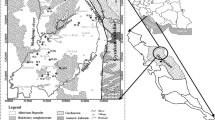
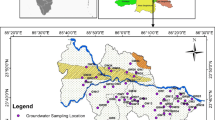
Water samples were collected from different formations of Gadilam river basin and analyzed to assess the major ion chemistry and suitability of water for domestic and drinking purposes. Chemical parameters of groundwater such as pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total dissolved solids (TDS), Sodium (Na + ), Potassium (K + ), Calcium (Ca + ), Magnesium (Mg + ), Bicarbonate (HCO\(_{3}^{\ \,-}\)), Sulphate (SO\(_{4}^{\ \,-}\)), Phosphate (PO\(_{4}^{\ \,-}\)) and Silica (H4SiO4) were determined. The geochemical study of the aquatic systems of the Gadilam river basin show that the groundwater is near-acidic to alkaline and mostly oxidizing in nature. Higher concentration of Sodium and Chloride indicates leaching of secondary salts and anthropogenic impact by industry and salt water intrusion. Spatial distribution of EC indicates anthropogenic impact in the downstream side of the basin. The concentration levels of trace metals such as Iron (Fe), Lead (Pb), Nickel (Ni), Bromide (Br), Iodide (I) and Aluminium (Al) have been compared with the world standard. Interpretation of data shows that some trace metals such as Al, Ni and Pb exceed the acceptable limit of world standard. Geophysical study was carried out to identify the weathered zone in the hard rock and contaminated zone by anthropogenic impact in the downstream of river Gadilam. A few of the groundwater samples in the study area were found to be unsuitable for domestic and drinking purposes.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anandhan P 2005 Hydrogeochemical studies in and around Neyveli mining region, Tamil Nadu, India; Unpublished Ph.D Thesis, Department of Earth Sciences, Annamalai University, 189p.
APHA 1998 Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater; 19th edn., APHA, Washington DC, USASS.
Atwia M G, Hassan A A and Ibrahim A 1997 Hydrogeology, log analysis and hydrochemistry of unconsolidated aquifers south of El-Sadat city, Egypt; J. Hydrol. 5 27–38.
Balaram Das, Maity S K and Tarafdar O N 2007 Application of electrical resistivity and induced polarization methods for detection of Fluoride contaminated groundwater; J. Geol. Soc. India 69 381–389.
Ballukraya P N and Ravi R 1999 Characterization of groundwater in the unconfined aquifers of Chennai City, India; Part I: Hydrogeochemistry; J. Geol. Soc. India 54 1–11.
Chidambaram S 2000 Hydrogeochemical studies of groundwater in Periyar district, Tamil Nadu, India; Unpublished Ph.D thesis, Department of Geology, Annamalai University.
Choudhury K and Saha D K 2004 Integrated geophysical and chemical study of saline water intrusion; Ground Water 42(5) 671–677.
Das Brijraj K and Kaur P 2007 Geochemistry of surface and sub-surface waters of Rewalsar lake, Mandi district, Himachal Pradesh: Constraints on weathering and erosion; J. Geol. Soc. India 69(5) 1020–1030.
Deevashish Kumar 2002 Characterisation of groundwater flow regime in a crystalline rock through fracture network program; J. Geophys. XXIII 123–129.
Domenico P A and Schwartz F W 1998 Physical and Chemical Hydrogeology, 2nd edn. (New York: Wiley) 506p.
Freeze A R and Cherry J A 1979 Groundwater; Prentice–Hall, Inc., Englewood Cliffs, New Jersey, 604p.
Fuge R 1973 Bromine-I, In: Handbook of geochemistry (ed.) Wedepohl K H (Berlin: Springer-Verlag) II(3) 351-1–351-4.
ISI 1995 Indian standard specification for driniking water; ISI New Delhi, IS. 10500.
Lakshmanan E, Kannan R and Senthil Kumar M 2003 Major ion chemistry and identification of hydrogeochemical processes of groundwater in a part of Kancheepuram district, Tamil Nadu, India; Environ. Geosci. 10(4) 157–166.
Mondal N C and Singh V S 2004 A new approach to delineate the groundwater recharge zone in hard rock terrain; J. Geol. Soc. India 87(5) 658–662.
National Academy of Sciences–National Academy of Engineering 1972 Water quality criteria 1972; Washington DC, National Academy of Sciences, 594p.
Panigrahy P I C, Sahu S D, Sahu B K and Sathyanarayana D 1996 Studies on the distribution of calcium and magnesium in Visakhapatnam harbour waters, Bay of Bengal; International Symposium on Applied Geochemistry, Osmania University, Hyderabad, 353–340.
Prasanna M V 2008 Hydrogeochemical studies in the Gadilam River Basin, Tamil Nadu; Unpublished Ph.D Thesis; Department of Earth Sciences, Annamalai University, India, 300p.
Prasanna M V, Chidambaram S, Vasu K, Hameed Shahul A, Unnikrishna Warrier C, Srinivasamoorthy K, Anandhan P and John Peter A 2008 Identification of the geochemical processes in coastal groundwater using hydrogeochemical and isotopic data: A Case study of the Gadilam river basin in southern India; Indian J. Marine Sci. 37(2) 200–206.
Rabemanana V, Violette S, de Marsily G, Robain H, Deffontaines B, Andrieux P, Bensimon M and Parriaux A 2005 Origin of the high variability of water mineral content in the bedrock aquifers of Southern Madagascar; J. Hydrol. 310 143–156.
Ramappa R and Suresh T S 2000 Quality of groundwater in relation to agricultural practices in Lokapavani river basin, Karnataka, India; Proceedings of International Seminar on Applied Hydrogeochemistry, Annamalai University, 136–142.
Rengarajan R and Balasubramanian A 1990 Corrosion and scale formation characteristic of groundwater in and around Nangavalli, Salem district, Tamil Nadu; J. Appl. Hydrol. 2 15–22.
Sadashivaiah C, Ramakrishnaiah C R and Ranganna G 2008 Hydrochemical analysis and evaluation of groundwater quality in Tumkur taluk, Karnataka state, India; Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 5(3) 158–164.
Sankaranarayanan P R and Ramanujachary K R 1967 An inverse slope method of determining absolute resistivities; Geophys. 32(6) 1036–1040.
Schock M R 1980 Response of lead solubility to dissolved carbonate in drinking water; Journal American Water Works Association 72 695–704.
Singh Abhay K R, Mondal G C, Singh S, Singh P K, Singh T B, Tewary B K and Sinha A 2007 Aquatic geochemistry of Dhanbad, Jharkhand: Source evaluation and quality assessment; J. Geol. Soc. India 69(5) 1088–1102.
Srinivasa Rao Y, Reddy T V K and Nayudu P T 1997 Groundwater quality in the Niva river basin, Chittoor district, Andhra Pradesh, India; J. Environ. Geol. 32(1) 56–63.
Srinivasamoorthy K 2004 Hydrogeochemistry of Groundwater in Salem District, Tamil Nadu, India; Unpublished Ph.D Thesis, Annamalai University, India.
Srinivasamoorthy K, Chidambaram S, Prasanna M V, Vasanthavihar M, John peter A and Anandhan P 2008 Identification of major sources controlling groundwater chemistry from a hard rock terrain – A case study from Mettur taluk, Salem District, Tamil Nadu, India: J. Earth System Sci. 117(1) 49–58.
Taylor S R and McLennan S M 1985 The Continental Crust: Its Composition and Evolution (Oxford, UK: Blackwell) 312.
Todd D K 1959 Ground Water Hydrology (New York: John Wiley & Sons).
USGS 1993 Nation water summary 1990–1991: Stream water quality; United State Geological Survey, Water supply paper no. 2400 590.
WHO 1993 Guidelines for drinking water quality; World Health Organization, Geneva, 171.
WHO 1996 Guidelines for drinking water quality; World Health Organization, Geneva 1 53–73.
WHO 2003 Lead in drinking-water; Background document for preparation of WHO Guidelines for drinking-water quality; Geneva, World Health Organization (WHO/SDE/WSH/03.04/9).
WHO 2004 Guidelines for drinking water quality; 3rd edn., Recommendations, Geneva 1 515.
Zohdy A A R, Eaton G P and Mabey D R 1974 Applications of surface geophysics to groundwater investigations; Techniques of water resource investigation of the US Geological Survey 2 116.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
PRASANNA, M.V., CHIDAMBARAM, S., HAMEED, A.S. et al. Hydrogeochemical analysis and evaluation of groundwater quality in the Gadilam river basin, Tamil Nadu, India. J Earth Syst Sci 120, 85–98 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0004-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-011-0004-6