Abstract
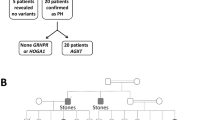
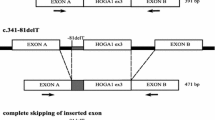
Primary hyperoxaluria type I (PH1) is an autosomal recessive metabolic disorder caused by inherited mutations in the AGXT gene encoding liver peroxisomal alanine : glyoxylate aminotransferase (AGT) which is deficient or mistargeted to mitochondria. PH1 shows considerable phenotypic and genotypic heterogeneity. The incidence and severity of PH1 varies in different geographic regions. DNA samples of the affected members from two unrelated Tunisian families were tested by amplifying and sequencing each of the AGXT exons and intron–exon junctions. We identified a novel frameshift mutation in the AGXT gene, the c.406_410dupACTGC resulting in a truncated protein (p.Gln137Hisfs*19). It is found in homozygous state in two nonconsanguineous unrelated families from Tunisia. These molecular findings provide genotype/phenotype correlations in the intrafamilial phenotypic and permit accurate carrier detection, and prenatal diagnosis. The novel p.Gln137Hisfs*19 mutation detected in our study extend the spectrum of known AGXT gene mutations in Tunisia.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amoroso A., Pirulli D., Florian F., Puzzer D., Boniotto M., Crovella S. et al. 2001 AGXT gene mutations and their influence on clinical heterogeneity of type 1 primary hyperoxaluria. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 12, 2072–2079.
Antonarakis S. E., Krawczak M. and Cooper D. N. 2001 The nature and mechanisms of human gene mutation. In: The metabolic and molecular bases of inherited disease, 8th edition, pp. 343–377.
Cochat P., Fargue S. and Harambat J. 2010 Primary hyperoxaluria type 1: strategy for organ transplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ Transplant. 15, 590–593.
Coulter-Mackie M. B., Lian Q., Applegarth D. and Toone J. 2005 The major allele of the alanine : glyoxylate aminotransferase gene: nine novel mutations and polymorphisms associated with primary hyperoxaluria type 1. Mol. Genet. Metab. 86, 172–178.
Danpure C. J. and Jennings P. R. 1986 Peroxisomal alanine: glyoxylate aminotransferase deficiency in primary hyperoxaluria type I. FEBS Lett. 201, 20–24.
Danpure C. J. and Rumsby G. 2004 Molecular aetiology of primary hyperoxaluria and its implications for clinical management. Expert. Rev. Mol. Med. 6, 1–16.
El Moncer W., Esteban E., Bahri R., Gaya-Vidal M., Carreras-Torres R., Athanasiadis G. et al. 2010 Mixed origin of the current Tunisian population from the analysis of Alu and Alu/STR compound systems. J. Hum. Genet. 55, 827–833.
Frischmeyer P. A. and Dietz H. C. 1999 Nonsense-mediated mRNA decay in health and disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 8, 1893–1900.
Jiang H., Orr A., Guernsey D. L., Robitaille J., Asselin G., Samuels M. E. et al. 2009 Application of homozygosity haplotype analysis to genetic mapping with high density SNP genotype data . PLoS One 4, e5280.
Hoppe B., Danpure C. J., Rumsby G., Fryer P., Jennings P. R., Blau N. et al. 1997 A vertical (pseudodominant) pattern of inheritance in the autosomal recessive disease primary hyperoxaluria type 1: lack of relationship between genotype, enzymic phenotype, and disease severity. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 29, 36–44.
Hoppe B., Beck B. B. and Milliner D. S. 2009 The primary hyperoxalurias. Kidney Int. 75, 1264–1271.
Lorenzo V., Torres A. and Salido E. 2014 Primary hyperoxaluria. Nefrologia 34, 398–412.
Lumb M. J. and Danpure C. J. 2000 Functional synergism between the most common polymorphism in human alanine : glyoxylate aminotransferase and four of the most common disease-causing mutations. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 36415–36422.
Mandrile G., Robbiano A., Giachino D., Sebastiano R., Dondi E., Fenoglio R. et al. 2008 Primary hyperoxaluria: report of an Italian family with clear sex conditioned penetrance. Urol. Res. 36, 309–312.
Miyazawa H., Kato M., Awata T., Kohda M., Iwasa H., Koyama N. et al. 2007 Homozygosity haplotype allows a genome wide search for the autosomal segments shared among patients . Am. J. Hum. Genet. 80, 1090–1102.
Monico C. G., Rossetti S., Schwanz H. A., Olson J. B., Lundquist P. A., Dawson D. B. et al. 2007 Comprehensive mutation screening in 55 probands with type 1 primary hyperoxaluria shows feasibility of a gene-based diagnosis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 18, 1905–1914.
Purdue P. E., Takada Y. and Danpure C. J. 1990 Identification of mutations associated with peroxisome-to-mitochondrion mistargeting of alanine/glyoxylate aminotransferase in primary hyperoxaluria type 1. J. Cell Biol. 111, 2341–2351.
Rinat C., Wanders R. J., Drukker A., Halle D. and Frishberg Y. 1999 Primary hyperoxaluria type I: a model for multiple mutations in a monogenic disease within a distinct ethnic group. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 10, 2352–2358.
Salido E. C., Li X. M., Lu Y., Wang X., Santana A., Roy-Chowdhury N. et al. 2006 Alanine-glyoxylate aminotransferase-deficient mice, a model for primary hyperoxaluria that responds to adenoviral gene transfer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 103, 18249–18254.
Salido E., Pey A. L., Rodriguez R. and Lorenzo V. 2012 Primary hyperoxalurias: disorders of glyoxylate detoxification. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1822, 1453–1464.
Santana A., Salido E., Torres A. and Shapiro L. J. 2003 Primary hyperoxaluria type 1 in the Canary Islands: a conformational disease due to I244T mutation in the P11L-containing alanine: glyoxylate aminotransferase. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100, 7277–7282.
Schwartz G. J., Brion L. P. and Spitzer A. 1987 The use of plasma creatinine concentration for estimating glomerular filtration rate in infants, children, and adolescents. Pediatr. Clin. North Am. 34, 571–590.
Von Schnakenburg C., Hulton S. A., Milford D. V., Roper H. P. and Rumsby G. 1998 Variable presentation of primary hyperoxaluria type 1 in 2 patients homozygous for a novel combined deletion and insertion mutation in exon 8 of the AGXT gene. Nephron 78, 485–488.
Williams E. and Rumsby G. 2007 Selected exonic sequencing of the AGXT gene provides a genetic diagnosis in 50% of patients with primary hyperoxaluria type 1. Clin. Chem. 53, 1216–1221.
Williams E. L., Acquaviva C., Amoroso A., Chevalier F., Coulter-Mackie M. B., Monico C. J. et al. 2009 Primary hyperoxaluria type 1: update and additional mutation analysis of the AGXT gene. Hum. Mutat. 30, 910–917.
Yendt E. R. and Cohanim M. 1985 Response to a physiologic dose of pyridoxine in type I primary hyperoxaluria. N. Engl. J. Med. 312, 953–957.
Zhang X., Mark Roe S., Hou Y., Bartlam M., Rao Z., Pearl L. H. et al. 2003 Crystal structure of alanine : glyoxylate aminotransferase and the relationship between genotype and enzymatic phenotype in primary hyperoxaluria type 1. J. Mol. Biol. 331, 643–652.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by Tunisian Ministry of Public Health and the Ministry of Higher Education and Scientific Research. We would like to thank our patients and their families for their collaboration to this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[M’Dimegh S., Aquaviva-Bourdain C., Omezzine A., M’Barek I., Souche G., Zellama D., Abidi K., Achour A., Gargah T., Abroug S. and Bouslama A. 2016 A novel mutation in the AGXT gene causing primary hyperoxaluria type I: genotype–phenotype correlation. J. Genet. 95, xx–xx]
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
M’DIMEGH, S., AQUAVIVA-BOURDAIN, C., OMEZZINE, A. et al. A novel mutation in the AGXT gene causing primary hyperoxaluria type I: genotype–phenotype correlation. J Genet 95, 659–666 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-016-0676-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-016-0676-4