Abstract
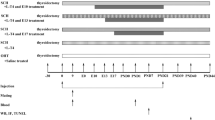
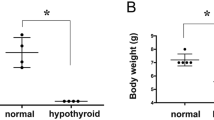
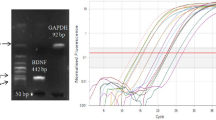
Thyroid hormone is indispensable for fetal brain development, and maternal thyroid hormone deficiency is thought to result in severe and irreversible brain impairments in learning and memory. Epidemiological and animal studies by our group had shown that maternal subclinical hypothyroidism had significant negative impact on neurodevelopment. But, the underlying mechanisms responsible for these neurological alterations remain unclear. In the present study, we performed thyroidectomy and injected L-T4 daily in Wistar rats to induce maternal subclinical hypothyroidism. Our data indicated that the pups from subclinical group showed prolonged latencies during the learning process in the Morris water maze as compared to the control group. Transcription factor cAMP response element-binding protein (CREB) signaling pathway is closely associated with synaptic plasticity, learning, and memory. Consistent with behavioral results, Western blotting also showed decreased activation of three important upstream modulators of CREB signaling pathway: phospho-mitogen-activated protein kinases (P-ERK1/2), phospho-calcium-dependent-calmodulin kinase IV (P-CaMKIV), phospho-serine/threonine protein kinase AKT(P-AKT), as well as total CREB and phospho-CREB as compared to the control at postnatal day 7 (PND 7) in hippocampus. Our findings suggested that decreased activation of the CREB signaling pathway in pups was related to impairments of cognitive function caused by maternal subclinical hypothyroidism.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed OM, El-Gareib AW, El-bakry AM, Abd El-Tawab SM, Ahmed RG (2008) Thyroid hormones states and brain development interactions. Int J Devl Neurosci 26:147–209
Mohacsik P, Zeold A, Bianco AC, Gereben B (2011) Thyroid hormone and the neuroglia: both source and target. J Thyroid Res. doi:10.4061/2011/215718
Morreale de Escobar G, Calvo R, Obregon M, Escobar del Rey F (1990) Contribution of maternal thyroxine to fetal thyroxine pools in normal rats near term. Endocrinology 126:2765–2767
Calvo RM, Jauniaux E, Gulbis B, AsuncionM GC, Contempre B, Morreale de Escobar G (2002) Fetal tissues are exposed to biologically relevant free thyroxine concentrations during early phases of development. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 87:1768–1777
Anderson GW, Schoonover CM, Jones SA (2003) Control of thyroid hormone action in the developing rat brain. Thyroid 13:1039–1056
Bernal J, Guadano-Ferraz A, Morte B (2003) Perspectives in the study of thyroid hormone in brain development and function. Thyroid 13:1005–1012
Mastorako G, Karoutsou EI, Mizamtsidi M, Greatsas G (2007) The menace of endocrine diruptors on thyroid hormone physiology and their impact on intrauterine development. Endocrine 31:219–237
Zoeller RT, Rover J (2004) Timing of thyroid hormone action in the developing brain: clinical observations and experimental findings. J Neuroendocrinol 16:809–818
Shan ZY, Chen YY, Teng WP, Yu XH, Li CY, Zhou WW, Gao B, Zhou JR, Ding B, Ma Y, Wu Y, Liu Q, Xu H, Liu W, Li J, Wang WW, Li YB, Fan CL, Wang H, Guo R, Zhang HM (2009) A study for maternal thyroid hormone deficiency during the first half of pregnancy in China. Eur J Clin Invest 39:37
Teng WP, Shan ZY, Patil-Sisodia K, Cooper DS (2013) Hypothyroidism in pregnancy. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol 1:228–37
Lazarus JH, Bestwick JP, Channon S, Clin-Psych D, Paradice R, Maina A, Rees R, Chiusano E, John R, Guaraldo V, George LM, Perona M, Dall’Amico D, Parkes AB, Joomun M, Wald NJ (2012) Antenatal thyroid screening and childhood cognitive function. N Engl J Med 366:493–501
Potlukova E, Potluka O, Jiskra J, Limanova Z, Telicka Z, Bartakova J, Springer D (2012) Is age a risk factor for hypothyroidism in pregnancy? an analysis of 5223 pregnant women. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 97:1945–52
Opazo MC, Gianini A, Pancetti F, Azkcona G, Alarco´n L, Lizana R, Noches V, Gonzalez PA, Porto M, Mora S, Rosenthal D, Eugenin E, Naranjo D, Bueno SM, Kalergis AM, Riedel CA (2008) Maternal hypothyroxinemia impairs spatial learning and synaptic nature and function in the offspring. Endocrinology 149:5097–5106
Li Y, Shan Z, Teng W, Yu X, Li Y, Fan C, Teng X, Guo R, Wang H, Li J, Chen Y, Wang W, Chawinga M, Zhang L, Yang L, Zhao Y, Hua T (2010) Abnormalities of maternal thyroid function during pregnancy affect neuropsychological development of their children at 25–30 months. Clin Endocrinol 72(6):825–9
Kornmeier J, Sosic-Vasic Z (2012) parallels between spacing effects during behavioural and celluar learning. Front Hum Neurosci 6:203
Escobar-Morreale HF, Obregon MJ, Escobar del Rey F, Morreale de Escobar G (1995) Replacement therapy for hypothyroidism with thyroxine alone does not ensure euthyroidism in all tissues, as studied in thyroidectomized rats. J Clin Invest 96:2828–2838
Lu L, Teng W, Shan Z (2012) Treatment with levothyroxine in pregnant rats with subclinical hypothyroidism improves cell migration in the developing brain of the progeny. J Endocrinol Invest 35(5):490–496
Liu DJ, Teng WP, Shan ZY, Yu XH, Gao Y, Wang S, Fan CL, Wang H, Zhang HM (2010) The effect of maternal subclinical hypothyroidism during pregnancy on brain development in rat offspring. Thyroid 20:909–15
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
Wang Y, Wei W, Wang Y, Dong J, Song B, Min H, Teng W, Chen J (2013) Neurotoxicity of developmental hypothyroxinemia and hypothyroidism in rats: impairments of long-term potentiation are mediated by phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase signaling pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 271:257–65
Wang S, Teng W, Gao Y, Fan C, Zhang H, Shan Z (2012) Early levothyroxine treatment on maternal subclinical hypothyroidism improves spatial learning of offspring in rats. J Neuroendocrinol 24:841–848
Barnes CA (1988) Spatial learning and memory processes: the search for their neurobiological mechanisms in the rat. Trends Neurosci 11:163–169
Siegelbaum SA, Kandel ER (1991) Learning-related synaptic plasticity: LTP and LTD. Curr Opin Neurobiol 1:113–120
Dong J, Liu WY, Wang Y, Hou Y, Qi Xi C (2009) Developmental iodine deficiency resulting in hypothyroidism reduces hippocampal ERK1/2 and CREB in lactational and adolescent rats. BMC Neurosci 10:149
Patterson M, Yasuda R (2011) Signalling pathways underlying structural plasticity of dendritic spines. Br J Pharmacol 163:1626–38
Kaang BK, Kandel ER, Grant SG (1993) Activation of cAMP-responsive genes by stimuli that produce long-term facilitation in Aplysia. Sens Neuron 10:427–35
Barco A, Alarcon JM, Kandel ER (2002) Expression of constitutively active CREB protein facilitates the late phase of long-term potentiation by enhancing synaptic capture. Cell 108:689–703
Kandel ER (2001) The molecular biology of memory storage: a dialogue between genes and synapses. Science 294:1030–1038
Gerges NZ, Alkadhi KA (2004) Hypothyroidism impairs late LTP in CA1 region but not in dentate gyrus of the intact rat hippocampus: MAPK involvement. Hippocampus 14:40–45
Thomas GM, Huganir RL (2004) MAPK cascade signalling and synaptic plasticity. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:173–83
Wymann MP, Zvelebil M, Laffargue M (2003) Phosphoinositide 3-kinase signaling-which way to target? Trends Neurosci 24:366–376
Hawkins PT, Anderson KE, Davidson K, Stephens LR (2006) Signalling throughclass I PI3Ks in mammalian cells. Biochem Soc Trans 34:647–662
Ho N, Liauw JA, Blaeser F, Wei F, Hanissian S, Muglia LM, Wozniak DF, Nard A, Arvin KL, Holtzman DM, Linden DJ, Zhuo M, Muglia LJ, Chatila TA (2000) Impaired synaptic plasticity and cAMP response element-binding protein activation in Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase type IV/Gr-deficient mice. J Neurosci 20:6459–6472
Kelly A, Lynch MA (2000) Long-term potentiation in dentate gyrus of the rat is inhibited by the phosphoinositide 3-kinase inhibitor, wortmannin. Neuropharmacol 39:643–651
Alzoubi KH, Gerges NZ, Aleisa AM, Alkadhi KA (2009) Levothyroxin restores hypothyroidism-induced impairment of hippocampus-dependent learning and memory: behavioral, electrophysiological, and molecular studies. Hippocampus 19:66–78
Poser S, Storm DR (2001) Role of Ca2+ stimulated adenylyl cyclases in LTP and memory formation. J Devl Neurosci 19:387–394
Miyamoto E (2006) Molecular mechanism of neuronal plasticity: induction and maintenance of long-term potentiation in the hippocampus. J Pharmacol Sci 100:433–442
Alzoubi KH, Alkadhi KA (2006) A critical role of CREB in the impairment of late-phase LTP by adult onset hypothyroidism. Exp Neurol 203:63–71
Roberson ED, English JD, Adams JP, Selcher JC, Kondratick C, Sweatt JD (1999) The mitogen-activated protein kinase cascade couples PKA and PKC to cAMP response element binding protein phosphorylation in area CA1 of hippocampus. J Neurosci 19:4337–4348
Adams JP, Roberson ED, English JD, Selcher JC, Sweatt JD (2000) MAPK regulation of gene expression in the central nervous system. Acta Neurobiol Exp (Wars) 60:377–394
Kelleher RJ III, Govindarajan A, Jung HY, Kang H, Tonegawa S (2004) Translational control by MAPK signaling in long-term synaptic plasticity and memory. Cell 116:467–479
Taylor MA, Swant J, Wagner JJ, Fisher JW, Ferguson DC (2008) Lower thyroid compensatory reserve of rat pups after maternal hypothyroidism: correlation of thyroid, hepatic, and cerebrocortical biomarkers with hippocampal neurophysiology. Endocrinology 149(7):3521–3530
Moorman S, Mello CV, Bolhuis JJ (2011) From songs to synapses: molecular mechanisms of birdsong memory. molecular mechanisms of auditory learning in songbirds involve immediate early genes, including zenk and arc, the ERK/MAPK pathway and synapsins. Bioessays 33(5):377–85
Sato K, Suematsu A, Nakashima T, Takemoto-Kimura S, Aoki K, Morishita Y, Asahara H, Ohya K, Yamaguchi A, Takai T, Kodama T, Chatila TA, Bito H, Takayanagi H (2006) Regulation of osteoclast differentiation and function by the CaMK-CREB pathway. Nat Med 12:1410–6
Marsden WN (2013) Synaptic plasticity in depression: molecular, cellular and functional correlates. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 43:168–84
Brunet A, Datta SR, Greenberg ME (2001) Transcription-dependent and -independent control of neuronal survival by the PI3K-Akt signaling pathway. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:297–305
Katso R, Okkenhaug K, Ahmad K, White S, Timms J, Waterfield MD (2001) Cellular function of phosphoinositide 3-kinases: implications for development, homeostasis, and cancer. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 17:615–675
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the 973 Science and Technology Research Foundation, Ministry of Science and Technology in China (Grant 2011CB512112); the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation (Grant 81170730, 30971400); and Program for Liaoning Excellent Talents in University (Grant LR2011022).
Conflict of Interest
The authors declares that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, Y., Fan, Y., Yu, X. et al. Maternal Subclinical Hypothyroidism Impairs Neurodevelopment in Rat Offspring by Inhibiting the CREB Signaling Pathway. Mol Neurobiol 52, 432–441 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8855-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8855-x