Abstract
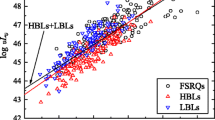
We use the correlation between the core-to-lobe radio luminosity ratio (R) and the linear size (D) of a sample of BL Lacertae objects to investigate the relativistic beaming and radio source orientation paradigm for high peaked and low-peaked BL Lacs (X-ray and radio selected BL Lacs respectively) and to constrain relativistic beaming model for this extreme class of active galactic nuclei. We show that the R − D distributions of the BL Lac populations contradict blazar orientation sequence, with the X-ray selected BL Lacs (XBLs) being more consistent with the beaming and orientation model. On the premise that Fanaroff-Riley Type I radio galaxies are the unbeamed parent population of these objects, we derive the bulk Lorentz factor of the jets, γ~7 − 20 corresponding to a critical cone angle for optimum boosting, φ c of ~ 1° − 4°, while on average, these objects are inclined at 5° − 12° to the line-of-sight. The implications of these results for the blazar unification sequence are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bai, J. M., Lee, M. G. 2001, Astrophys. J., 548, 244.
Beckmann, V., Engles, D., Bade, N., Wucknitz, O. 2003, Astron. Astrophys., 401, 927.
Blandford, R. D., Königl, A. 1979, Astrophys. J., 232, 34.
Brinkmann, W., Siebert, J., Kollgaard, R. I., Thomas, H. C. 1996, Astron. Astrophys., 313, 356.
Capetti, A., de Ruitar, H. R., Fanti, R. et al. 2000, Astron. Astrophys., 362, 871.
Caccianiga, A., Maccacaro, T., Wolter, O., della Ceca, R., Gioia, I. M. 1999, Astrophys. J., 513, 51.
Caccianiga, A., Marcha, M. J. 2004, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 348, 937.
Cohen, M. H., Lister, M. L., Homan, D. et al. 2007, Astrophys. J., 658, 232.
Fan, J. H., Zhang, J. S., 2003, Astron. Astrophys., 407, 899.
Fanaroff, B. L., Riley, J. M. 1974, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 167, 13.
Fossati, G., Celloti, A., Ghisellini, G., Maraschi, L. 1997, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 289, 136.
Gabuzda, D. C., Mullan, C. M., Cawthorne, T. V., Wardle, J. F., Roberts, D. H. 1994, Astrophys. J., 435, 140.
Ghisellini, G., Padovani, P., Celotti, A., Maraschi, L. 1993, Astrophys. J., 407, 67.
Ghisellini, G., Tavecchio, F., Bodo, G., Celotti, A. 2009, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 393, L16.
Ghisellini, G., Tavecchio, F., Foschini, L., Ghirlanda, G. 2010, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 414, 2674.
Giroletti, M., Giovannini, G., Taylor, G. B., Falomo, R. 2006, Astrophys. J., 646, 801.
Kapahi, V. K., Saikia, D. J. 1982, J. Astrophys. Astron., 3, 465.
Kharb, P., Lister, M. L., Cooper, N. J. 2010, Astrophys. J., 710, 764.
Kollgaard, R. I. 1994, Vistas in Astronomy, 38, 29.
Kollgaard, R. I., Palma, C., Laurent-Muchleisen, S., Feigelson, E. D. 1996, Astrophys. J., 46, 115.
Landt, H., Bignall, H. E. 2008, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 391, 967.
Landt, H., Padovani, P., Perlman, E. S. 2006, Astrophys. J., 637, 183.
Landt, H., Padovani, P., Perlman, E. S., Giommi, P. 2002, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 336, 945.
Laurent-Muehleisen, S. A., Kollgaard, R. I., Feigelson, E. D., Brickmann, W., Siebert, J. 1999, Astrophys. J., 525, 127.
Ledden, J. E., O’Dell, S. L. 1985, Astrophys. J., 258, 630.
Meyer, E. T., Fossati, G., Georganopoulos, M., Lister, M. L. 2011, Astrophys. J., 740, 98.
Murphy D. W., Browne, I. W. A., Perley, R. A. 1993, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 264, 298.
Nieppola, E., Tornikoski, M., Valtaoja, E., Hakala, T. et al. 2007, Astron. J., 133, 1947.
Nieppola, E., Tornikoski, M., Valtaoja, E. 2006, Astron. Astrophys., 445, 441.
Odo, F. C., Ubachukwu, A. A., Chukwude, A. E. 2011, African Skies, 15, 15.
Okoye, S. E., Onuora, L. I. 1982, Astrophys. J., 260, 37.
Orr, M. J., Browne, I. W. A. 1982, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc., 200, 1067.
Padovani, P., Giommi, P. 1995, Astrophys. J., 444, 567.
Perlman, E. S., Stocke, J. T. 1993, Astrophys. J., 406, 430.
Rector, T. A., Stocke, J. T. 2001, Astron. J., 122, 565.
Sambruna, R. M., Maraschi, L., Urry, C. M. 1996, Astrophys. J., 463, 444.
Stickel, M., Padovani, P., Urry, C. M., Fried, H. 1991, Astrophys. J., 374, 431.
Stocke, J. T., Liebert, J., Schmidt, G. et al. 1985, Astrophys. J., 298, 619.
Stocke, J. T., Morris, S. L., Giola, I. M. et al. 1991, Astrophys. J. Suppl., 76, 813.
Ubachukwu, A. A. 1998, Astrophys. Space Sci., 257, 23.
Ubachukwu, A. A. 2002, Astrophys. Space Sci., 279, 251.
Ubachukwu, A. A., Chukwude, A. E. 2002, J. Astrophys. Astron., 23, 253.
Urry, C. M. 1998, Publ. Adv. Sp. Res., 21, 189.
Urry, C. M., Padovani, P. 1995, Publ. Astron. Soc. Pacific, 803, 107.
Vermeulen, R. C., Cohen, M. H. 1994, Astrophys. J., 430, 467.
Zirbel, E., Baum, S. A. 1995, Astrophys. J., 448, 521.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Odo, F.C., Ubachukwu, A.A. & Chukwude, A.E. Relativistic Beaming and Orientation Effects in BL Lacertae Objects. J Astrophys Astron 33, 279–290 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12036-012-9141-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12036-012-9141-9