Abstract
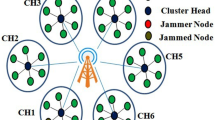
Wireless multi-hop networks are often exposed to serious physical layer jamming attack. In this attack, the jammer node corrupts the packet by injecting high level of noise and keeps the channel busy and thus blocks the legitimate communication. If multiple jammers collude together, this attack will become very severe. To prevent this attack, a simple yet effective Reliability Behavior Neuro-Fuzzy system has been proposed and it operates in three modules. In module one, each route node obtains its behavior value from the route path and neighboring paths using direct and indirect behavior observations. In module two, based on the behavior value, three factor identification methods have been presented to identify the reliability value of nodes. In module three, using the reliability value the route nodes are level positioned and classified into groups by a neuro-fuzzy classifier. By simulation studies, it is observed that the proposed scheme significantly not only identifies misbehaving nodes with higher detection rate and lower false positive and but also achieves higher network throughput and lower jamming throughput.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adnane A, Bidan C and Rafael T S 2013 Trust-based security for the OLSR routing protocol. Comput. Commun.
Amariucai G T 2009 Physical layer security in wireless networks: Intelligent jamming and Eavesdropping. Ph.D. Louisiana State University. Louisiana
Bao F, Chen I R, Chang M J and Cho J H 2012 Hierarchical trust management for wireless sensor networks and its applications to trust-based routing and intrusion detection. IEEE Trans. Network Service Manag. 9(2): 169–183
Chiang J T and Hu Y C 2011 Cross-layer jamming detection and mitigation in wireless broadcast networks. IEEE/ACM Trans. Networking 19(1): 1063–6692
Furdek M and Kapov N S 2013 Attack-survivable routing and wavelength assignment for high-power jamming. In: 17 th international conference optical network design and modeling (ONDM). 70–75
Josang A, Ismail R and Boyd C 2007 A survey of trust and reputation systems for online service provision. Decis. Support Syst. 43(2): 618–644
Li C, Dai H, Xiao L and Ning P 2012 Communication efficiency of anti-jamming broadcast in large-scale multi-channel wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Signal Process. 60(10): 5281–5292
Liu H, Frias J D and Hongxun S M 2007 Using a two-timer scheme to detect selfish nodes in mobile ad-hoc networks. Proceedings of international conference on communications, internet and information technology 38(1): 40–46
Mar J, Yeh Y C and Hsiao I F 2010 An ANFIS-IDS against de-authentication DOS attacks for a WLAN. International symposium on information theory and its applications (ISITA) 548–553
Mustafa H, Zhang X, Liu Z, Xu W and Perrig A 2012 Jamming-resilient multipath routing. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secure Comput. 9(6): 852–864
Nguyen H, Pongthawornkamol T and Nahrstedt K 2011 Alibi framework for identifying reactive jamming nodes in wireless LAN. IEEE Globecom
Noubir G and Lin G 2003 Low-power DoS attacks in data wireless lans and countermeasures. Mobile Comput. Commun. Rev. 7(3): 29–30
Pelechrinis K, Koufogiannakis C and Krishnamurthy S V 2010 On the efficacy of frequency hopping in coping with jamming attacks in 802.11 networks. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 9(10): 3258–3271
Proano A and Lazos L 2012 Packet-hiding methods for preventing selective jamming attacks. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secure Comput. 9(1): 101–114
Ratna S R, Ravi R and Beulah S 2014 An intelligent approach based on neuro- fuzzy detachment scheme for preventing jamming attack in wireless networks. J. Intell. Fuzzy Logic. doi: 10.3233/IFS-141363. ISSN 1064–1246(Print). 1875-8967 Online (in press)
Richa A, Scheideler C, Schmid S and Zhang J 2013 An efficient and fair MAC protocol robust to reactive interference. IEEE/ACM Trans. Networking 21(3): 760–771
Sarker J H and Mouftah H T 2012 Mitigating the effect of jamming signals in wireless ad hoc and sensor networks. IET Commun. 6(3): 311–317
Shila D M, Yu C and Anjali T 2010 Mitigating selective forwarding attacks with a channel-aware approach in WMNs. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 9(5): 1661–1675
Shiu Y S, Chang S Y, Wu H C, Huang S C H and Chen H H 2011 Physical layer security in wireless networks: A tutorial. IEEE Wireless Commun. 18(2): 66–74
Singh S, Sarje A K and Misra M 2012 Client-side counter phishing application using adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference system. Fourth international conference on computational intelligence and communication networks (CICN) 788–792
Spuhler M, Giustiniano D, Lenders V, Wilhelm M and Jens B S 2014 Detection of reactive jamming in DSSS-based wireless communications. IEEE Trans. Wireless Commun. 13(3): 1593–1603
Tomohiro T and Michio S 1985 Fuzzy identification of systems and its applications to modelling and control. IEEE Trans. Syst., Man Cybern. 15(1): 116–132
Xiaoyong L, Zhou F and Du J 2013 LDTS: A lightweight and dependable trust system for clustered wireless sensor networks. IEEE Trans. Inform. Forensics Security 8(6): 924–935
Xuan Y, Shen Y, Nguyen N P and Thai M T 2012 A trigger identification service for defending reactive jammers in WSN. IEEE Trans. Mobile Comput. 11(5): 793–806
Zhan G, Shi W and Deng J 2012 TARF: Design and implementation of TARF: A trust-aware routing framework for WSNs. IEEE Trans. Dependable Secure Comput. 9(2): 184–197
Acknowledgements
This work was supported in part by Anna University, Chennai recognized research center lab at Francis Xavier Engineering College, Tirunelveli, India.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
RATNA, S.R., RAVI, R. Securing jammed network using reliability behavior value through neuro-fuzzy analysis. Sadhana 40, 1139–1153 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-015-0377-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12046-015-0377-3