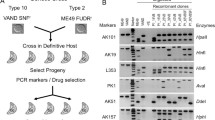
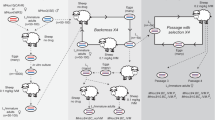
Abstract
Coccidial parasites including Cryptosporidium parvum, Cyclospora cayetanensis, Neospora caninum, Toxoplasma gondii and the Eimeria species can cause severe disease of medical and veterinary importance. As many as one-third of the human population may carry T. gondii infection, and Eimeria are thought to cost the global poultry production industry in excess of US$2 billion per annum. Despite their significance, effective vaccines are scarce and have been confined to the veterinary field. As sequencing and genotyping technologies continue to develop, genetic mapping remains a valuable tool for the identification of genes that underlie phenotypic traits of interest and the assembly of contiguous genome sequences. For the coccidian, cross-fertilization still requires in vivo infection, a feature of their life cycle which limits the use of genetic mapping strategies. Importantly, the development of population-based approaches has now removed the need to isolate clonal lines for genetic mapping of selectable traits, complementing the classical clone-based techniques. To date, four coccidial species, representing three genera, have been investigated using genetic mapping. In this review we will discuss recent progress with these species and examine the prospects for future initiatives.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abrahamsen MS, Templeton TJ, Enomoto S, Abrahante JE, Zhu G, Lancto CA, Deng M, Liu C, et al. 2004 Complete genome sequence of the apicomplexan, Cryptosporidium parvum. Science 304 441–445
Ajzenberg D, Banuls AL, Su C, Dumetre A, Demar M, Carme B and Darde ML 2004 Genetic diversity, clonality and sexuality in Toxoplasma gondii. Int. J. Parasitol. 34 1185–1196
Beach J and Corl J 1925 Studies in the control of avian coccidiosis. Poultry Sci. 4 83–93
Beck HP, Blake D, Darde ML, Felger I, Pedraza-Diaz S, Regidor-Cerrillo J, Gomez-Bautista M, Ortega-Mora LM, et al. 2009 Molecular approaches to diversity of populations of apicomplexan parasites. Int. J. Parasitol. 39 175–189
Blake DP, Hesketh P, Archer A, Carroll F, Smith AL and Shirley MW 2004 Parasite genetics and the immune host: recombination between antigenic types of Eimeria maxima as an entree to the identification of protective antigens. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 138 143–152
Blake DP, Billington KJ, Copestake SL, Oakes RD, Quail MA, Wan KL, Shirley MW and Smith AL 2011a Genetic mapping identifies novel highly protective antigens for an apicomplexan parasite. PLoS Pathog. 7 e1001279
Blake DP, Oakes R and Smith AL 2011b A genetic linkage map for the apicomplexan protozoan parasite Eimeria maxima and comparison with Eimeria tenella. Int. J. Parasitol. 41 263–270
Boyle JP, Saeij JP, Harada SY, Ajioka JW and Boothroyd JC 2008 Expression quantitative trait locus mapping of toxoplasma genes reveals multiple mechanisms for strain-specific differences in gene expression. Eukaryot. Cell. 7 1403–1414
Carreno R, Martin D and Barta J 1999 Cryptosporidium is more closely related to the gregarines than to coccidia as shown by phylogenetic analysis of apicomplexan parasites inferred using small-subunit ribosomal RNA gene sequences. Parasitol. Res. 85 899–904
Chapman H 1997 Biochemical, genetic and applied aspects of drug resistance in Eimeria parasites of the fowl. Avian Pathol. 26 221–244
Clark JD, Billington K, Bumstead JM, Oakes RD, Soon PE, Sopp P, Tomley FM and Blake DP 2008 A toolbox facilitating stable transfection of Eimeria species. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 162 77–86
Cornelissen AW and Overdulve JP 1985 Sex determination and sex differentiation in coccidia: gametogony and oocyst production after monoclonal infection of cats with free-living and intermediate host stages of Isospora (Toxoplasma) gondii. Parasitology 90 35–44
Dubey JP and Frenkel JK 1976 Feline toxoplasmosis from acutely infected mice and the development of Toxoplasma cysts. J. Protozool. 23 537–546
Dubey JP, Navarro IT, Sreekumar C, Dahl E, Freire RL, Kawabata HH, Vianna MC, Kwok OC, Shen SK, Thulliez P and Lehmann T 2004 Toxoplasma gondii infections in cats from Parana, Brazil: seroprevalence, tissue distribution, and biologic and genetic characterization of isolates. J. Parasitol. 90 721–726
Dubey JP, Velmurugan GV, Chockalinga AM, Pena HF, LN de Oliveira, Leifer CA, Gennari SM, Bahia LM Oliveira and Su C 2008 Genetic diversity of Toxoplasma gondii isolates from chickens from Brazil. Vet. Parasitol. 157 299–305
Elsheikha HM, Lacher DW and Mansfield LS 2005 Phylogenetic relationships of Sarcocystis neurona of horses and opossums to other cyst-forming coccidia deduced from SSU rRNA gene sequences. Parasitol. Res. 97 345–357
Feng X, Rich SM, Akiyoshi D, Tumwine JK, Kekitiinwa A, Nabukeera N, Tzipori S and Widmer G 2000 Extensive polymorphism in Cryptosporidium parvum identified by multilocus microsatellite analysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 66 3344–3349
Feng X, Rich S, Tzipori S and Widmer G 2002 Experimental evidence for genetic recombination in the opportunistic pathogen Cryptosporidium parvum. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 119 55–62
Gibson-Kueh S, Thuy NT, Elliot A, Jones JB, Nicholls PK and Thompson RC 2011 An intestinal Eimeria infection in juvenile Asian seabass (Lates calcarifer) cultured in Vietnam--a first report. Vet. Parasitol. 181 106–112
Guindon S, Dufayard JF, Lefort V, Anisimova M, Hordijk W and Gascuel O 2010 New algorithms and methods to estimate maximum-likelihood phylogenies: assessing the performance of PhyML 3.0. Syst. Biol. 59 307–321
Hashim A, Mulcahy G, Bourke B and Clyne M 2006 Interaction of Cryptosporidium hominis and Cryptosporidium parvum with primary human and bovine intestinal cells. Infect. Immun. 74 99–107
Howe DK and Sibley LD 1995 Toxoplasma gondii comprises three clonal lineages: correlation of parasite genotype with human disease. J. Infect. Dis. 172 1561–1566
Innes EA, Bartley PM, Buxton D and Katzer F 2009 Ovine toxoplasmosis. Parasitology 136 1887–1894
Jirku M, Obornik M, Lukes J and Modry D 2009 A model for taxonomic work on homoxenous coccidia: redescription, host specificity, and molecular phylogeny of Eimeria ranae Dobell 1909, with a review of anuran-host Eimeria (Apicomplexa: Eimeriorina). J. Eukaryot. Microbiol. 56 39–51
Karanis P and Aldeyarbi HM 2011 Evolution of Cryptosporidium in vitro culture. Int. J. Parasitol. 41 1231–1242
Katzer F, Lizundia R, Ngugi D, Blake D and D McKeever 2011 Construction of a genetic map for Theileria parva: identification of hotspots of recombination. Int. J. Parasitol. 41 669–675
Khan A, Taylor S, Su C, Mackey AJ, Boyle J, Cole R, Glover D, Tang K, et al. 2005 Composite genome map and recombination parameters derived from three archetypal lineages of Toxoplasma gondii. Nucleic Acids Res. 33 2980–2992
Lander ES, Green P, Abrahamson J, Barlow A, Daly MJ, Lincoln SE and Newberg LA 1987 MAPMAKER: an interactive computer package for constructing primary genetic linkage maps of experimental and natural populations. Genomics 1 174–181
Ling KH, Rajandream MA, Rivailler P, Ivens A, Yap SJ, Madeira AM, Mungall K, Billington K, et al.2007 Sequencing and analysis of chromosome 1 of Eimeria tenella reveals a unique segmental organization. Genome Res. 17 311–319
Manly KF, Cudmore RH, Jr. and Meer JM 2001 Map Manager QTX, cross-platform software for genetic mapping. Mamm. Genome 12 930–932
Martinelli A, Cheesman S, Hunt P, Culleton R, Raza A, Mackinnon M and Carter R 2005a A genetic approach to the de novo identification of targets of strain-specific immunity in malaria parasites. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 102 814–819
Martinelli A, Hunt P, Fawcett R, Cravo PV, Walliker D and Carter R 2005b An AFLP-based genetic linkage map of Plasmodium chabaudi chabaudi. Malar J. 4 11
Mead JR 2002 Cryptosporidiosis and the challenges of chemotherapy. Drug Resist. Updat. 5 47–57
Meznar ER, Gadau J, Koeniger N and Rueppell O 2010 Comparative linkage mapping suggests a high recombination rate in all honeybees. Hered. J. 101 S118–S126
Montoya JG and Liesenfeld O 2004 Toxoplasmosis. Lancet 363 1965–1976
Morens DM, Folkers GK and Fauci AS 2004 The challenge of emerging and re-emerging infectious diseases. Nature 430 242–249
Perry B, Randolph T, J McDermott, Sones K and Thornton P 2002 Investing in animal health research to alleviate poverty (Nairobi, Kenya: International Livestock Research Institute)
Piper MB, Bankier AT and Dear PH 1998 A HAPPY map of Cryptosporidium parvum. Genome Res. 8 1299–1307
Putignani L, Sallicandro P, Alano P, Abrahamsen MS, Crisanti A and Spano F 1999 Chromosome mapping in Cryptosporidium parvum and establishment of a long-range restriction map for chromosome VI. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 175 231–238
Shirley MW and Harvey DA 2000 A genetic linkage map of the apicomplexan protozoan parasite Eimeria tenella. Genome Res. 10 1587–1593
Shirley MW, Smith AL and Tomley FM 2005 The biology of avian Eimeria with an emphasis on their control by vaccination. Adv. Parasitol. 60 285–330
Sibley LD and Boothroyd JC 1992 Virulent strains of Toxoplasma gondii comprise a single clonal lineage. Nature 359 82–85
Sibley L, LeBlanc A, Pfefferkorn E and Boothroyd J 1992 Generation of a restriction fragment length polymorphism linkage map for Toxoplasma gondii. Genetics 132 1003–1015
Sibley LD, Mordue DG, Su C, Robben PM and Howe DK 2002 Genetic approaches to studying virulence and pathogenesis in Toxoplasma gondii. Philos. Trans. R Soc. London B Biol. Sci. 357 81–88
Sturtevant A 1913 The linear arrangement of six sex-linked factors in Drosophila, as shown by their mode of association. J. Exp. Zool. 14 43–59
Su X, Ferdig M, Huang Y, Huynh C, Liu A, You J, Wootton J and Wellems T 1999 A genetic map and recombination parameters of the human malaria parasite Plasmodium falciparum. Science 286 1351–1353
Su C, Howe DK, Dubey JP, Ajioka JW and Sibley LD 2002 Identification of quantitative trait loci controlling acute virulence in Toxoplasma gondii. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 99 10753–10758
Su C, Evans D, Cole RH, Kissinger JC, Ajioka JW and Sibley LD 2003 Recent expansion of Toxoplasma through enhanced oral transmission. Science 299 414–416
Tanriverdi S, Blain JC, Deng B, Ferdig MT and Widmer G 2007 Genetic crosses in the apicomplexan parasite Cryptosporidium parvum define recombination parameters. Mol. Microbiol. 63 1432–1439
Taylor MA, Coop RL and Wall RL 2007 Veterinary parasitology (Blackwell Publishing Ltd.)
Williams DM, Grumet FC and Remington JS 1978 Genetic control of murine resistance to Toxoplasma gondii. Infect. Immun. 19 416–420
Williams RB, Carlyle WW, Bond DR and Brown IA 1999 The efficacy and economic benefits of Paracox, a live attenuated anticoccidial vaccine, in commercial trials with standard broiler chickens in the United Kingdom. Int. J. Parasitol. 29 341–355
Yan W, Liu X, Shi T, Hao L, Tomley FM and Suo X 2009 Stable transfection of Eimeria tenella: constitutive expression of the YFP-YFP molecule throughout the life cycle. Int. J. Parasitol. 39 109–117
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Clark EL and Blake DP 2012 Genetic mapping and coccidial parasites: Past achievements and future prospects. J. Biosci. 37 1–8] DOI 10.1007/s12038-012-9251-1
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clark, E.L., Blake, D.P. Genetic mapping and coccidial parasites: Past achievements and future prospects. J Biosci 37, 879–886 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-012-9251-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-012-9251-1