Abstract
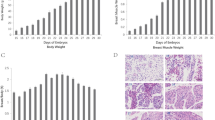
Transmembrane protein 8C (Tmem8C) is a muscle-specific membrane protein that controls myoblast fusion, which is essential for the formation of multinucleated muscle fibres. As most of the birds can fly, they have enormous requirement for the muscle, but there are only a few studies of Tmem8C in birds. In this study, we obtained the coding sequence (CDS) of Tmem8C in goose, predicted miRNAs that can act on the 3′UTR, analysed expression profiles of this gene in breast and leg muscles (BM and LM) during the embryonic period and neonatal stages, and identified miRNAs that might affect the targeted gene. The results revealed a high homology between Tmem8C in goose and other animals (indicated by sequence comparisons and phylogenetic trees), some conservative characteristics (e.g., six transmembrane domains and two E-boxes in the 5′UTR might be the potential binding sites of muscle regulatory factors (MRFs)), and the d N/d S ratio indicated purifying selection acting on this gene, facilitating conservatism in vertebrates. Q-PCR indicated Tmem8C had a peak expression pattern, reaching its highest expression levels in stage E15 in LM and E19 in BM, and then dropping transiently in E23 (P<0.05). We examined 13 candidate miRNAs, and negative relationships were detected both in BM and LM (mir-125b-5p, mir-15a, mir-16-1 and mir-n23). Notably, mir-16-1 significantly decreased luciferase activity in dual luciferase reporter gene (LRG) assay, suggesting that it can be identified as potential factors affecting Tmem8C. This study investigated Tmem8C in water bird for the first time, and provided useful information about this gene and its candidate miRNAs in goose.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartel D. P. 2004 MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell 116, 281–297.
Biggar K. K., Dubuc A. and Storey K. 2009 MicroRNA regulation below zero: differential expression of miRNA-21 and miRNA-16 during freezing in wood frogs. Cryobiology 59, 317–321.
Boutet S. C., Cheung T. H., Quach N. L., Liu L., Prescott S. L., Edalati A., Iori K. and Rando T. A. 2012 Alternative polyadenylation mediates microRNA regulation of muscle stem cell function. Cell Stem Cell 10, 327–336.
Brennecke J., Stark A., Russell R. B. and Cohen S. M. 2005 Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol. 3, e85.
Buckingham M. and Rigby P. W. 2014 Gene regulatory networks and transcriptional mechanisms that control myogenesis. Dev. Cell 28, 225–238.
Campos-Juanatey F., Gutierrez-Baños J. L., Portillo-Martin J. A. and Zubillaga-Guerrero S. 2015 Assessment of the urodynamic diagnosis in patients with urinary incontinence associated with normal pressure hydrocephalus. Neurourol. Urodynam. 34, 465–468.
Charrin S., Latil M., Soave S., Polesskaya A., Christien F., Boucheix C. and Rubinstein E. 2013 Normal muscle regeneration requires tight control of muscle cell fusion by tetraspanins CD9 and CD81. Nat. Commun. 4, 1674.
Doherty K. R., Cave A., Davis D. B., Delmonte A. J., Posey A., Earley J. U. et al. 2005 Normal myoblast fusion requires myoferlin. Development 132, 5565–5575.
Goljanek-Whysall K., Sweetman D., Abu-Elmagd M., Chapnik E., Dalmay T., Hornstein E. and Monsterberg A. 2011 MicroRNA regulation of the paired-box transcription factor Pax3 confers robustness to developmental timing of myogenesis. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 108, 11936–11941.
Gu L., Xu T., Huang W., Xie M., Sun S. and Hou S. 2014 Identification and profiling of microRNAs in the embryonic breast muscle of Pekin duck. PLoS One 9, e86150.
Landemaine A., Rescan P. -Y. and Gabillard J. -C. 2014 Myomaker mediates fusion of fast myocytes in zebrafish embryos. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 451, 480–484.
Li G., Miskimen K. L., Wang Z., Xie X. Y., Brenzovich J., Ryan J. J., Tse W. et al. 2010a STAT5 requires the N-domain for suppression of miR15/16, induction of bcl-2, and survival signaling in myeloproliferative disease. Blood 115, 1416–1424.
Li L., Liu H. -H., Xu F., Si J. -M., Jia J. and Wang J. -W. 2010b MyoD expression profile and developmental differences of leg and breast muscle in Peking duck (Anas platyrhynchos Domestica) during embryonic to neonatal stages. Micron 41, 847–852.
Li T., Wu R., Zhang Y. and Zhu D. 2011 A systematic analysis of the skeletal muscle miRNA transcriptome of chicken varieties with divergent skeletal muscle growth identifies novel miRNAs and differentially expressed miRNAs. BMC Genomics 12, 186.
Liu H. -H., Wang J. -W., Li L., Han C. -C., Huang K. -L., Si J. -M. et al. 2011 Molecular evolutionary analysis of the duck MYOD gene family and its differential expression pattern in breast muscle development. Brit. Poultry Sci. 52, 423–431.
Liu N., Williams A. H., Maxeiner J. M., Bezprozvannaya S., Shelton J. M., Richardson J. A., Bassel-Duby R. and Olson E. N. 2012 MicroRNA-206 promotes skeletal muscle regeneration and delays progression of Duchenne muscular dystrophy in mice. J. Clin. Invest. 122, 2054–2065.
Luo W., Li E., Nie Q. and Zhang X. 2015 Myomaker, regulated by MYOD, MYOG and miR-140-3p, promotes chicken myoblast fusion. Int. J. Molec. Sci. 16, 26186–26201.
Millay D. P., O’Rourke J. R., Sutherland L. B., Bezprozvannaya S., Shelton J. M., Bassel-Duby R. and Olson E. N. 2013 Myomaker is a membrane activator of myoblast fusion and muscle formation. Nature 499, 301–305.
Millay D. P., Sutherland L. B., Bassel-Duby R. and Olson E. N. 2014 Myomaker is essential for muscle regeneration. Genes and Devel. 28, 1641.
Nie M., Deng Z. -L., Liu J. and Wang D. -Z. 2015 Noncoding RNAs, emerging regulators of skeletal muscle development and diseases. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 676575.
Relaix F., Montarras D., Zaffran S., Gayraud-Morel B., Rocancourt D., Tajbakhsh S. et al. 2006 Pax3 and Pax7 have distinct and overlapping functions in adult muscle progenitor cells. J. Cell Biol. 172, 91–102.
Saitou N. and Nei M. 1987 The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol. Biol. Evol. 4, 406–425.
Scott G. R., Richards J. G. and Milsom W. K. 2009 Control of respiration in flight muscle from the high-altitude bar-headed goose and low-altitude birds. Am. J. Phys.-Regul. Integrat. Compar. Phys. 297, R1066–R1074.
Sohn R. L., Huang P., Kawahara G., Mitchell M., Guyon J., Kalluri R. et al. 2009 A role for nephrin, a renal protein, in vertebrate skeletal muscle cell fusion. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 106, 9274–9279.
Tamura K., Peterson D., Peterson N., Stecher G., Nei M. and Kumar S. 2011 MEGA5: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Molec. Biol. Evol. 28, 2731–2739.
Thomas M., Langley B., Berry C., Sharma M., Kirk S., Bass J. and Kambadur R. 2000 Myostatin, a negative regulator of muscle growth, functions by inhibiting myoblast proliferation. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 40235–40243.
Vasyutina E., Martarelli B., Brakebusch C., Wende H. and Birchmeier C. 2009 The small G-proteins Rac1 and Cdc42 are essential for myoblast fusion in the mouse. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 106, 8935–8940.
Yafe A., Shklover J., Weisman-Shomer P., Bengal E. and Fry M. 2008 Differential binding of quadruplex structures of muscle-specific genes regulatory sequences by MyoD, MRF4 and myogenin. Nucleic Acids Res. 36, 3916–3925.
Yang S., Liu X., Li X., Sun S., Sun F., Fan B. and Zhao S. 2013 MicroRNA-124 reduces caveolar density by targeting caveolin-1 in porcine kidney epithelial PK15 cells. Molec. Cell. Biochem. 384, 213–219.
Zhu C., Gi G., Tao Z., Song C., Zhu W., Song W. and Li H. 2014 Development of skeletal muscle and expression of myogenic regulatory factors during embryonic development in Jinding ducks (Anas platyrhynchos domestica). Poultry Sci. 93, 1211–1216.
Acknowledgements
This project was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China (31372349), and the scientific research Foundation of Zhejiang A&F University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Indrajit Nanda
[He K., Ren T., Zhu S., Liang S. and Zhao A. 2017 Transiently expressed pattern during myogenesis and candidate miRNAs of Tmem8C in goose. J. Genet. 96, xx–xx]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
HE, K., REN, T., ZHU, S. et al. Transiently expressed pattern during myogenesis and candidate miRNAs of Tmem8C in goose. J Genet 96, 39–46 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-016-0737-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-016-0737-8