck Surg 1(1):42–43
Kizilay A, AladagI, Cokkeser Y, Ozturan O (2002) Dural bone defects and encephalocele associated with chronic otitis media or its surgery. Kulak BurunBogazIhtisDerg Nov–Dec, 9 (6):403–9
Aristequi M, Falcioni M, Saleh E, Taibah A, Russo A, Landolfi M, Sanna M (1995) Meningoencephalic herniation into the middle ear: a report of 27 cases. Laryngoscope 105(5 Pt 1):512–518
Fenstra L, Sanna M, Zini C (1985) Surgical treatment of brain herniation. Am J Otolaryngol 6(4):311–315
Kariyattil R, Muthukuttiparambil U (2012) Traumatic acute brain herniation through the ear in a child. Sultan Qaboos Univ Med J 12(3):352–356
Escada P, Vital JP, Capucho C, Lima C, da Silva JM, Penha RS (1999) Meningoencephalic herniation into the middle ear. Rev Laryngol Otol Rhinol (Bord) 120(1):47–52
Soubere C, Langman AW (1998) Combined mastoid/middle cranial fossa approach. Skull base Surg 8:185–189
Iurato S, Ettorre GC, Selvini C (1989) Brain herniation into the middle ear: two idiopathic cases treated by a combined intracranial-mastoid approach. Laryngoscope 99(9):950–954
Lundy LB, Graham MD, Kartush JM, LaRouere MJ (1996) Temporal bone encephalocele and cerebrospinal fluid leaks. Am J Otolaryngol 17(3):461–469
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Varshney, S., Mishra, S., Bist, S.S. et al. Fungus Cerebri (Brain Fungus): A Rare Complication of Mastoidectomy. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 65, 48–51 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-012-0601-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12070-012-0601-y