Abstract
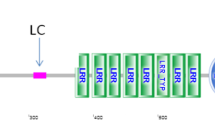
Mastitis is an infectious disease of the mammary gland that leads to reduced milk production and change in milk composition. Complement component C3 plays a major role as a central molecule of the complement cascade involving in killing of microorganisms, either directly or in cooperation with phagocytic cells. C3 cDNA were isolated, from Egyptian buffalo and cattle, sequenced and characterized. The C3 cDNA sequences of buffalo and cattle consist of 5025 and 5019 bp, respectively. Buffalo and cattle C3 cDNAs share 99% of sequence identity with each other. The 4986 bp open reading frame in buffalo encodes a putative protein of 1661 amino acids—as in cattle—and includes all the functional domains. Further, analysis of the C3 cDNA sequences detected six novel single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in buffalo and three novel SNPs in cattle. The association analysis of the detected SNPs with milk somatic cell score as an indicator of mastitis revealed that the most significant association in buffalo was found in the C >A substitution (ss: 1752816097) in exon 27, whereas in cattle it was in the C >T substitution (ss: 1752816085) in exon 12. Our findings provide preliminary information about the contribution of C3 polymorphisms to mastitis resistance in buffalo and cattle.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Shafy H., Bortfeldt R. H., Tetens J. and Brockmann G. A. 2014 Single nucleotide polymorphism and haplotype effects associated with somatic cell score in German Holstein cattle. Genet. Sel. Evol. 46, 35–44.
Akhtar S. and Ali S. 1994 Monitoring of bovine health problems of small dairy herds in Islamabad capital territory; design, data and disease frequencies. Trop. Anim. Health Pro. 26, 193–198.
Ali A. K. A. and Shook G. E. 1980 An optimum transformation for somatic-cell concentration in milk. J. Dairy Sci. 63, 487–490.
Ameratunga R., Winkelstein J. A., Brody L., Binns M., Cork L. C., Colombani P. and Valle D. 1998 Molecular analysis of the third component of canine complement (c3) and identification of the mutation responsible for hereditary canine c3 deficiency. J. Immunol. 160, 2824–2830.
Barrio M. B., Rainard P. and Poutrel B. 2003 Milk complement and the opsonophagocytosis and killing of Staphylococcus aureus mastitis isolates by bovine neutrophils. Microb. Pathogenesis 34, 1–9.
Botto M., Kirschfink M., Macor P., Pickering M. C., Würzner R. and Tedesco F. 2009 Complement in human disease: lessons from complement deficiencies. Mol. Immunol. 46, 2774–2783.
Bramham J., Thai C. -T., Soares D. C., Uhrın D., Ogata R. T. and Barlow P. N. 2005 Functional insights from the structure of the multifunctional C345c domain of C5 of complement. J. Biol. Chem. 280, 10636–10645.
Cole J. B., Wiggans G. R., Ma L., Sonstegard T. S., Lawlor T. J., Crooker B. A. et al. 2011 Genome-wide association analysis of thirty one production, health, reproduction and body conformation traits in contemporary U.S. Holstein cows. BMC Genomics 12, 408–424.
Dassault Systèmes BIOVIA 2015 Discovery Studio Modeling Environment, Release 4.5. Dassault Systèmes, San Diego.
de Bruijn M. H. L. and Fey G. H. 1985 Human complement component C3: cDNA coding sequence and derived primary structure. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82, 708–712.
Detilleux J. C. 2002 Genetic factors affecting susceptibility of dairy cows to udder pathogens. Vet. Immunol. Immunop. 88, 103–110.
DiScipio R. G. and Hugli T. E. 1989 The molecular architecture of human complement component C6. J. Biol. Chem. 264, 16197–16206.
Falconer D. S. and Mackay T. F. C. 1996 Introduction to quantitative genetics, 4th edition. Longman Scientific and Technical, New York, USA.
Firth M. A., Moore D. P., Pei Y., Shewen P. E., Lo R. Y. C., Yoo D. and Hodgins D. C. 2006 Cloning of a gene fragment encoding bovine complement component C3d with expression and characterization of derived fusion proteins. Vet. Immunol. Immunop. 114, 61–71.
Frank M. M. and Fries L. F. 1991 The role of complement in inflammation and phagocytosis. Immunol. Today 12, 322–326.
Fredslund F., Jenner L., Husted L. B., Nyborg J., Andersen G. R. and Sottrup-Jensen L. 2006 The structure of bovine complement component 3 reveals the basis for thioester function. J. Mol. Biol. 361, 115–127.
Goldberg M., Fremeaux-Bacchi V., Koch P., Fishelson Z. and Katz Y. 2011 A novel mutation in the C3 gene and recurrent invasive pneumococcal infection: a clue for vaccine development. Mol. Immunol. 48, 1926–1931.
Hazlewood M. A., Kumararatne D. S., Webster A. D., Goodall M., Bird P. and Daha M. 1992 An association between homozygous C3 deficiency and low levels of antipneumococcal capsular polysaccharide antibodies. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 87, 404– 409.
Humphrey W., Dalke A. and Schulten K. 1996 VMD: visual molecular dynamics. J. Mol. Graphics 14, 33–38.
Ibeagha-Awemu E. M., Kgwatalala E. M., Ibeagha A. E. and Zhao X. 2008 A critical analysis of disease-associated DNA polymorphisms in the genes of cattle, goat, sheep, and pig. Mamm. Genome 19, 226–245.
Isaac L. and Isenman D. E. 1992 Structural requirements for thioester bond formation in human complement component C3. Reassessment of the role of thioester bond integrity on the conformation of C3. J. Biol. Chem. 267, 10062–10069.
Jamrozik J. and Schaeffer L. R. 2010 Recursive relationships between milk yield and somatic cell score of Canadian Holsteins from finite mixture random regression models. J. Dairy Sci. 93, 5474–5486.
Janssen B. J. C., Huizinga E. G., Raaijmakers H. C. A., Roos A., Daha M. R., Nilsson-Ekdahl K. et al. 2005 Structures of complement component C3 provide insights into the function and evolution of immunity. Nature 437, 505–511.
Kidmose R. T., Laursen N. S., Dobó J., Kjaer T. R., Sirotkina S., Yatime L. et al. 2012 Structural basis for activation of the complement system by component C4 cleavage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 109, 15425–15430.
Kimchi-Sarfaty C., Oh J. M., Kim I. W., Sauna Z. E., Calcagno A. M., Ambudkar S. V. and Gottesman M. M. 2007 A silent polymorphism in the MDR1 gene changes substrate specificity. Science 315, 525–528.
Komar A. A. 2007 Silent SNPs: impact on gene function and phenotype. Pharmacogenomics 8, 1075–1080.
Law S. K. and Dodds A. W. 1997 The internal thioester and the covalent binding properties of the complement proteins C3 and C4. Protein Sci. 6, 263–274.
MacKerell A. D., Bashford D., Bellott M., Dunbrack R. L., Evanseck J. D., Field M. J. et al. 1998 All atom empirical potential for molecular modeling and dynamics studies of proteins. J. Phys. Chem. B 102, 3586–3616.
MacKerell A. D., Feig M. and Brooks C. L. 2004 Extending the treatment of backbone energetics in protein force fields: limitations of gas-phase quantum mechanics in reproducing protein conformational distributions in molecular dynamics simulations. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1400–1415.
Meredith B. K., Kearney F. J., Finlay E. K., Bradley D. G., Fahey A. G., Berry D. P. and Lynn D. J. 2012 Genome-wide associations for milk production and somatic cell score in Holstein–Friesian cattle in Ireland. BMC Genet. 13, 21–31.
Miyagawa H., Yamai M., Sakaguchi D., Kiyohara C., Tsukamoto H., Kimoto Y. et al. 2008 Association of polymorphisms in complement component C3 gene with susceptibility to systemic lupus erythematosus. Rheumatology 47, 158–164.
Morgan B. P., Marchbank K. J., Longhi M. P., Harris C. L. and Gallimore A. M. 2005 Complement: central to innate immunity and bridging to adaptive responses. Immunol. Lett. 97, 171–179.
Moroni P., Rossi C. S., Pisoni G., Bronzo V., Castiglioni B. and Boettcher P. J. 2006 Relationships between somatic cell count and intramammary infection in buffaloes. J. Dairy Sci. 89, 998–1003.
Nani J. P., Raschia M. A., Poli M. A., Calvinho L. F. and Amadio A. F. 2015 Genome-wide association study for somatic cell score in Argentinean dairy cattle. Livest. Sci. 175, 1–9.
Ogorevc J., Kunej T., Razpet A. and Dovc P. 2009 Database of cattle candidate genes and genetic markers for milk production and mastitis. Anim. Genet. 40, 832–851.
Oviedo-Boyso J., Valdez-Alarcón J. J., Cajero-Juarez M., Ochoa-Zarzosa A., López-Meza J. E., Ravo-Patiño A. and Baizabal-Aguirre V. M. 2007 Innate immune response of bovine mammary gland to pathogenic bacteria responsible for mastitis. J. Infection 54, 399–409.
Peakall R. and Smouse P. E. 2012 GenAlEx 6.5: genetic analysis in Excel. Population genetic software for teaching and research—an update. Bioinformatics 28, 2537–2539.
Pearson T. A. and Manolio T. A. 2008 How to interpret a genome-wide association study. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 299, 1335–1344.
Pettersen E. F., Goddard T. D., Huang C. C., Couch G. S., Greenblatt D. M., Meng E. C. and Ferrin T. E. 2004 UCSF chimera—a visualization system for exploratory research and analysis. J. Comput. Chem. 25, 1605–1612.
Phillips J. C., Braun R., Wang W., Gumbart J., Tajkhorshid E., Villa E. et al. 2005 Scalable molecular dynamics with NAMD. J. Comput. Chem. 26, 1781–1802.
Rainard P. 2003 The complement in milk and defense of the bovine mammary gland against infections. Vet. Res. 34, 647–670.
Rainard P. and Poutrel B. 1995 Deposition of complement components on Streptococcus agalactiae in bovine milk in the absence of inflammation. Infect. Immun. 63, 3422–3427.
Ricklin D. and Lambris J. D. 2013 Complement in immune and inflammatory disorders: pathophysiological mechanisms. J. Immunol. 190, 3831–3838.
Ricklin D., Hajishengallis G., Yang K. and Lambris J. D. 2010 Complement: a key system for immune syrveillance and homeostasis. Nat. Immunol. 11, 785–797.
Rupp R. and Boichard D. 2003 Genetics of resistance to mastitis in dairy cattle. Vet. Res. 34, 671–688.
Šali A. and Blundell T. L. 1993 Comparative protein modelling by satisfaction of spatial restraints. J. Mol. Biol. 234, 779–815.
Sambrook J., Fritsch E. F. and Maniatis T. 1989 Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Cold Spring Harbor, New York, USA.
Santos-Valente E., Reisli I., Artaç H., Ott R., Sanal Ö. and Boztug K. 2013 A novel mutation in the complementcomponent 3 gene in a patient with selective IGA deficiency. J. Clin. Immunol. 33, 127–133.
Skattum L., vanDeuren M., vanderPoll T. and Truedsson L. 2011 Complement deficiency states and associated infections. Mol. Immunol. 48, 1643–1655.
Swanson K. M., Stelwagen K., Dobson J., Henderson H. V., Davis S. R., Farr V. C. and Singh K. 2009 Transcriptome profiling of Streptococcus uberis-induced mastitis reveals fundamental differences between immune gene expression in the mammary gland and in a primary cell culture model. J. Dairy Sci. 92, 117–129.
Tomlinson S. 1993 Complement defense mechanisms. Curr. Opin. Immunol. 5, 83–89.
Torreira E., Tortajada A., Montes T., de Cordoba R. S. and Lorca O. 2009 3D structure of the C3bB complex provides insights into the activation and regulation of the complement alternative pathway convertase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 106, 882–887.
Walport M. J. 2001 Complement: first of two parts. N. Engl. J. Med. 344, 1058–1066.
Wanger E. and Frank M. M. 2009 Therapeutic potential of complement modulation. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 9, 43–56.
Welinder K. G. and Svendsen A. 1986 Amino acid sequence analysis of the glycopeptides from human complement component C3. FEBS Lett. 202, 59–62.
Wijga S., Bastiaansen J. W., Wall E., Strandberg E., de Haas Y., Giblin L. and Bovenhuis H. 2012 Genomic associations with somatic cell score in first-lactation Holstein cows. J. Dairy Sci. 95, 899–908.
Wilmink J. B. M. 1987 Efficiency of selection for different cumulative milk, fat and protein yields in first lactation. Livest. Prod. Sci. 17, 211–224.
Wimmers K., Mekchay S., Schellander K. and Ponsuksili S. 2003 Molecular characterization of the pig C3 gene and its association with complement activity. Immunogenetics 54, 714–724.
Yates J. R. W., Sepp T., Matharu B. K., Khan J. C., Thurlby D. A., Shahid H. et al. 2007 Complement C3 variant and the risk of age-related macular degeneration. N. Engl. J. Med. 357, 553–561.
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by the Science and Technology Development Fund (STDF) in Egypt (grant no. 2047).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Silvia Garagna
[El-Halawany N., Abd-El-Morif S. A., Al-Tohamy A. F. M., Hegazy L., Abdel-Shafy H., Abdel-Latif M. A., Ghazi Y. A., Neuhoff C., Salilew-Wondim D. and Schellander K. 2017 Complement component 3: characterization and association with mastitis resistance in Egyptian water buffalo and cattle. J. Genet. 96, xx–xx]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
EL-HALAWANY, N., SHAWKY, AEM.A., M. AL-TOHAMY, A.F. et al. Complement component 3: characterization and association with mastitis resistance in Egyptian water buffalo and cattle. J Genet 96, 65–73 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-017-0740-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-017-0740-8