Abstract
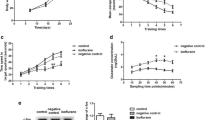
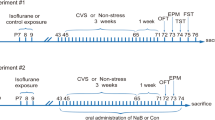
Isoflurane-induced cognitive impairments are well documented in animal models; yet, the molecular mechanisms remain largely to be determined. In the present study, 22-month-old male Sprague-Dawley rats received 2 h of 1.5 % isoflurane or 100 % oxygen daily for 3 consecutive days. For the intervention study, the rats were intraperitoneally injected with 1.2 g/kg sodium butyrate 2 h before isoflurane exposure. Our data showed that repeated isoflurane exposure significantly decreased the freezing time to context and the freezing time to tone in the fear conditioning test, which was associated with upregulated histone deacetylase 2, reduced histone acetylation, and increased inflammation and apoptosis in the hippocampus, and impairments of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF)-tyrosine kinase receptor B (TrkB) and the downstream signaling pathway phospho-calmodulin-dependent protein kinase and phospho-cAMP response element-binding protein. These results suggest that isoflurane-induced cognitive impairments are associated with the declines in chromatin histone acetylation and the resulting downregulation of BDNF-TrkB signaling pathway. Moreover, the cognitive impairments and the signaling deficits can be rescued by histone deacetylase inhibitor sodium butyrate. Therefore, epigenetic enhancement of BDNF-TrkB signaling may be a promising strategy for reversing isoflurane-induced cognitive impairments.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
McDonagh DL, Mathew JP, White WD, Phillips-Bute B, Laskowitz DT, Podgoreanu MV, Newman MF (2010) Cognitive function after major noncardiac surgery, apolipoprotein E4 genotype, and biomarkers of brain injury. Anesthesiology 112:852–859
Steinmetz J, Christensen KB, Lund T, Lohse N, Rasmussen LS, ISPOCD Group (2009) Long-term consequences of postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Anesthesiology 110:548–555
Monk TG, Weldon BC, Garvan CW, Dede DE, van der Aa MT, Heilman KM, Gravenstein JS (2008) Predictors of cognitive dysfunction after major noncardiac surgery. Anesthesiology 108:18–30
Moller JT, Cluitmans P, Rasmussen LS, Houx P, Rasmussen H, Canet J, Rabbitt P, Jolles J, Larsen K, Hanning CD, Langeron O, Johnson T, Lauven PM, Kristensen PA, Biedler A, van Beem H, Fraidakis O, Silverstein JH, Beneken JE, Gravenstein JS (1998) Long-term postoperative cognitive dysfunction in the elderly ISPOCD1 study. ISPOCD investigators. International Study of Post-Operative Cognitive Dysfunction. Lancet 351:857–861
Williams-Russo P, Sharrock NE, Mattis S, Szatrowski TP, Charlson ME (1995) Cognitive effects after epidural vs general anesthesia in older adults. A randomized trial. JAMA 274:44–50
Rasmussen LS, Johnson T, Kuipers HM, Kristensen D, Siersma VD, Vila P, Jolles J, Papaioannou A, Abildstrom H, Silverstein JH, Bonal JA, Raeder J, Nielsen IK, Korttila K, Munoz L, Dodds C, Hanning CD, Moller JT, ISPOCD2 (International Study of Postoperative Cognitive Dysfunction) Investigators (2003) Does anaesthesia cause postoperative cognitive dysfunction? A randomised study of regional versus general anaesthesia in 438 elderly patients. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand 47:260–266
Zhang B, Tian M, Zhen Y, Yue Y, Sherman J, Zheng H, Li S, Tanzi RE, Marcantonio ER, Xie Z (2012) The effects of isoflurane and desflurane on cognitive function in humans. Anesth Analg 114:410–415
Wang WY, Luo Y, Jia LJ, Hu SF, Lou XK, Shen SL, Lu H, Zhang HH, Yang R, Wang H, Ma ZW, Xue QS, Yu BW (2013) Inhibition of aberrant cyclin-dependent kinase 5 activity attenuates isoflurane neurotoxicity in the developing brain. Neuropharmacology 77C:90–99
Zhu C, Gao J, Karlsson N, Li Q, Zhang Y, Huang Z, Li H, Kuhn HG, Blomgren K (2010) Isoflurane anesthesia induced persistent, progressive memory impairment, caused a loss of neural stem cells, and reduced neurogenesis in young, but not adult, rodents. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 30:1017–1030
Lin D, Zuo Z (2011) Isoflurane induces hippocampal cell injury and cognitive impairments in adult rats. Neuropharmacology 61:1354–1359
Eckenhoff RG, Johansson JS, Wei H, Carnini A, Kang B, Wei W, Pidikiti R, Keller JM, Eckenhoff MF (2004) Inhaled anesthetic enhancement of amyloid-beta oligomerization and cytotoxicity. Anesthesiology 101:703–709
Peleg S, Sananbenesi F, Zovoilis A, Burkhardt S, Bahari-Javan S, Agis-Balboa RC, Cota P, Wittnam JL, Gogol-Doering A, Opitz L, Salinas-Riester G, Dettenhofer M, Kang H, Farinelli L, Chen W, Fischer A (2010) Altered histone acetylation is associated with age-dependent memory impairment in mice. Science 328:753–756
Guan JS, Haggarty SJ, Giacometti E, Dannenberg JH, Joseph N, Gao J, Nieland TJ, Zhou Y, Wang X, Mazitschek R, Bradner JE, DePinho RA, Jaenisch R, Tsai LH (2009) HDAC2 negatively regulates memory formation and synaptic plasticity. Nature 459:55–60
Gräff J, Rei D, Guan JS, Wang WY, Seo J, Hennig KM, Nieland TJ, Fass DM, Kao PF, Kahn M, Su SC, Samiei A, Joseph N, Haggarty SJ, Delalle I, Tsai LH (2012) An epigenetic blockade of cognitive functions in the neurodegenerating brain. Nature 483:222–226
Kazantsev AG, Thompson LM (2008) Therapeutic application of histone deacetylase inhibitors for central nervous system disorders. Nat Rev Drug Discov 7:854–868
Gräff J, Tsai LH (2013) The potential of HDAC inhibitors as cognitive enhancers. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 53:311–330
Wu J, Dong L, Zhang M, Jia M, Zhang G, Qiu L, Ji M, Yang J (2013) Class I histone deacetylase inhibitor valproic acid reverses cognitive deficits in a mouse model of septic encephalopathy. Neurochem Res 38:2440–2449
Govindarajan N, Agis-Balboa RC, Walter J, Sananbenesi F, Fischer A (2011) Sodium butyrate improves memory function in an Alzheimer's disease mouse model when administered at an advanced stage of disease progression. J Alzheimers Dis 26:187–197
Kayser EB, Suthammarak W, Morgan PG, Sedensky MM (2011) Isoflurane selectively inhibits distal mitochondrial complex I in Caenorhabditis elegans. Anesth Analg 112:1321–1329
Ji MH, Yuan HM, Zhang GF, Li XM, Dong L, Li WY, Zhou ZQ, Yang JJ (2013) Changes in plasma and cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in aged patients with early postoperative cognitive dysfunction following total hip-replacement surgery. J Anesth 27:236–242
Cibelli M, Fidalgo AR, Terrando N, Ma D, Monaco C, Feldmann M, Takata M, Lever IJ, Nanchahal J, Fanselow MS, Maze M (2010) Role of interleukin-1beta in postoperative cognitive dysfunction. Ann Neurol 68:360–368
Zhang Y, Xu Z, Wang H, Dong Y, Shi HN, Culley DJ, Crosby G, Marcantonio ER, Tanzi RE, Xie Z (2012) Anesthetics isoflurane and desflurane differently affect mitochondrial function, learning, and memory. Ann Neurol 71:687–698
MacDonald JL, Roskams AJ (2009) Epigenetic regulation of nervous system development by DNA methylation and histone deacetylation. Prog Neurobiol 88:170–183
Sun J, Sun J, Ming GL, Song H (2011) Epigenetic regulation of neurogenesis in the adult mammalian brain. Eur J Neurosci 33:1087–1093
Hsieh J, Eisch AJ (2010) Epigenetics, hippocampal neurogenesis, and neuropsychiatric disorders: unraveling the genome to understand the mind. Neurobiol Dis 39:73–84
Zeng Y, Tan M, Kohyama J, Sneddon M, Watson JB, Sun YE, Xie CW (2011) Epigenetic enhancement of BDNF signaling rescues synaptic plasticity in aging. J Neurosci 31:17800–17810
Devi L, Ohno M (2012) 7,8-dihydroxyflavone, a small-molecule TrkB agonist, reverses memory deficits and BACE1 elevation in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuropsychopharmacology 37:434–444
Diógenes MJ, Costenla AR, Lopes LV, Jerónimo-Santos A, Sousa VC, Fontinha BM, Ribeiro JA, Sebastião AM (2011) Enhancement of LTP in aged rats is dependent on endogenous BDNF. Neuropsychopharmacology 36:1823–1836
Shakespear MR, Halili MA, Irvine KM, Fairlie DP, Sweet MJ (2011) Histone deacetylases as regulators of inflammation and immunity. Trends Immunol 32:335–343
Jurgens HA, Johnson RW (2012) Environmental enrichment attenuates hippocampal neuroinflammation and improves cognitive function during influenza infection. Brain Behav Immun 26:1006–1016
Stratmann G, May LD, Sall JW, Alvi RS, Bell JS, Ormerod BK, Rau V, Hilton JF, Dai R, Lee MT, Visrodia KH, Ku B, Zusmer EJ, Guggenheim J, Firouzian A (2009) Effect of hypercarbia and isoflurane on brain cell death and neurocognitive dysfunction in 7-day-old rats. Anesthesiology 110:849–861
Li XM, Zhou MT, Wang XM, Ji MH, Zhou ZQ, Yang JJ (2013) Resveratrol pretreatment attenuates the isoflurane-induced cognitive impairment through its anti-inflammation and -apoptosis actions in aged mice. J Mol Neurosci Oct 15
Kong F, Chen S, Cheng Y, Ma L, Lu H, Zhang H, Hu W (2013) Minocycline attenuates cognitive impairment induced by isoflurane anesthesia in aged rats. PLoS One 8:e61385
Acknowledgments
The authors declare no conflict of interest. This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (no. 81271216 and 81300946) and the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province (no. BK2012778).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ji, M., Dong, L., Jia, M. et al. Epigenetic Enhancement of Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Signaling Pathway Improves Cognitive Impairments Induced by Isoflurane Exposure in Aged Rats. Mol Neurobiol 50, 937–944 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8659-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-014-8659-z