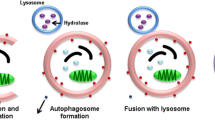
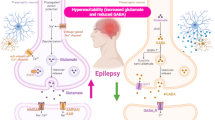
Abstract
Recent evidence suggests that an altered mammalian (mechanistic) target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway and its pharmacological modulation might be implicated in several neurological diseases including epileptogenesis. mTOR is a molecular sensor, which regulates protein synthesis, enhancing mRNA translation of genes involved in the regulation of cell proliferation and survival, working as part of two distinct multimeric complexes known as mTORC1 and mTORC2. mTOR is an evolutionarily highly conserved serine/threonine kinase belonging to the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-related kinase family and represents one of the most recently studied pathways in relation to epilepsy and epileptogenesis, due to its suggested pivotal role in many aspects of cellular proliferation and growth also including neurodegeneration, neurogenesis, and synaptic plasticity. In this review, we report the cellular and molecular features of mTOR and related pathways, analyze their function in the brain including all current related evidence of their role, and finally, discuss the possible involvement of mTOR signaling in epileptogenesis and epilepsy, giving further consideration to future developments in this area.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Weichhart T (2012) Mammalian target of rapamycin: a signaling kinase for every aspect of cellular life. Methods Mol Biol 821:1–14
Powell JD, Pollizzi KN, Heikamp EB, Horton MR (2012) Regulation of immune responses by mTOR. Annu Rev Immunol 30:39–68
Sofroniadou S, Goldsmith D (2011) Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors: potential uses and a review of haematological adverse effects. Drug Saf 34:97–115
Cho CH (2011) Frontier of epilepsy research—mTOR signaling pathway. Exp Mol Med 43:231–274
Chong ZZ, Shang YC, Zhang L, Wang S, Maiese K (2010) Mammalian target of rapamycin: hitting the bull's-eye for neurological disorders. Oxid Med Cell Longev 3:374–391
McDaniel SS, Wong M (2011) Therapeutic role of mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibition in preventing epileptogenesis. Neurosci Lett 497:231–239
Pitkänen A, Lukasiuk K (2011) Mechanisms of epileptogenesis and potential treatment targets. Lancet Neurol 10:173–186
Pitkänen A, Lukasiuk K (2009) Molecular and cellular basis of epileptogenesis in symptomatic epilepsy. Epilepsy Behav 14:16–25
Zara F, Bianchi A (2009) The impact of genetics on the classification of epilepsy syndromes. Epilepsia 50(Suppl 5):11–14
Friedman A, Dingledine R (2011) Molecular cascades that mediate the influence of inflammation on epilepsy. Epilepsia 52:33–39
Aronica E, Gorter JA (2007) Gene expression profile in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neuroscientist 13:100–108
Wang YY, Smith P, Murphy M, Cook M (2010) Global expression profiling in epileptogenesis: does it add to the confusion? Brain Pathol 20:1–16
Pitkänen A, Sutula TP (2002) Is epilepsy a progressive disorder? Prospects for new therapeutic approaches in temporal-lobe epilepsy. Lancet Neurol 1:173–181
Temkin NR (2009) Preventing and treating posttraumatic seizures: the human experience. Epilepsia 2:S10–S13
Jacobs MP, Leblanc GG, Brooks-Kayal A, Jensen FE, Lowenstein DH, Noebels JL, Spencer DD, Swann JW (2009) Curing epilepsy: progress and future directions. Epilepsy Behav 14:438–445
Lasoń W, Dudra-Jastrzębska M, Rejdak K, Czuczwar SJ (2011) Basic mechanisms of antiepileptic drugs and their pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic interactions: an update. Pharmacol Rep 63:271–292
Mula M (2009) New antiepileptic drugs: molecular targets. Cent Nerv Syst Agents Med Chem 9:79–86
Stafstrom CE (2010) Mechanisms of action of antiepileptic drugs: the search for synergy. Curr Opin Neurol 23:157–163
Meldrum BS, Rogawski MA (2007) Molecular targets for antiepileptic drug development. Neurotherapeutics 4:18–61
Reid CA, Jackson GD, Berkovic SF, Petrou S (2010) New therapeutic opportunities in epilepsy: a genetic perspective. Pharmacol Ther 128:274–280
Garelick MG, Kennedy BK (2011) TOR on the brain. Exp Gerontol 46:155–163
Bjedov I, Partridge L (2011) A longer and healthier life with TOR down-regulation: genetics and drugs. Biochem Soc Trans 39:460–465
Rossi M, Caraglia M (2012) Molecular targets for the treatment of multiple myeloma. Current Cancer Drug Targets (in press)
Russell RC, Fang C, Guan KL (2011) An emerging role for TOR signaling in mammalian tissue and stem cell physiology. Development 138:3343–3356
Zhang YJ, Duan Y, Zheng XF (2011) Targeting the mTOR kinase domain: the second generation of mTOR inhibitors. Drug Discov Today 16:325–331
Hay N, Sonenberg N (2004) Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev 18:1926–1945
Zhou H, Huang S (2010) The complexes of mammalian target of rapamycin. Curr Protein Pept Sci 11:409–424
Dowling RJ, Topisirovic I, Fonseca BD, Sonenberg N (2010) Dissecting the role of mTOR: lessons from mTOR inhibitors. Biochim Biophys Acta 1804:433–439
Swiech L, Perycz M, Malik A, Jaworski J (2008) Role of mTOR in physiology and pathology of the nervous system. Biochim Biophys Acta 1784:116–132
Hoeffer CA, Klann E (2010) mTOR signaling: at the crossroads of plasticity, memory and disease. Trends Neurosci 233:67–75
Loewith R, Jacinto E, Wullschleger S, Lorberg A, Crespo JL, Bonenfant D, Oppliger W, Jenoe P, Hall MN (2002) Two TOR complexes, only one of which is rapamycin sensitive, have distinct roles in cell growth control. Mol Cell 10:457–468
Proud CG (2011) A new link in the chain from amino acids to mTORC1 activation. Mol Cell 44:7–8
Kim DH, Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Latek RR, Guntur KV, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Sabatini DM (2003) GbetaL, a positive regulator of the rapamycin-sensitive pathway required for the nutrient-sensitive interaction between raptor and mTOR. Mol Cell 11:895–904
Peterson TR, Laplante M, Thoreen CC, Sancak Y, Kang SA, Kuehl WM, Gray NS, Sabatini DM (2009) DEPTOR is an mTOR inhibitor frequently overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells and required for their survival. Cell 137:873–886
Wang L, Harris TE, Roth RA, Lawrence JC Jr (2007) PRAS40 regulates mTORC1 kinase activity by functioning as a direct inhibitor of substrate binding. J Biol Chem 282:20036–20044
Huang J, Wu S, Wu CL, Manning BD (2009) Signaling events downstream of mammalian target of rapamycin complex 2 are attenuated in cells and tumors deficient for the tuberous sclerosis complex tumor suppressors. Cancer Res 69:6107–6114
Frias MA, Thoreen CC, Jaffe JD, Schroder W, Sculley T, Carr SA, Sabatini DM (2006) mSin1 is necessary for Akt/PKB phosphorylation, and its isoforms define three distinct mTORC2s. Curr Biol 16:1865–1870
Pearce LR, Huang X, Boudeau J, Pawłowski R, Wullschleger S, Deak M, Ibrahim AF, Gourlay R, Magnuson MA, Alessi DR (2007) Identification of Protor as a novel Rictor-binding component of mTOR complex-2. Biochem J 405:513–522
Pearce LR, Sommer EM, Sakamoto K, Wullschleger S, Alessi DR (2011) Protor-1 is required for efficient mTORC2-mediated activation of SGK1 in the kidney. Biochem J 436:169–179
Jacinto E, Loewith R, Schmidt A, Lin S, Rüegg MA, Hall A, Hall MN (2004) Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive. Nat Cell Biol 6:1122–1128
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Sengupta S, Sheen JH, Hsu PP, Bagley AF, Markhard AL, Sabatini DM (2006) Prolonged rapamycin treatment inhibits mTORC2 assembly and Akt/PKB. Mol Cell 22:159–168
Bhagwat SV, Crew AP (2010) Novel inhibitors of mTORC1 and mTORC2. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 11:638–645
Dancey JE, Monzon J (2011) Ridaforolimus: a promising drug in the treatment of soft-tissue sarcoma and other malignancies. Future Oncol 7:827–839
Khokhar NZ, Altman JK, Platanias LC (2011) Emerging roles for mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors in the treatment of solid tumors and hematological malignancies. Curr Opin Oncol 23:578–586
Marshall G, Howard Z, Dry J, Fenton S, Heathcote D, Gray N, Keen H, Logie A, Holt S, Smith P, Guichard SM (2011) Benefits of mTOR kinase targeting in oncology: pre-clinical evidence with AZD8055. Biochem Soc Trans 39:456–459
Fingar DC, Blenis J (2004) Target of rapamycin (TOR): an integrator of nutrient and growth factor signals and coordinator of cell growth and cell cycle progression. Oncogene 23:3151–3171
Huang S, Houghton PJ (2003) Targeting mTOR signaling for cancer therapy. Curr Opin Pharmacol 3:371–377
Gao X, Zhang Y, Arrazola P, Hino O, Kobayashi T, Yeung RS, Ru B, Pan D (2002) Tsc tumour suppressor proteins antagonize amino-acid-TOR signalling. Nat Cell Biol 4:699–704
Inoki K, Li Y, Zhu T, Wu J, Guan KL (2002) TSC2 is phosphorylated and inhibited by Akt and suppresses mTOR signalling. Nat Cell Biol 4:648–657
Tee AR, Fingar DC, Manning BD, Kwiatkowski DJ, Cantley LC, Blenis J (2002) Tuberous sclerosis complex-1 and −2 gene products function together to inhibit mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-mediated downstream signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:13571–13576
Zeng LH, Rensing NR, Zhang B, Gutmann DH, Gambello MJ, Wong M (2011) Tsc2 gene inactivation causes a more severe epilepsy phenotype than Tsc1 inactivation in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Hum Mol Genet 20:445–454
Bai X, Ma D, Liu A, Shen X, Wang QJ, Liu Y, Jiang Y (2007) Rheb activates mTOR by antagonizing its endogenous inhibitor, FKBP38. Science 318:977–980
Wang X, Fonseca BD, Tang H, Liu R, Elia A, Clemens MJ, Bommer UA, Proud CG (2008) Re-evaluating the roles of proposed modulators of mammalian target of Rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling. J Biol Chem 283:30482–33092
Inoki K, Zhu T, Guan KL (2003) TSC2 mediates cellular energy response to control cell growth and survival. Cell 115:577–590
Towler MC, Hardie DG (2007) AMP-activated protein kinase in metabolic control and insulin signaling. Circ Res 100:328–341
Hahn-Windgassen A, Nogueira V, Chen CC, Skeen JE, Sonenberg N, Hay N (2005) Akt activates the mammalian target of rapamycin by regulating cellular ATP level and AMPK activity. J Biol Chem 280:32081–32089
Brugarolas J, Lei K, Hurley RL, Manning BD, Reiling JH, Hafen E, Witters LA, Ellisen LW, Kaelin WG Jr (2004) Regulation of mTOR function in response to hypoxia by REDD1 and the TSC1/TSC2 tumor suppressor complex. Genes Dev 18:2893–2904
Schneider A, Younis RH, Gutkind JS (2008) Hypoxia-induced energy stress inhibits the mTOR pathway by activating an AMPK/REDD1 signaling axis in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Neoplasia 10:1295–1302
Vadysirisack DD, Ellisen LW (2012) mTOR activity under hypoxia. Methods Mol Biol 821:45–58
Kim MS, Kuehn HS, Metcalfe DD, Gilfillan AM (2008) Activation and function of the mTORC1 pathway in mast cells. J Immunol 180:4586–4595
Sancak Y, Peterson TR, Shaul YD, Lindquist RA, Thoreen CC, Bar-Peled L, Sabatini DM (2008) The Rag GTPases bind raptor and mediate amino acid signaling to mTORC1. Science 320:1496–1501
Cully M, You H, Levine AJ, Mak TW (2006) Beyond PTEN mutations: the PI3K pathway as an integrator of multiple inputs during tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer 6:184–192
Ahn JY, Ye K (2005) PIKE GTPase signaling and function. Int J Biol Sci 1:44–50
Burnett PE, Barrow RK, Cohen NA, Snyder SH, Sabatini DM (1998) RAFT1 phosphorylation of the translational regulators p70 S6 kinase and 4E-BP1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95:1432–1437
Park IH, Bachmann R, Shirazi H, Chen J (2002) Regulation of ribosomal S6 kinase 2 by mammalian target of rapamycin. J Biol Chem 277:31423–31429
Reinhard C, Thomas G, Kozma SC (1992) A single gene encodes two isoforms of the p70 S6 kinase: activation upon mitogenic stimulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 89:4052–4056
Cole-Edwards KK, Bazan NG (2005) Lipid signaling in experimental epilepsy. Neurochem Res 30:847–853
Levy DE, Lee CK (2002) What does Stat3 do? J Clin Invest 109:1143–1148
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Sabatini DM (2005) Growing roles for the mTOR pathway. Cur Opin Cell Biol 17:596–603
Yang Q, Inoki K, Kim E, Guan KL (2006) TSC1/TSC2 and Rheb have different effects on TORC1 and TORC2 activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:6811–6816
Tanaka K, Babic I, Nathanson D, Akhavan D, Guo D, Gini B, Dang J, Zhu S, Yang H, de Jesus J, Amzajerdi AN, Zhang Y, Dibble CC, Dan H, Rinkenbaugh A, Yong WH, Vinters HV, Gera JF, Cavenee WK, Cloughesy TF, Manning BD, Baldwin AS, Mischel PS (2011) Oncogenic EGFR signaling activates an mTORC2–NF-κB pathway that promotes chemotherapy resistance. Cancer Discov 1:524–538
Zinzalla V, Stracka D, Oppliger W, Hall MN (2011) Activation of mTORC2 by association with the ribosome. Cell 144:757–768
Manning BD, Cantley LC (2007) AKT/PKB signaling: navigating downstream. Cell 129:1261–1274
Aeder SE, Martin PM, Soh JW, Hussaini IM (2004) PKC-eta mediates glioblastoma cell proliferation through the Akt and mTOR signaling pathways. Oncogene 23:9062–9069
Guertin DA, Stevens DM, Thoreen CC, Burds AA, Kalaany NY, Moffat J, Brown M, Fitzgerald KJ, Sabatini DM (2006) Ablation in mice of the mTORC components raptor, rictor, or mLST8 reveals that mTORC2 is required for signaling to Akt-FOXO and PKCalpha, but not S6K1. Dev Cell 11:859–871
Sarbassov DD, Ali SM, Kim DH, Guertin DA, Latek RR, Erdjument-Bromage H, Tempst P, Sabatini DM (2004) Rictor, a novel binding partner of mTOR, defines a rapamycin-insensitive and raptor-independent pathway that regulates the cytoskeleton. Curr Biol 14:1296–1302
Lang F, Böhmer C, Palmada M, Seebohm G, Strutz-Seebohm N, Vallon V (2006) (Patho)physiological significance of the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase isoforms. Physiol Rev 86:1151–1178
García-Martínez JM, Alessi DR (2008) mTOR complex 2 (mTORC2) controls hydrophobic motif phosphorylation and activation of serum- and glucocorticoid-induced protein kinase 1 (SGK1). Biochem J 416:375–385
Jones KT, Greer ER, Pearce D, Ashrafi K (2009) Rictor/TORC2 regulates Caenorhabditis elegans fat storage, body size, and development through sgk-1. PLos Biol 7:e60
Proud CG (2007) Amino acids and mTOR signalling in anabolic function. Biochem Soc Trans 35:1187–1190
Holz MK, Ballif BA, Gygi SP, Blenis J (2005) mTOR and S6K1 mediate assembly of the translation preinitiation complex through dynamic protein interchange and ordered phosphorylation events. Cell 123:569–580
Wang X, Li W, Williams M, Terada N, Alessi DR, Proud CG (2001) Regulation of elongation factor 2 kinase by p90(RSK1) and p70 S6 kinase. EMBO J 20:4370–4379
Meijer AJ, Codogno P (2006) Signalling and autophagy regulation in health, aging and disease. Mol Aspects Med 27:411–425
Rubinsztein DC, Gestwicki JE, Murphy LO, Klionsky DJ (2007) Potential therapeutic applications of autophagy. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6:304–312
Nyfeler B, Bergman P, Wilson CJ, Murphy LO (2012) Quantitative visualization of autophagy induction by mTOR inhibitors. Methods Mol Biol 821:239–250
Cammalleri M, Lütjens R, Berton F, King AR, Simpson C, Francesconi W, Sanna PP (2003) Time-restricted role for dendritic activation of the mTOR–p70S6K pathway in the induction of late-phase long-term potentiation in the CA1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:14368–14373
Jaworski J, Spangler S, Seeburg DP, Hoogenraad CC, Sheng M (2005) Control of dendritic arborization by the phosphoinositide-3-kinase-Akt-mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. J Neurosci 25:11300–11312
Cota D, Proulx K, Smith KA, Kozma SC, Thomas G, Woods SC, Seeley RJ (2006) Hypothalamic mTOR signaling regulates food intake. Science 312:927–930
Kumar V, Zhang MX, Swank MW, Kunz J, Wu GY (2005) Regulation of dendritic morphogenesis by Ras–PI3K–Akt–mTOR and Ras–MAPK signaling pathways. J Neurosci 25:11288–11299
Miller FD, Kaplan DR (2003) Signaling mechanisms underlying dendrite formation. Curr Opin Neurobiol 13:391–398
Bramham CR, Wells DG (2007) Dendritic mRNA: transport, translation and function. Nat Rev Neurosci 8:776–789
Raab-Graham KF, Haddick PCG, Jan YN, Jan LY (2006) Activity- and mTOR-dependent suppression of Kv1.1 channel mRNA translation in dendrites. Science 314:144–148
Tang SJ, Reis G, Kang H, Gingras AC, Sonenberg N, Schuman EM (2002) A rapamycin-sensitive signaling pathway contributes to long-term synaptic plasticity in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 99:467–472
Slipczuk L, Bekinschtein P, Katche C, Cammarota M, Izquierdo I, Medina JH (2009) BDNF activates mTOR to regulate GluR1 expression required for memory formation. PLoS One 4:e6007
Gobert D, Topolnik L, Azzi M, Huang L, Badeaux F, Desgroseillers L, Sossin WS, Lacaille JC (2008) Forskolin induction of late-LTP and up-regulation of 5′ TOP mRNAs translation via mTOR, ERK, and PI3K in hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Neurochem 106:1160–1174
Kelleher RJ 3rd, Govindarajan A, Tonegawa S (2004) Translational regulatory mechanisms in persistent forms of synaptic plasticity. Neuron 44:59–73
Tsokas P, Grace EA, Chan P, Ma T, Sealfon SC, Iyengar R, Landau EM, Blitzer RD (2005) Local protein synthesis mediates a rapid increase in dendritic elongation factor 1A after induction of late long-term potentiation. J Neurosci 25:5833–5843
Tsokas P, Ma T, Iyengar R, Landau EM, Blitzer RD (2007) Mitogen-activated protein kinase upregulates the dendritic translation machinery in long-term potentiation by controlling the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. J Neurosci 27:5885–5894
Jaworski J, Sheng M (2006) The growing role of mTOR in neuronal development and plasticity. Mol Neurobiol 34:205–219
Schratt GM, Nigh EA, Chen WG, Hu L, Greenberg ME (2004) BDNF regulates the translation of a select group of mRNAs by a mammalian target of rapamycin-phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent pathway during neuronal development. J Neurosci 24:7366–7377
Gong R, Park CS, Abbassi NR, Tang SJ (2006) Roles of glutamate receptors and the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling pathway in activity-dependent dendritic protein synthesis in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 281:18802–18815
Kelly MT, Crary JF, Sacktor TC (2007) Regulation of protein kinase Mzeta synthesis by multiple kinases in long-term potentiation. J Neuroscience 27:3439–3444
Lee CC, Huang CC, Wu MY, Hsu KS (2005) Insulin stimulates postsynaptic density-95 protein translation via the phosphoinositide 3-kinase–Akt–mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway. J Biol Chem 280:18543–18550
Abel T, Lattal KM (2001) Molecular mechanisms of memory acquisition, consolidation and retrieval. Curr Opin Neurobiol 11:180–187
Dash PK, Orsi SA, Moore AN (2006) Spatial memory formation and memory enhancing effect of glucose involves activation of the tuberous sclerosis complex mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. J Neurosci 26:8048–8056
Hoeffer CA, Tang W, Wong H, Santillan A, Patterson RJ, Martinez LA, Tejada-Simon MV, Paylor R, Hamilton SL, Klann E (2008) Removal of FKBP12 enhances mTOR–RAPTOR interactions, LTP, memory, and perseverative/repetitive behavior. Neuron 60:832–845
Parsons RG, Gafford GM, Helmstetter FJ (2006) Translational control via the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway is critical for the formation and stability of long-term fear memory in amygdala neurons. J Neurosci 26:12977–12983
Schicknick H, Schott BH, Budinger E, Smalla KH, Riedel A, Seidenbecher CI, Scheich H, Gundelfinger ED, Tischmeyer W (2008) Dopaminergic modulation of auditory cortex-dependent memory consolidation through mTOR. Cereb Cortex 18:2646–2658
Tischmeyer W, Schicknick H, Kraus M, Seidenbecher CI, Staak S, Scheich H, Gundelfinger ED (2003) Rapamycin-sensitive signalling in long-term consolidation of auditory cortex-dependent memory. Eur J Neurosci 18:942–950
Belelovsky K, Kaphzan H, Elkobi A, Rosenblum K (2009) Biphasic activation of the mTOR pathway in the gustatory cortex is correlated with and necessary for taste learning. J Neurosci 29:7424–7431
Sui L, Wang J, Li BM (2008) Role of the phosphoinositide 3-kinase–Akt–mammalian target of the rapamycin signaling pathway in long-term potentiation and trace fear conditioning memory in rat medial prefrontal cortex. Learn Mem 15:762–776
Ehninger D, de Vries PJ, Silva AJ (2009) From mTOR to cognition: molecular and cellular mechanisms of cognitive impairments in tuberous sclerosis. J Intellect Disabil Res 53:838–851
Ehninger D, Han S, Shilyansky C, Zhou Y, Li W, Kwiatkowski DJ, Ramesh V, Silva AJ (2008) Reversal of learning deficits in a Tsc2+/S mouse model of tuberous sclerosis. Nat Med 14:843–848
Puighermanal E, Marsicano G, Busquets-Garcia A, Lutz B, Maldonado R, Ozaita A (2009) Cannabinoid modulation of hippocampal long-term memory is mediated by mTOR signaling. Nat Neurosci 12:1152–1158
Blouet C, Ono H, Schwartz GJ (2008) Mediobasal hypothalamic p70 S6 kinase 1 modulates the control of energy homeostasis. Cell Metab 8:459–467
Mori H, Inoki K, Opland D, Muenzberg H, Villanueva EC, Faouzi M, Ikenoue T, Kwiatkowski D, Macdougald OA, Myers MG Jr, Guan KL (2009) Critical roles for theTSC-mTOR pathway in {beta}-cell function. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 2297:1013–1022
Um SH, Frigerio F, Watanabe M, Picard F, Joaquin M, Sticker M, Fumagalli S, Allegrini PR, Kozma SC, Auwerx J, Thomas G (2004) Absence of S6K1 protects against age- and diet-induced obesity while enhancing insulin sensitivity. Nature 431:200–205
Roa J, Garcia-Galiano D, Varela L, Sánchez-Garrido MA, Pineda R, Castellano JM, Ruiz-Pino F, Romero M, Aguilar E, López M, Gaytan F, Diéguez C, Pinilla L, Tena-Sempere M (2009) The mammalian target of rapamycin as novel central regulator of puberty onset via modulation of hypothalamic Kiss1 system. Endocrinology 150:5016–5026
Cao R, Obrietan K (2010) mTOR signaling and entrainment of the mammalian circadian clock. Mol Cell Pharmacol 2:125–130
Inoki K, Corradetti MN, Guan KL (2005) Dysregulation of the TSC–mTOR pathway in human disease. Nat Genet 37:19–24
Tsang CK, Qi H, Liu LF, Zheng XF (2007) Targeting mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) for health and diseases. Drug Discov Today 12:112–124
Ehninger D, Silva AJ (2011) Rapamycin for treating tuberous sclerosis and Autism Spectrum disorders. Trends Mol Med 17:78–87
Pitkanen A (2010) Therapeutic approaches to epileptogenesis—hope on the horizon. Epilepsia 51:2–17
Ljungberg MC, Sunnen CN, Lugo JN, Anderson AE, D’Arcangelo G (2009) Rapamycin suppresses seizures and neuronal hypertrophy in a mouse model of cortical dysplasia. Dis Model Mech 2:389–398
Krab LC, Goorden SM, Elgersma Y (2008) Oncogenes on my mind: ERK and MTOR signaling in cognitive diseases. Trends in Genetics: TIG 24:498–510
Gorman PM, Kim S, Guo M, Melnyk RA, McLaurin J, Fraser PE, Bowie JU, Chakrabartty A (2008) Dimerization of the transmembrane domain of amyloid precursor proteins and familial Alzheimer's disease mutants. BMC Neurosci 30:9–17
Bossy-Wetzel E, Schwarzenbacher R, Lipton SA (2004) Molecular pathways to neurodegeneration. Nat Med 10:S2–S9
Ravikumar B, Vacher C, Berger Z, Davies JE, Luo S, Oroz LG, Scaravilli F, Easton DF, Duden R, O’Kane CJ, Rubinsztein DC (2004) Inhibition of Mtor induces autophagy and reduces toxicity of polyglutamine expansions in fly and mouse models of Huntington disease. Nat Genet 36:585–595
Berger Z, Ravikumar B, Menzies FM, Oroz LG, Underwood BR, Pangalos MN, Schmitt I, Wullner U, Evert BO, O'Kane CJ, Rubinsztein DC (2006) Rapamycin alleviates toxicity of different aggregate-prone proteins. Hum Mol Genet 15:433–442
An WL, Cowburn RF, Li L, Braak H, Alafuzoff I, Iqbal K, Winblad B, Pei JJ (2003) Upregulation of phosphorylated/activated p70S6 kinase and its relationship to neurofibrillary pathology in Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Pathol 163:591–607
Li X, Alafuzoff I, Soininen H, Winblad B, Pei JJ (2005) Levels of mTOR and its downstream targets 4E-BP1, eEF2, and eEF2 kinase in relationships with tau in Alzheimer's disease brain. FEBS J 272:4211–4220
Paccalin M, Pain-Barc S, Pluchon C, Paul C, Besson MN, Carret-Rebillat AS, Rioux-Bilan A, Gil R, Hugon J (2006) Activated mTOR and PKR kinases in lymphocytes correlate with memory and cognitive decline in Alzheimer's disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 22:320–326
Pei JJ, Hugon J (2008) mTOR-dependent signalling in Alzheimer's disease. J Cell Mol Med 12:2525–2532
Spilman P, Podlutskaya N, Hart MJ, Debnath J, Gorostiza O, Bredesen D, Richardson A, Strong R, Galvan V (2010) Inhibition of mTOR by rapamycin abolishes cognitive deficits and reduces amyloid-beta levels in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 5:9979
Khurana V, Lu Y, Steinhilb ML, Oldham S, Shulman JM, Feany MB (2006) TOR mediated cell-cycle activation causes neurodegeneration in a Drosophila tauopathy model. Curr Biol 16:230–241
Corradetti MN, Inoki K, Guan KL (2005) The stress-inducted proteins RTP801 and RTP801L are negative regulators of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. J Biol Chem 280:9769–9772
Malagelada C, Ryu EJ, Biswas SC, Jackson-Lewis V, Greene LA (2006) RTP801 is elevated in Parkinson brain substantia nigral neurons and mediates death in cellular models of Parkinson’s disease by amechanism involving mammalian target of rapamycin inactivation. J Neurosci 26:9996–10005
Malagelada C, Jin ZH, Jackson-Lewis V, Przedborski S, Greene LA (2010) Rapamycin protects against neuron death in in vitro and in vivo models of Parkinson's disease. J Neurosci 30:1166–1175
Santini E, Alcacer C, Cacciatore S, Heiman M, Hervé D, Greengard P, Girault JA, Valjent E, Fisone G (2009) L-DOPA activates ERK signaling and phosphorylates histone H3 in the striatonigral medium spiny neurons of hemiparkinsonian mice. J Neurochem 108:621–633
Blommaart EF, Luiken JJ, Blommaart PJ, van Woerkom GM, Meijer AJ (1995) Phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 is inhibitory for autophagy in isolated rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem 270:2320–2326
Jung CH, Ro SH, Cao J, Otto NM, Kim DH (2010) mTOR regulation of autophagy. FEBS Lett 584:1287–1295
Kalkman HO (2006) The role of the phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase-protein kinase B pathway in schizophrenia. Pharmacol Ther 110:117–134
Karolewicz B, Cetin M, Aricioglu F (2011) Beyond the glutamate N-methyl D-aspartate receptor in major depressive disorder: the mTOR signaling pathway. Bull Clin Psychopharmacol 21:1–6
Jernigan CS, Goswami DB, Austin MC, Iyo AH, Chandran A, Stockmeier CA, Karolewicz B (2011) The mTOR signaling pathway in the prefrontal cortex is compromised in major depressive disorder. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiatry 35:1774–1779
Li N, Lee B, Liu RJ, Banasr M, Dwyer JM, Iwata M, Li XY, Aghajanian G, Duman RS (2010) mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science 329:959–964
Chan S, Scheulen ME, Johnston S, Mross K, Cardoso F, Dittrich C, Eiermann W, Hess D, Morant R, Semiglazov V, Borner M, Salzberg M, Ostapenko V, Illiger HJ, Behringer D, Bardy-Bouxin N, Boni J, Kong S, Cincotta M, Moore L (2005) Phase II study of temsirolimus (CCI-779), a novel inhibitor of mTOR, in heavily pretreated patients with locally advanced or metastatic breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 23:5314–5322
Martínez-Sanchis S, Bernal MC, Montagud JV, Candela G, Crespo J, Sancho A, Pallardó LM (2011) Effects of immunosuppressive drugs on the cognitive functioning of renal transplant recipients: a pilot study. J Clin Exp Neuropsychol 33:1016–1024
Soefje SA, Karnad A, Brenner AJ (2011) Common toxicities of mammalian target of rapamycin inhibitors. Target Oncol 6:125–129
van de Beek D, Kremers WK, Kushwaha SS, McGregor CG, Wijdicks EF (2009) No major neurologic complications with sirolimus use in heart transplant recipients. Mayo Clin Proc 84:330–332
Lang F, Görlach A, Vallon V (2009) Targeting SGK1 in diabetes. Expert Opin Ther Targets 13:1303–1311
Hoppe C, Elger CE (2011) Depression in epilepsy: a critical review from a clinical perspective. Nat Rev Neurol 7:462–472
Luoni C, Bisulli F, Canevini MP, De Sarro G, Fattore C, Galimberti CA, Gatti G, La Neve A, Muscas G, Specchio LM, Striano S, Perucca E, on behalf of the SOPHIE Study Group (2011) Determinants of health-related quality of life in pharmacoresistant epilepsy: results from a large multicenter study of consecutively enrolled patients using validated quantitative assessments. Epilepsia 52:2181–2191
Manni R, Terzaghi M (2010) Comorbidity between epilepsy and sleep disorders. Epilepsy Res 90:171–177
Costa J, Fareleira F, Ascenção R, Borges M, Sampaio C, Vaz-Carneiro A (2011) Clinical comparability of the new antiepileptic drugs in refractory partial epilepsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsia 52:1280–1291
Okamoto OK, Janjoppi L, Bonone FM, Pansani AP, da Silva AV, Scorza FA, Cavalheiro EA (2010) Whole transcriptome analysis of the hippocampus: toward a molecular portrait of epileptogenesis. BMC Genomics 11:230
Poduri A, Lowenstein D (2011) Epilepsy genetics—past, present, and future. Curr Opin Genet Dev 21:325–332
Cheadle JP, Reeve MP, Sampson JR, Kwiatkowski DJ (2000) Molecular genetic advances in tuberous sclerosis. Hum Genet 107:97–114
Onda H, Crino PB, Zhang H, Murphey RD, Rastelli L, Gould Rothberg BE, Kwiatkowski DJ (2002) Tsc2 null murine neuroepithelial cells are a model for human tuber giant cells, and show activation of an mTOR pathway. Mol Cell Neurosci 21:561–574
Crino PB, Nathanson KL, Henske EP (2006) The tuberous sclerosis complex. N Engl J Med 355:1345–1356
Franz DN (2007) mTOR in tuberous sclerosis and other neurological disorders. Epilepsia 48:1630–1631
Meikle L, Pollizzi K, Egnor A, Kramvis I, Lane H, Sahin M, Kwiatkowski DJ (2008) Response of a neuronal model of tuberous sclerosis to mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors: effects on mTORC1 and Akt signaling lead to improved survival and function. J Neurosci 28:5422–5432
Zeng LH, Xu L, Gutmann DH, Wong M (2008) Rapamycin prevents epilepsy in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Ann Neurol 63:444–453
Waltereit R, Welzl H, Dichgans J, Lipp HP, Schmidt WJ, Weller M (2006) Enhanced episodic-like memory and kindling epilepsy in a rat model of tuberous sclerosis. J Neurochem 96:407–413
Wenzel HJ, Patel LS, Robbins CA, Emmi A, Yeung RS, Schwartzkroin PA (2004) Morphology of cerebral lesions in the Eker rat model of tuberous sclerosis. Acta Neuropathol 108:97–108
Goto J, Talos DM, Klein P, Qin W, Chekaluk YI, Anderl S, Malinowska IA, Di Nardo A, Bronson RT, Chan JA, Vinters HV, Kernie SG, Jensen FE, Sahin M, Kwiatkowski DJ (2011) Regulable neural progenitor-specific Tsc1 loss yields giant cells with organellar dysfunction in a model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:1070–1079
Anderl S, Freeland M, Kwiatkowski DJ, Goto J (2011) Therapeutic value of prenatal rapamycin treatment in a mouse brain model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Hum Mol Genet 20:4597–4604
Wong M, Ess KC, Uhlmann EJ, Jansen LA, Li W, Crino PB, Mennerick S, Yamada KA, Gutmann DH (2003) Impaired glial glutamate transport in a mouse tuberous sclerosis epilepsy model. Ann Neurol 54:251–256
Zeng LH, McDaniel SS, Rensing N, Wong M (2010) Regulation of cell death and epileptogenesis by the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): a double-edged sword? Cell Cycle 9:2281–2285
Fu C, Cawthon B, Clinkscales W, Bruce A, Winzenburger P, Ess KC (2012) GABAergic interneuron development and function is modulated by the Tsc1 gene. Cereb Cortex (in press)
Buckmaster PS, Wen X (2011) Rapamycin suppresses axon sprouting by somatostatin interneurons in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 52:2057–2064
Buckmaster PS, Lew FH (2011) Rapamycin suppresses mossy fiber sprouting but not seizure frequency in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci 31:2337–2347
Buckmaster PS, Ingram EA, Wen X (2009) Inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway suppresses dentate granule cell axon sprouting in a rodent model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neurosci 29:8259–8269
Huang X, Zhang H, Yang J, Wu J, McMahon J, Lin Y, Cao Z, Gruenthal M, Huang Y (2010) Pharmacological inhibition of the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway suppresses acquired epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 40:193–199
Sunnen CN, Brewster AL, Lugo JN, Vanegas F, Turcios E, Mukhi S, Parghi D, D'Arcangelo G, Anderson AE (2011) Inhibition of the mammalian target of Rapamycin blocks epilepsy progression in NS-Pten conditional knockout mice. Epilepsia 52:2065–2075
Zeng LH, Rensing NR, Wong M (2009) The mammalian target of rapamycin signaling pathway mediates epileptogenesis in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Neuroscience 29:6964–6972
Asnaghi L, Calastretti A, Bevilacqua A, D’Agnano I, Gatti G, Canti G, Delia D, Capaccioli S, Nicolin A (2004) Bcl-2 phosphorylation and apoptosis activated by damaged microtubules require mTOR and are regulated by Akt. Oncogene 23:5781–5791
Castedo M, Ferri KF, Kroemer G (2002) Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): pro- and anti-apoptotic. Cell Death Differ 9:99–100
Sliwa A, Plucinska G, Bednarczyk J, Lukasiuk K (2012) Post-treatment with rapamycin does not prevent epileptogenesis in the amygdala stimulation model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurosci Lett 509(2):105–109
Zhang B, Wong M (2012) Pentylenetetrazole-induced seizures cause acute, but not chronic, mTOR pathway activation in rat. Epilepsia 53(3):506–511
Baybis M, Yu J, Lee A, Golden JA, Weiner H, McKhann G 2nd, Aronica E, Crino PB (2004) mTOR cascade activation distinguishes tubers from focal cortical dysplasia. Ann Neurol 56:478–487
Wong (2011) Rapamycin for treatment of epilepsy: antiseizure, antiepileptogenic, both, or neither? Epilepsy Curr 11:66–68
Ljungberg MC, Bhattacharjee MB, Lu Y, Armstrong DL, Yoshor D, Swann JW, Sheldon M, D'Arcangelo G (2006) Activation of mammalian target of rapamycin in cytomegalic neurons of human cortical dysplasia. Ann Neurol 60:420–429
Wolf HK, Wiestler OD (1999) Malformative and neoplastic glioneuronal lesions in patients with chronic pharmacoresistant epilepsies. Adv Neurol 81:69–79
Boer K, Troost D, Timmermans W, van Rijen PC, Spliet WG, Aronica E (2010) Pi3K–mTOR signaling and AMOG expression in epilepsy-associated glioneuronal tumors. Brain Pathol 20:234–244
Krueger DA, Care MM, Holland K, Agricola K, Tydor C, Mangeshkar P, Wilson KA, Byars A, Sahmoud T, Franz DN (2010) Everolimus for subependymal giant-cell astrocytomas in tuberous sclerosis. N Engl J Med 363:1801–1811
McDaniel SS, Rensing NR, Thio LL, Yamada KA, Wong M (2011) The ketogenic diet inhibits the mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway. Epilepsia 52:7–11
Ruegg S, Baybis M, Juul H, Dichter M, Crino PB (2007) Effects of rapamycin on gene expression, morphology, and electrophysiological properties of rat hippocampal neurons. Epilepsy Res 77:85–92
Wang Y, Barbaro MF, Baraban SC (2006) A role for the mTOR pathway in surface expression of AMPA receptors. Neurosci Lett 401:35–39
Shacka JJ, Lu J, Xie ZL, Uchiyama Y, Roth KA, Zhang J (2007) Kainic acid induces early and transient autophagic stress in mouse hippocampus. Neurosci Lett 414:57–60
Cao L, Xu J, Lin Y, Zhao X, Liu X, Chi Z (2009) Autophagy is upregulated in rats with status epilepticus and partly inhibited by vitamin E. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 379:949–953
Vezzani A, French J, Bartfai T, Baram TZ (2011) The role of inflammation in epilepsy. Nat Rev Neurol 7:31–40
Aronica E, Crino PB (2011) Inflammation in epilepsy: clinical observations. Epilepsia 52:26–32
Battaglia M, Stabilini A, Migliavacca B, Horejs-Hoeck J, Kaupper T, Roncarolo MG (2006) Rapamycin promotes expansion of functional CD4 + CD25 + FOXP3+ regulatory T cells of both healthy subjects and type 1 diabetic patients. J Immunol 177:8338–83347
Gomez-Cambronero J (2003) Rapamycin inhibits GM-CSF-induced neutrophil migration. FEBS Lett 550:94–100
Weichhart T, Säemann MD (2009) The multiple facets of mTOR in immunity. Trends Immunol 30:218–226
Dello Russo C, Lisi L, Tringali G, Navarra P (2009) Involvement of mTOR kinase in cytokine-dependent microglial activation and cell proliferation. Biochem Pharmacol 78:1242–1251
Weichhart T, Costantino G, Poglitsch M, Rosner M, Zeyda M, Stuhlmeier KM, Kolbe T, Stulnig TM, Hörl WH, Hengstschläger M, Müller M, Säemann MD (2008) The TSC–mTOR signaling pathway regulates the innate inflammatory response. Immunity 29:565–577
Hardie DG (2011) AMP-activated protein kinase: an energy sensor that regulates all aspects of cell function. Genes Dev 25:1895–1908
Kang CB, Hong Y, Dhe-Paganon S, Yoon HS (2008) FKBP family proteins: immunophilins with versatile biological functions. Neurosignals 16:318–325
Edlich F, Lücke C (2011) From cell death to viral replication: the diverse functions of the membrane-associated FKBP38. Curr Opin Pharmacol 11:348–353
Wouters BG, Koritzinsky M (2008) Hypoxia signalling through mTOR and the unfolded protein response in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 8:851–864
Haeusler RA, Accili D (2008) The double life of Irs. Cell Metab 8:7–9
White MF (2003) Insulin signaling in health and disease. Science 302:1710–1711
Raimondi C, Falasca M (2011) Targeting PDK1 in cancer. Curr Med Chem 18:2763–2769
Ciraolo E, Morello F, Hirsch E (2011) Present and future of PI3K pathway inhibition in cancer: perspectives and limitations. Curr Med Chem 18:2674–2685
Vazquez F, Devreotes P (2006) Regulation of PTEN function as a PIP3 gatekeeper through membrane interaction. Cell Cycle 5:1523–1527
Hollander MC, Blumenthal GM, Dennis PA (2011) PTEN loss in the continuum of common cancers, rare syndromes and mouse models. Nat Rev Cancer 11:289–301
DeYoung MP, Horak P, Sofer A, Sgroi D, Ellisen LW (2008) Hypoxia regulates TSC1/2-mTOR signaling and tumor suppression through REDD1-mediated 14-3-3 shuttling. Genes Dev 22:239–251
Avruch J, Hara K, Lin Y, Liu M, Long X, Ortiz-Vega S, Yonezawa K (2006) Insulin and amino-acid regulation of mTOR signaling and kinase activity through the Rheb GTPase. Oncogene 25:6361–6372
Avruch J, Long X, Lin Y, Ortiz-Vega S, Rapley J, Papageorgiou A, Oshiro N, Kikkawa U (2009) Activation of mTORC1 in two steps: Rheb-GTP activation of catalytic function and increased binding of substrates to raptor. Biochem Soc Trans 37:223–226
Han JM, Sahin M (2011) TSC1/TSC2 signaling in the CNS. FEBS Lett 585:973–980
Jiang X, Yeung RS (2006) Regulation of microtubule-dependent protein transport by the TSC2/mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. Cancer Res 66:5258–5269
Kaul G, Pattan G, Rafeequi T (2011) Eukaryotic elongation factor-2 (eEF2): its regulation and peptide chain elongation. Cell Biochem Funct 29:227–234
Origanti S, Nowotarski SL, Carr TD, Sass-Kuhn S, Xiao L, Wang JY, Shantz LM (2012) Ornithine decarboxylase mRNA is stabilized in an mTORC1-dependent manner in Ras-transformed cells. Biochem J 442(1):199–207
Moschella PC, Rao VU, McDermott PJ, Kuppuswamy D (2007) Regulation of mTOR and S6K1 activation by the nPKC isoforms, PKCepsilon and PKCdelta, in adult cardiac muscle cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol 43:754–766
Stark DT, Bazan NG (2011) Neuroprotectin D1 induces neuronal survival and downregulation of amyloidogenic processing in Alzheimer's disease cellular models. Mol Neurobiol 43:131–138
Zhan J, Easton JB, Huang S, Mishra A, Xiao L, Lacy ER, Kriwacki RW, Houghton PJ (2007) Negative regulation of ASK1 by p21Cip1 involves a small domain that includes Serine 98 that is phosphorylated by ASK1 in vivo. Mol Cell Biol 27:3530–3541
Lee M, Theodoropoulou M, Graw J, Roncaroli F, Zatelli MC, Pellegata NS (2011) Levels of p27 sensitize to dual PI3K/mTOR inhibition. Mol Cancer Ther 10:1450–1459
Usui I, Haruta T, Iwata M, Takano A, Uno T, Kawahara J, Ueno E, Sasaoka T, Kobayashi M (2000) Retinoblastoma protein phosphorylation via PI 3-kinase and mTOR pathway regulates adipocyte differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 275:115–120
Acknowledgments
Funding needed to purchase articles for this survey were granted by the “Rete Regionale di informazione sul farmaco: informazione, formazione, e farmacovigilanza” Project Sponsored by Regione Calabria on the Behalf of Agenzia Italiana del Farmaco (AIFA).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Russo, E., Citraro, R., Constanti, A. et al. The mTOR Signaling Pathway in the Brain: Focus on Epilepsy and Epileptogenesis. Mol Neurobiol 46, 662–681 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8314-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-012-8314-5