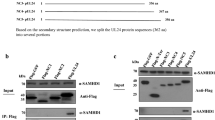
Abstract
The interplay between the host and Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) plays a pivotal role in the outcome of an infection. HCMV growth in endothelial and epithelial cells requires expression of viral proteins UL128, UL130, and UL131 proteins (UL128-131), of which UL130 is the largest gene and the only one that is not interrupted by introns. Mutation of the C terminus of the UL130 protein causes reduced tropism of endothelial cells (EC). However, very few host factors have been identified that interact with the UL130 protein. In this study, HCMV UL130 protein was shown to directly interact with the human protein Snapin in human embryonic kidney HEK293 cells by Yeast two-hybrid screening, in vitro glutathione S-transferase (GST) pull-down, and co-immunoprecipitation. Additionally, heterologous expression of protein UL130 revealed co-localization with Snapin in the cell membrane and cytoplasm of HEK293 cells using fluorescence confocal microscopy. Furthermore, decreasing the level of Snapin via specific small interfering RNAs decreased the number of viral DNA copies and titer in HCMV-infected U373-S cells. Taken together, these results suggest that Snapin, the pUL130 interacting protein, has a role in modulating HCMV DNA synthesis.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Co-IP:
-
Co-immunoprecipitation
- HCMV:
-
Human cytomegalovirus
- ORF:
-
open reading frame
- PCR:
-
polymerase chain reaction
- siRNAs:
-
small interfering RNAs
References
Akter P, Cunningham C, McSharry BP, Dolan A, Addison C, Dargan DJ, Hassan-Walker AF, Emery VC, et al. 2003 Two novel spliced genes in human cytomegalovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 84 1117–1122
Bissinger AL, Sinzger C, Kaiserling E and Jahn G 2002 Human cytomegalovirus as a direct pathogen: correlation of multiorgan involvement and cell distribution with clinical and pathological findings in a case of congenital inclusion disease. J. Med. Virol. 67 200–206
Britt W 2008 Manifestations of human cytomegalovirus infection: proposed mechanisms of acute and chronic disease. Curr. Top. Microbiol. Immunol. 325 417–470
Buxton P, Zhang XM, Walsh B, Sriratana A, Schenberg I, Manickam E and Rowe T 2003 Identification and characterization of Snapin as a ubiquitously expressed SNARE-binding protein that interacts with SNAP23 in non-neuronal cells. Biochem. J. 375 433–440
Hahn G, Revello MG, Patrone M, Percivalle E, Campanini G, Sarasini A, Wagner M, Gallina A, et al. 2004 Human cytomegalovirus UL131-128 genes are indispensable for virus growth in endothelial cells and virus transfer to leukocytes. J. Virol. 78 10023–10033
Haspot F, Lavault A, Sinzger C, Laib Sampaio K, Stierhof YD, Pilet P, Bressolette-Bodin C and Halary F 2012 Human cytomegalovirus entry into dendritic cells occurs via a macropinocytosis-like pathway in a pH-independent and cholesterol-dependent manner. PLoS One 7 e34795
Hertel L and Mocarski ES 2004 Global analysis of host cell gene expression late during cytomegalovirus infection reveals extensive dysregulation of cell cycle gene expression and induction of Pseudomitosis independent of US28 function. J. Virol. 78 11988–12011
Ilardi JM, Mochida S and Sheng ZH 1999 Snapin: a SNARE-associated protein implicated in synaptic transmission. Nat. Neurosci. 2 119–124
Kahl M, Siegel-Axel D, Stenglein S, Jahn G and Sinzger C 2000 Efficient lytic infection of human arterial endothelial cells by human cytomegalovirus strains. J. Virol. 74 7628–7635
Kalejta RF and Shenk T 2002 Manipulation of the cell cycle by human cytomegalovirus. Front. Biosci. 7 d295–d306
Landolfo S, Gariglio M, Gribaudo G and Lembo D 2003 The human cytomegalovirus. Pharmacol. Ther. 98 269–297
McMahon TP and Anders DG 2002 Interactions between human cytomegalovirus helicase-primase proteins. Virus Res. 86 39–52
Mocarski ES, Shenk T and Pass RF 2007 Cytomegalovirus; in Fields virology 5th ed. (eds) DM Knipe, PM Howley, DE Griffin, MA Martin, RA Lamb, B Roizman and SE Straus (Philadelphia: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins) pp 2701–2772
Nogalski MT, Chan GC, Stevenson EV, Collins-McMillen DK and Yurochko AD 2013 The HCMV gH/gL/UL128-131 complex triggers the specific cellular activation required for efficient viral internalization into target monocytes. PLoS Pathog. 9 e1003463
Patrone M, Secchi M, Fiorina L, Ierardi M, Milanesi G and Gallina A 2005 Human cytomegalovirus UL130 protein promotes endothelial cell infection through a producer cell modification of the virion. J. Virol. 79 8361–8373
Revello MG and Gerna G 2010 Human cytomegalovirus tropism for endothelial/epithelial cells: scientific background and clinical implications. Rev. Med. Virol. 20 136–155
Riegler S, Hebart H, Einsele H, Brossart P, Jahn G and Sinzger C 2000 Monocyte-derived dendritic cells are permissive to the complete replicative cycle of human cytomegalovirus. J. Gen. Virol. 81 393–399
Ruder C, Reimer T, Delgado-Martinez I, Hermosilla R, Engelsberg A, Nehring R, Dorken B and Rehm A 2005 EBAG9 adds a new layer of control on large dense-core vesicle exocytosis via interaction with Snapin. Mol. Biol. Cell. 16 1245–1257
Ryckman BJ, Jarvis MA, Drummond DD, Nelson JA and Johnson DC 2006 Human cytomegalovirus entry into epithelial and endothelial cells depends on genes UL128 to UL150 and occurs by endocytosis and low-pH fusion. J. Virol. 80 710–722
Ryckman BJ, Chase MC and Johnson DC 2008a HCMV gH/gL/UL128-131 interferes with virus entry into epithelial cells: evidence for cell type-specific receptors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 105 14118–14123
Ryckman BJ, Rainish BL, Chase MC, Borton JA, Nelson JA, Jarvis MA and Johnson DC 2008b Characterization of the human cytomegalovirus gH/gL/UL128-131 complex that mediates entry into epithelial and endothelial cells. J. Virol. 82 60–70
Scholz B, Rechter S, Drach JC, Townsend LB and Bogner E 2003 Identification of the ATP-binding site in the terminase subunit pUL56 of human cytomegalovirus. Nucleic Acids Res. 31 1426–1433
Schuessler A, Sampaio KL, Scrivano L and Sinzger C 2010 Mutational mapping of UL130 of human cytomegalovirus defines peptide motifs within the C-terminal third as essential for endothelial cell infection. J. Virol. 84 9019–9026
Schuessler A, Sampaio KL, Straschewski S and Sinzger C 2012 Mutational mapping of pUL131A of human cytomegalovirus emphasizes its central role for endothelial cell tropism. J. Virol. 86 504–512
Shen A, Lei J, Yang E, Pei Y, Chen YC, Gong H, Xiao G and Liu F 2011 Human cytomegalovirus primase UL70 specifically interacts with cellular factor Snapin. J. Virol. 85 11732–11741
Sinzger C 2008 Entry route of HCMV into endothelial cells. J. Clin. Virol. 41 174–179
Sinzger C, Plachter B, Grefte A, The TH and Jahn G 1996 Tissue macrophages are infected by human cytomegalovirus in vivo. J. Infect. Dis. 173 240–245
Sinzger C, Kahl M, Laib K, Klingel K, Rieger P, Plachter B and Jahn G 2000 Tropism of human cytomegalovirus for endothelial cells is determined by a post-entry step dependent on efficient translocation to the nucleus. J. Gen. Virol. 81 3021–3035
Stanton RJ, Baluchova K, Dargan DJ, Cunningham C, Sheehy O, Seirafian S, McSharry BP, Neale ML, et al. 2010 Reconstruction of the complete human cytomegalovirus genome in a BAC reveals RL13 to be a potent inhibitor of replication. J. Clin. Invest. 120 3191–3208
Starcevic M and Dell'Angelica EC 2004 Identification of snapin and three novel proteins (BLOS1, BLOS2, and BLOS3/reduced pigmentation) as subunits of biogenesis of lysosome-related organelles complex-1 (BLOC-1). J. Biol. Chem. 279 28393–28401
Straschewski S, Patrone M, Walther P, Gallina A, Mertens T and Frascaroli G 2011 Protein pUL128 of human cytomegalovirus is necessary for monocyte infection and blocking of migration. J. Virol. 85 5150–5158
Sun ZR, Ji YH, Ruan Q, He R, Ma YP, Qi Y, Mao ZQ and Huang YJ 2009 Structure characterization of human cytomegalovirus UL131A, UL130 and UL128 genes in clinical strains of China. Genet. Mol. Res. 8 1191–1201
Sun Z, Ren G, Ma Y, Wang N, Ji Y, Qi Y, Li M, He R, et al. 2010 Transcription pattern of UL131A-128 mRNA in clinical strains of human cytomegalovirus. J. Biosci. 35 365–370
To A, Bai Y, Shen A, Gong H, Umamoto S, Lu S and Liu F 2011 Yeast two hybrid analyses reveal novel binary interactions between human cytomegalovirus-encoded virion proteins. PLoS One 6 e17796
Vites O, Rhee JS, Schwarz M, Rosenmund C and Jahn R 2004 Reinvestigation of the role of snapin in neurotransmitter release. J. Biol. Chem. 279 26251–26256
Wang SC, Lin JT and Chern Y 2009 Novel regulation of adenylyl cyclases by direct protein-protein interactions: insights from snapin and ric8a. Neurosignals 17 169–180
Wills MR, Ashiru O, Reeves MB, Okecha G, Trowsdale J, Tomasec P, Wilkinson GW, Sinclair J, et al. 2005 Human cytomegalovirus encodes an MHC class I-like molecule (UL142) that functions to inhibit NK cell lysis. J. Immunol. 175 7457–7465
Wussow F, Chiuppesi F, Martinez J, Campo J, Johnson E, Flechsig C, Newell M, Tran E, et al. 2014 Human cytomegalovirus vaccine based on the envelope gH/gL pentamer complex. PLoS Pathog. 10 e1004524
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81171580 and 81171581) and the Outstanding Scientific Fund of Shengjing Hospital.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Corresponding editor: Shahid Jameel
Corresponding editor: Shahid Jameel
[Wang G, Ren G, Cui X, Lu Z, Ma Y, Qi Y, Huang Y, Liu Z, Sun Z and Ruan Q 2016 Host protein Snapin interacts with human cytomegalovirus pUL130 and affects viral DNA replication. J. Biosci.] DOI 10.1007/s12038-016-9604-2
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, G., Ren, G., Cui, X. et al. Host protein Snapin interacts with human cytomegalovirus pUL130 and affects viral DNA replication. J Biosci 41, 173–182 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-016-9604-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-016-9604-2