Abstract
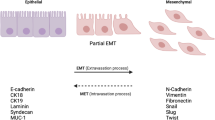
Stromal cell-derived factor 1 (SDF-1) and its receptor, CXCR4, play an important role in tumor progression. Epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) process is linked to disease pathophysiology. This study aimed to investigate the roles and underlying mechanisms of SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in EMT process of glioblastoma. In the present study, CXCR4 activation and inhibition in U87 were induced with exogenous SDF-1 and with CXCR4 small interfering RNA (siRNA), respectively. CXCR4 downstream signal molecules AKT, ERK, and EMT biomarkers (vementin, snail, N-cadherin, and E-cadherin) were tested using the Western blot. Our results showed that SDF-1 can induce AKT and ERK phosphorylation in a dose-dependent manner, and endogenous CXCR4 can be blocked thoroughly by CXCR4 siRNA in U87. Notably SDF-1 alone treatment can induce the upregulation of vementin, snail, and N-cadherin of U87; besides, the downregulation of E-cadherin also occurred. On the contrary, CXCR4 siRNA significantly prohibited SDF-1-induced AKT and ERK phosphorylation, at the same time, EMT biomarker changes were not observed. Function analysis revealed that CXCR4 siRNA obviously interfered with U87 cell migration and proliferation, according to wound healing assay. In conclusion, this study suggested that EMT process can be triggered by the SDF-1/CXCR4 axis in glioblastoma, and then involved in the tumor cell invasion and proliferation via activation of PI3K/AKT and ERK pathway. Our study lays a new foundation for the treatment of glioblastoma through antagonizing CXCR4.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wilson TA, Karajannis MA, Harter DH (2014) Glioblastoma multiforme: state of the art and future therapeutics. Surg Neurol Int 5:64
Weathers SP, Gilbert MR (2014) Advances in treating glioblastoma. F1000Prime Rep 6:46
Stupp R, Mason WP, van den Bent MJ, Weller M, Fisher B, Taphoorn Martin JB, Belanger K, Brandes AA, Marosi C, Bogdahn U, Curschmann J, Janzer RC, Ludwin SK, Gorlia T, Allgeier A, Lacombe D, Cairncross JG, Eisenhauer E, Mirimanoff RO (2005) Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 352(10):987–996
Gilbert MR, Wang M, Aldape KD, Stupp R, Hegi ME, Jaeckle KA, Armstrong TS, Wefel JS, Won M, Blumenthal DT, Mahajan A, Schultz CJ, Erridge S, Baumert B, Hopkins KI, Tzuk-Shina T, Brown PD, Chakravarti A, Curran WJ, Mehta MP (2013) Dose-dense temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma: a randomized phase III clinical trial. J Clin Oncol 31(32):4085–4091
Moustakas A, Heldin P (2014) TGFβ and matrix-regulated epithelial to mesenchymal transition. Biochim Biophys Acta 1840(8):2621–2634
Lamouille S, Xu J, Derynck R (2014) Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 15(3):178–196
Nieto MA (2013) Epithelial plasticity: a common theme in embryonic and cancer cells. Science 342(6159):1234850
Li Y, Ma J, Qian X, Wu Q, Xia J, Miele L, Sarkar FH, Wang Z (2013) Regulation of EMT by notch signaling pathway in tumor progression. Curr Cancer Drug Targets 13(9):957–962
Balogh P, Katz S, Kiss AL (2013) The role of endocytic pathways in TGF-β signaling. Pathol Oncol Res 19(2):141–148
Fuxe J, Karlsson MC (2012) TGF-β-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition: a link between cancer and inflammation. Semin Cancer Biol 22(5–6):455–461
Gao D, Vahdat LT, Wong S, Chang JC, Mittal V (2012) Microenvironmental regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in cancer. Cancer Res 72(19):4883–4889
Dave B, Mittal V, Tan NM, Chang JC (2012) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cancer stem cells and treatment resistance. Breast Cancer Res 14(1):202
Roy I, Evans DB, Dwinell MB (2014) Chemokines and chemokine receptors: update on utility and challenges for the clinician. Surgery 155(6):961–973
Yoshie O (2013) Chemokine receptors as therapeutic targets. Nihon Rinsho Meneki Gakkai Kaishi 36(4):189–196
Domanska UM, Kruizinga RC, Nagengast WB, Timmer-Bosscha H, Huls G, de Vries EG, Walenkamp AM (2013) A review on CXCR4/CXCL12 axis in oncology: no place to hide. Eur J Cancer 49(1):219–230
Feng Y, Broder CC, Kennedy PE, Berger EA (1996) HIV-1 entry cofactor: Functional cDNA cloning of a seven-transmembrane, G protein-coupled receptor. Science 272(5263):872–877
Balkwill F (2004) Cancer and the chemokine network. Nat Rev Cancer 4(7):540–550
Luker KE, Luker GD (2006) Functions of CXCL12 and CXCR4 in breast cancer. Cancer Lett 238(1):30–41
Fernandis AZ, Prasad A, Band H, Klösel R, Ganju RK (2004) Regulation of CXCR4-mediated chemotaxis and chemoinvasion of breast cancer cells. Oncogene 23(1):157–167
Bates RC, DeLeo Iii MJ, Mercurio AM (2004) The epithelial–mesenchymal transition of colon carcinoma involves expression of IL-8 and CXCR-1-mediated chemotaxis. Exp Cell Res 299(2):315–324
Wu Y, Ginther C, Kim J, Mosher N, Chung S, Slamon D, Vadgama JV (2012) Expression of Wnt3 activates Wnt/β-catenin pathway and promotes EMT-like phenotype in trastuzumab-resistant HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res 10(12):1597–1606
Deshmukh AB, Patel JK, Prajapati AR, Shah S (2012) Perspective in chronic kidney disease: targeting hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) as potential therapeutic approach. Ren Fail 34(4):521–532
Li Y, Qiu X, Zhang S, Zhang Q, Wang E (2009) Hypoxia induced CXCR4 expression via HIF-1alpha and HIF-2alpha correlates with migration and invasion in lung cancer cells. Cancer Biol Ther 8(4):322–330
Higgins DF, Kimura K, Bernhardt WM, Shrimanker N, Akai Y, Hohenstein B, Saito Y, Johnson RS, Kretzler M, Cohen CD, Eckardt KU, Iwano M, Haase VH (2007) Hypoxia promotes fibrogenesis in vivo via HIF-1 stimulation of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest 117(12):3810–3820
Sahlgren C, Gustafsson MV, Jin S, Poellinger L, Lendahl U (2008) Notch signaling mediates hypoxia-induced tumor cell migration and invasion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(17):6392–6397
Kaidi A, Williams AC, Paraskeva C (2007) Interaction between beta-catenin and HIF-1 promotes cellular adaptation to hypoxia. Nat Cell Biol 9(2):210–217
Yang F, Sun L, Li Q, Han X, Lei L, Zhang H, Shang Y (2012) SET8 promotes epithelial–mesenchymal transition and confers TWIST dual transcriptional activities. EMBO J 31(1):110–123
Luo D, Wang J, Li J, Post M (2011) Mouse snail is a target gene for HIF. Mol Cancer Res 9(2):234–245
Imai T, Horiuchi A, Wang C, Oka K, Ohira S, Nikaido T, Konishi I (2003) Hypoxia attenuates the expression of E-cadherin via up-regulation of SNAIL in ovarian carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol 163(4):1437–1447
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Science and Technology Project of Shandong Province Academy of Medical Sciences (2013015). We greatly thank other members of the Yang and Sandy Lab for their valuable suggestions and writing.
Conflicts of interest
The authors state that there are no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This article has been retracted at the request of the Editor-in-Chief and the Publisher per the Committee on Publication Ethics guidelines. The article shows evidence of irregularities in authorship during the submission process, there is strong reason to believe that the peer review process was compromised and the authors have plagiarized parts from the following article
Anyan Liao, Weijie Wang, Dawei Sun, Yuliang Jiang, Suqing Tian, Jinna Li, Xiangshan Yang, Ranran Shi, Bone morphogenetic protein 2 mediates epithelial-mesenchymal transition via AKT and ERK signaling pathways in gastric cancer, Tumor Biology April 2015, Volume 36, Issue 4, pp 2773–2778, DOI: 10.1007/s13277-014-2901-1 Received: 11 October 2014
In addition, the article shows similarities with the following arcle which was submitted within a close timeframe:
Hao Yu, Linlin Zhang, Peishu Liu, CXCR7 signaling induced epithelial–mesenchymal transition by AKT and ERK pathways in epithelial ovarian carcinomas, Tumor Biology March 2015, Volume 36, Issue 3, pp 1679–1683, DOI: 10.1007/s13277-014-2768-1 Received: 7 October 2014
The article “CXCR4 Signaling Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by PI3K/AKT and ERK Pathways in Glioblastoma” was received: : 15 September 2014
As such the validity of the content of this article cannot be verified.
An erratum to this article is available at http://dx.doi.org/10.1007/s12035-017-0464-z.
About this article
Cite this article
Lv, B., Yang, X., Lv, S. et al. RETRACTED ARTICLE: CXCR4 Signaling Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition by PI3K/AKT and ERK Pathways in Glioblastoma. Mol Neurobiol 52, 1263–1268 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8935-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8935-y