Abstract
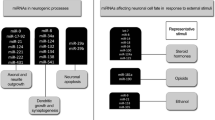
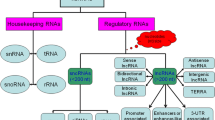
The development of the central nervous system (CNS) relies on precisely orchestrated gene expression regulation. Dysregulation of both genetic and environmental factors can affect proper CNS development and results in neurological diseases. Recent studies have shown that similar to protein coding genes, noncoding RNA molecules have a significant impact on normal CNS development and on causes and progression of human neurological disorders. In this review, we have highlighted discoveries of functions of noncoding RNAs, in particular microRNAs and long noncoding RNAs, in neural development and neurological diseases. Emerging evidence has shown that microRNAs play an essential role in many aspects of neural development, such as proliferation of neural stem cells and progenitors, neuronal differentiation, maturation, and synaptogenesis. Misregulation of microRNAs is associated with some mental disorders and neurodegeneration diseases. In addition, long noncoding RNAs are found to play a role in neural development by regulating the expression of protein coding genes. Therefore, examining noncoding RNA-mediated gene regulations has revealed novel mechanisms of neural development and provided new insights into the etiology of human neurological diseases.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kapsimali M, Kloosterman WP, de Bruijn E, Rosa F, Plasterk RH, Wilson SW (2007) MicroRNAs show a wide diversity of expression profiles in the developing and mature central nervous system. Genome Biol 8(8):R173
Bak M, Silahtaroglu A, Moller M, Christensen M, Rath MF, Skryabin B, Tommerup N, Kauppinen S (2008) MicroRNA expression in the adult mouse central nervous system. RNA 14(3):432–444
Landgraf P, Rusu M, Sheridan R, Sewer A, Iovino N, Aravin A, Pfeffer S, Rice A, Kamphorst AO, Landthaler M et al (2007) A mammalian microRNA expression atlas based on small RNA library sequencing. Cell 129(7):1401–1414
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Sunkin SM, Mehler MF, Mattick JS (2008) Specific expression of long noncoding RNAs in the mouse brain. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(2):716–721
Belgard TG, Marques AC, Oliver PL, Abaan HO, Sirey TM, Hoerder-Suabedissen A, Garcia-Moreno F, Molnar Z, Margulies EH, Ponting CP (2011) A transcriptomic atlas of mouse neocortical layers. Neuron 71(4):605–616
Khraiwesh B, Arif MA, Seumel GI, Ossowski S, Weigel D, Reski R, Frank W (2010) Transcriptional control of gene expression by microRNAs. Cell 140(1):111–122
Borchert GM, Lanier W, Davidson BL (2006) RNA polymerase III transcribes human microRNAs. Nat Struct Mol Biol 13(12):1097–1101
Gregory RI, Chendrimada TP, Shiekhattar R (2006) MicroRNA biogenesis: isolation and characterization of the microprocessor complex. Methods Mol Biol 342:33–47
Lund E, Dahlberg JE (2006) Substrate selectivity of exportin 5 and Dicer in the biogenesis of microRNAs. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol 71:59–66
Rana TM (2007) Illuminating the silence: understanding the structure and function of small RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 8(1):23–36
Neilson JR, Sharp PA (2008) Small RNA regulators of gene expression. Cell 134(6):899–902
Wang XJ, Reyes JL, Chua NH, Gaasterland T (2004) Prediction and identification of Arabidopsis thaliana microRNAs and their mRNA targets. Genome Biol 5(9):R65
Pratt AJ, MacRae IJ (2009) The RNA-induced silencing complex: a versatile gene-silencing machine. J Biol Chem 284(27):17897–17901
Gao FB (2008) Posttranscriptional control of neuronal development by microRNA networks. Trends Neurosci 31(1):20–26
Lau NC, Lim LP, Weinstein EG, Bartel DP (2001) An abundant class of tiny RNAs with probable regulatory roles in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294(5543):858–862
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2001) Identification of novel genes coding for small expressed RNAs. Science 294(5543):853–858
Lee RC, Ambros V (2001) An extensive class of small RNAs in Caenorhabditis elegans. Science 294(5543):862–864
Altuvia Y, Landgraf P, Lithwick G, Elefant N, Pfeffer S, Aravin A, Brownstein MJ, Tuschl T, Margalit H (2005) Clustering and conservation patterns of human microRNAs. Nucleic Acids Res 33(8):2697–2706
Lander ES, Linton LM, Birren B, Nusbaum C, Zody MC, Baldwin J, Devon K, Dewar K, Doyle M, FitzHugh W et al (2001) Initial sequencing and analysis of the human genome. Nature 409(6822):860–921
Kapranov P, Cheng J, Dike S, Nix DA, Duttagupta R, Willingham AT, Stadler PF, Hertel J, Hackermuller J, Hofacker IL et al (2007) RNA maps reveal new RNA classes and a possible function for pervasive transcription. Science 316(5830):1484–1488
Carninci P, Kasukawa T, Katayama S, Gough J, Frith MC, Maeda N, Oyama R, Ravasi T, Lenhard B, Wells C et al (2005) The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science 309(5740):1559–1563
Birney E, Stamatoyannopoulos JA, Dutta A, Guigo R, Gingeras TR, Margulies EH, Weng Z, Snyder M, Dermitzakis ET, Thurman RE et al (2007) Identification and analysis of functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot project. Nature 447(7146):799–816
Pasmant E, Laurendeau I, Heron D, Vidaud M, Vidaud D, Bieche I (2007) Characterization of a germ-line deletion, including the entire INK4/ARF locus, in a melanoma–neural system tumor family: identification of ANRIL, an antisense noncoding RNA whose expression coclusters with ARF. Cancer Res 67(8):3963–3969
Kotake Y, Nakagawa T, Kitagawa K, Suzuki S, Liu N, Kitagawa M, Xiong Y (2010) Long non-coding RNA ANRIL is required for the PRC2 recruitment to and silencing of p15(INK4B) tumor suppressor gene. Oncogene 30(16):1956–1962
Tochitani S, Hayashizaki Y (2008) Nkx2.2 antisense RNA overexpression enhanced oligodendrocytic differentiation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 372(4):691–696
Feng J, Bi C, Clark BS, Mady R, Shah P, Kohtz JD (2006) The Evf-2 noncoding RNA is transcribed from the Dlx-5/6 ultraconserved region and functions as a Dlx-2 transcriptional coactivator. Genes Dev 20(11):1470–1484
Yu W, Gius D, Onyango P, Muldoon-Jacobs K, Karp J, Feinberg AP, Cui H (2008) Epigenetic silencing of tumour suppressor gene p15 by its antisense RNA. Nature 451(7175):202–206
Wang X, Arai S, Song X, Reichart D, Du K, Pascual G, Tempst P, Rosenfeld MG, Glass CK, Kurokawa R (2008) Induced ncRNAs allosterically modify RNA-binding proteins in cis to inhibit transcription. Nature 454(7200):126–130
Shamovsky I, Ivannikov M, Kandel ES, Gershon D, Nudler E (2006) RNA-mediated response to heat shock in mammalian cells. Nature 440(7083):556–560
Willingham AT, Orth AP, Batalov S, Peters EC, Wen BG, Aza-Blanc P, Hogenesch JB, Schultz PG (2005) A strategy for probing the function of noncoding RNAs finds a repressor of NFAT. Science 309(5740):1570–1573
Yang Z, Zhu Q, Luo K, Zhou Q (2001) The 7SK small nuclear RNA inhibits the CDK9/cyclin T1 kinase to control transcription. Nature 414(6861):317–322
Nguyen VT, Kiss T, Michels AA, Bensaude O (2001) 7SK small nuclear RNA binds to and inhibits the activity of CDK9/cyclin T complexes. Nature 414(6861):322–325
Sanchez-Elsner T, Gou D, Kremmer E, Sauer F (2006) Noncoding RNAs of trithorax response elements recruit Drosophila Ash1 to Ultrabithorax. Science 311(5764):1118–1123
Mazo A, Hodgson JW, Petruk S, Sedkov Y, Brock HW (2007) Transcriptional interference: an unexpected layer of complexity in gene regulation. J Cell Sci 120(Pt 16):2755–2761
Rinn JL, Kertesz M, Wang JK, Squazzo SL, Xu X, Brugmann SA, Goodnough LH, Helms JA, Farnham PJ, Segal E et al (2007) Functional demarcation of active and silent chromatin domains in human HOX loci by noncoding RNAs. Cell 129(7):1311–1323
Denisenko O, Shnyreva M, Suzuki H, Bomsztyk K (1998) Point mutations in the WD40 domain of Eed block its interaction with Ezh2. Mol Cell Biol 18(10):5634–5642
Wutz A, Rasmussen TP, Jaenisch R (2002) Chromosomal silencing and localization are mediated by different domains of Xist RNA. Nat Genet 30(2):167–174
Mancini-Dinardo D, Steele SJ, Levorse JM, Ingram RS, Tilghman SM (2006) Elongation of the Kcnq1ot1 transcript is required for genomic imprinting of neighboring genes. Genes Dev 20(10):1268–1282
Tsai MC, Manor O, Wan Y, Mosammaparast N, Wang JK, Lan F, Shi Y, Segal E, Chang HY (2010) Long noncoding RNA as modular scaffold of histone modification complexes. Science 329(5992):689–693
De Pietri Tonelli D, Pulvers JN, Haffner C, Murchison EP, Hannon GJ, Huttner WB: miRNAs are essential for survival and differentiation of newborn neurons but not for expansion of neural progenitors during early neurogenesis in the mouse embryonic neocortex. Development 2008, 135(23):3911–3921
Kawase-Koga Y, Low R, Otaegi G, Pollock A, Deng H, Eisenhaber F, Maurer-Stroh S, Sun T (2010) RNAase-III enzyme Dicer maintains signaling pathways for differentiation and survival in mouse cortical neural stem cells. J Cell Sci 123(Pt 4):586–594
Andersson T, Rahman S, Sansom SN, Alsio JM, Kaneda M, Smith J, O'Carroll D, Tarakhovsky A, Livesey FJ (2010) Reversible block of mouse neural stem cell differentiation in the absence of dicer and microRNAs. PLoS One 5(10):e13453
Kawase-Koga Y, Otaegi G, Sun T (2009) Different timings of Dicer deletion affect neurogenesis and gliogenesis in the developing mouse central nervous system. Dev Dyn 238(11):2800–2812
Davis TH, Cuellar TL, Koch SM, Barker AJ, Harfe BD, McManus MT, Ullian EM (2008) Conditional loss of Dicer disrupts cellular and tissue morphogenesis in the cortex and hippocampus. J Neurosci 28(17):4322–4330
Li Q, Bian S, Hong J, Kawase-Koga Y, Zhu E, Zheng Y, Yang L, Sun T: Timing specific requirement of microRNA function is essential for embryonic and postnatal hippocampal development. PLoS One 2011, in press
Cuellar TL, Davis TH, Nelson PT, Loeb GB, Harfe BD, Ullian E, McManus MT (2008) Dicer loss in striatal neurons produces behavioral and neuroanatomical phenotypes in the absence of neurodegeneration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(14):5614–5619
Zehir A, Hua LL, Maska EL, Morikawa Y, Cserjesi P (2010) Dicer is required for survival of differentiating neural crest cells. Dev Biol 340(2):459–467
Huang T, Liu Y, Huang M, Zhao X, Cheng L (2010) Wnt1-cre-mediated conditional loss of Dicer results in malformation of the midbrain and cerebellum and failure of neural crest and dopaminergic differentiation in mice. J Mol Cell Biol 2(3):152–163
Zheng K, Li H, Zhu Y, Zhu Q, Qiu M (2010) MicroRNAs are essential for the developmental switch from neurogenesis to gliogenesis in the developing spinal cord. J Neurosci 30(24):8245–8250
Zhao X, He X, Han X, Yu Y, Ye F, Chen Y, Hoang T, Xu X, Mi QS, Xin M et al (2010) MicroRNA-mediated control of oligodendrocyte differentiation. Neuron 65(5):612–626
Budde H, Schmitt S, Fitzner D, Opitz L, Salinas-Riester G, Simons M (2010) Control of oligodendroglial cell number by the miR-17-92 cluster. Development 137(13):2127–2132
Fukagawa T, Nogami M, Yoshikawa M, Ikeno M, Okazaki T, Takami Y, Nakayama T, Oshimura M (2004) Dicer is essential for formation of the heterochromatin structure in vertebrate cells. Nat Cell Biol 6(8):784–791
Kanellopoulou C, Muljo SA, Kung AL, Ganesan S, Drapkin R, Jenuwein T, Livingston DM, Rajewsky K (2005) Dicer-deficient mouse embryonic stem cells are defective in differentiation and centromeric silencing. Genes Dev 19(4):489–501
Temple S (2001) The development of neural stem cells. Nature 414(6859):112–117
Gage FH (2000) Mammalian neural stem cells. Science 287(5457):1433–1438
Doe CQ (2008) Neural stem cells: balancing self-renewal with differentiation. Development 135(9):1575–1587
Arsenijevic Y (2003) Mammalian neural stem-cell renewal: nature versus nurture. Mol Neurobiol 27(1):73–98
Reinhart BJ, Slack FJ, Basson M, Pasquinelli AE, Bettinger JC, Rougvie AE, Horvitz HR, Ruvkun G (2000) The 21-nucleotide let-7 RNA regulates developmental timing in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature 403(6772):901–906
Zhao C, Sun G, Li S, Lang MF, Yang S, Li W, Shi Y (2010) MicroRNA let-7b regulates neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation by targeting nuclear receptor TLX signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(5):1876–1881
Rybak A, Fuchs H, Smirnova L, Brandt C, Pohl EE, Nitsch R, Wulczyn FG (2008) A feedback loop comprising lin-28 and let-7 controls pre-let-7 maturation during neural stem-cell commitment. Nat Cell Biol 10(8):987–993
Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A, Meyer J, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2002) Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr Biol 12(9):735–739
Maiorano NA, Mallamaci A (2009) Promotion of embryonic cortico-cerebral neuronogenesis by miR-124. Neural Dev 4:40
Cheng LC, Pastrana E, Tavazoie M, Doetsch F (2009) miR-124 regulates adult neurogenesis in the subventricular zone stem cell niche. Nat Neurosci 12(4):399–408
Arvanitis DN, Jungas T, Behar A, Davy A (2010) Ephrin-B1 reverse signaling controls a posttranscriptional feedback mechanism via miR-124. Mol Cell Biol 30(10):2508–2517
Makeyev EV, Zhang J, Carrasco MA, Maniatis T (2007) The MicroRNA miR-124 promotes neuronal differentiation by triggering brain-specific alternative pre-mRNA splicing. Mol Cell 27(3):435–448
Zhao C, Sun G, Li S, Shi Y (2009) A feedback regulatory loop involving microRNA-9 and nuclear receptor TLX in neural stem cell fate determination. Nat Struct Mol Biol 16(4):365–371
Delaloy C, Liu L, Lee JA, Su H, Shen F, Yang GY, Young WL, Ivey KN, Gao FB (2010) MicroRNA-9 coordinates proliferation and migration of human embryonic stem cell-derived neural progenitors. Cell Stem Cell 6(4):323–335
Bonev B, Pisco A, Papalopulu N (2011) MicroRNA-9 reveals regional diversity of neural progenitors along the anterior-posterior axis. Dev Cell 20(1):19–32
Leucht C, Stigloher C, Wizenmann A, Klafke R, Folchert A, Bally-Cuif L (2008) MicroRNA-9 directs late organizer activity of the midbrain–hindbrain boundary. Nat Neurosci 11(6):641–648
Otaegi G, Pollock A, Hong J, Sun T (2011) MicroRNA miR-9 modifies motor neuron columns by a tuning regulation of FoxP1 levels in developing spinal cords. J Neurosci 31(3):809–818
Shibata M, Nakao H, Kiyonari H, Abe T, Aizawa S (2011) MicroRNA-9 regulates neurogenesis in mouse telencephalon by targeting multiple transcription factors. J Neurosci 31(9):3407–3422
Gaughwin P, Ciesla M, Yang H, Lim B, Brundin P: Stage-specific modulation of cortical neuronal development by Mmu-miR-134. Cereb Cortex 2011
Brett JO, Renault VM, Rafalski VA, Webb AE, Brunet A (2011) The microRNA cluster miR-106b 25 regulates adult neural stem/progenitor cell proliferation and neuronal differentiation. Aging (Albany NY) 3(2):108–124
Renault VM, Rafalski VA, Morgan AA, Salih DA, Brett JO, Webb AE, Villeda SA, Thekkat PU, Guillerey C, Denko NC et al (2009) FoxO3 regulates neural stem cell homeostasis. Cell Stem Cell 5(5):527–539
Szulwach KE, Li X, Smrt RD, Li Y, Luo Y, Lin L, Santistevan NJ, Li W, Zhao X, Jin P (2010) Cross talk between microRNA and epigenetic regulation in adult neurogenesis. J Cell Biol 189(1):127–141
Liu C, Teng ZQ, Santistevan NJ, Szulwach KE, Guo W, Jin P, Zhao X (2010) Epigenetic regulation of miR-184 by MBD1 governs neural stem cell proliferation and differentiation. Cell Stem Cell 6(5):433–444
Yu JY, Chung KH, Deo M, Thompson RC, Turner DL (2008) MicroRNA miR-124 regulates neurite outgrowth during neuronal differentiation. Exp Cell Res 314(14):2618–2633
Hall A (1998) Rho GTPases and the actin cytoskeleton. Science 279(5350):509–514
Rajasethupathy P, Fiumara F, Sheridan R, Betel D, Puthanveettil SV, Russo JJ, Sander C, Tuschl T, Kandel E (2009) Characterization of small RNAs in Aplysia reveals a role for miR-124 in constraining synaptic plasticity through CREB. Neuron 63(6):803–817
Sanuki R, Onishi A, Koike C, Muramatsu R, Watanabe S, Muranishi Y, Irie S, Uneo S, Koyasu T, Matsui R et al: miR-124a is required for hippocampal axogenesis and retinal cone survival through Lhx2 suppression. Nat Neurosci, 14(9):1125–1134
Smrt RD, Szulwach KE, Pfeiffer RL, Li X, Guo W, Pathania M, Teng ZQ, Luo Y, Peng J, Bordey A et al (2010) MicroRNA miR-137 regulates neuronal maturation by targeting ubiquitin ligase mind bomb-1. Stem Cells 28(6):1060–1070
Kim J, Inoue K, Ishii J, Vanti WB, Voronov SV, Murchison E, Hannon G, Abeliovich A (2007) A MicroRNA feedback circuit in midbrain dopamine neurons. Science 317(5842):1220–1224
Nunes I, Tovmasian LT, Silva RM, Burke RE, Goff SP (2003) Pitx3 is required for development of substantia nigra dopaminergic neurons. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100(7):4245–4250
Magill ST, Cambronne XA, Luikart BW, Lioy DT, Leighton BH, Westbrook GL, Mandel G, Goodman RH (2010) microRNA-132 regulates dendritic growth and arborization of newborn neurons in the adult hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107(47):20382–20387
Hansen KF, Sakamoto K, Wayman GA, Impey S, Obrietan K (2010) Transgenic miR132 alters neuronal spine density and impairs novel object recognition memory. PLoS One 5(11):e15497
Edbauer D, Neilson JR, Foster KA, Wang CF, Seeburg DP, Batterton MN, Tada T, Dolan BM, Sharp PA, Sheng M (2010) Regulation of synaptic structure and function by FMRP-associated microRNAs miR-125b and miR-132. Neuron 65(3):373–384
Schratt GM, Tuebing F, Nigh EA, Kane CG, Sabatini ME, Kiebler M, Greenberg ME (2006) A brain-specific microRNA regulates dendritic spine development. Nature 439(7074):283–289
Bai F, Witzmann FA (2007) Synaptosome proteomics. Subcell Biochem 43:77–98
Siegel G, Obernosterer G, Fiore R, Oehmen M, Bicker S, Christensen M, Khudayberdiev S, Leuschner PF, Busch CJ, Kane C et al (2009) A functional screen implicates microRNA-138-dependent regulation of the depalmitoylation enzyme APT1 in dendritic spine morphogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 11(6):705–716
Banerjee S, Neveu P, Kosik KS (2009) A coordinated local translational control point at the synapse involving relief from silencing and MOV10 degradation. Neuron 64(6):871–884
Abelson JF, Kwan KY, O'Roak BJ, Baek DY, Stillman AA, Morgan TM, Mathews CA, Pauls DL, Rasin MR, Gunel M et al (2005) Sequence variants in SLITRK1 are associated with Tourette's syndrome. Science 310(5746):317–320
Jin P, Zarnescu DC, Ceman S, Nakamoto M, Mowrey J, Jongens TA, Nelson DL, Moses K, Warren ST (2004) Biochemical and genetic interaction between the fragile X mental retardation protein and the microRNA pathway. Nat Neurosci 7(2):113–117
Yi YH, Sun XS, Qin JM, Zhao QH, Liao WP, Long YS (2010) Experimental identification of microRNA targets on the 3′ untranslated region of human FMR1 gene. J Neurosci Methods 190(1):34–38
Han J, Lee Y, Yeom KH, Nam JW, Heo I, Rhee JK, Sohn SY, Cho Y, Zhang BT, Kim VN (2006) Molecular basis for the recognition of primary microRNAs by the Drosha–DGCR8 complex. Cell 125(5):887–901
Digilio MC, Marino B, Cappa M, Cambiaso P, Giannotti A, Dallapiccola B (2001) Auxological evaluation in patients with DiGeorge/velocardiofacial syndrome (deletion 22q11.2 syndrome). Genet Med 3(1):30–33
Stark KL, Xu B, Bagchi A, Lai WS, Liu H, Hsu R, Wan X, Pavlidis P, Mills AA, Karayiorgou M et al: Altered brain microRNA biogenesis contributes to phenotypic deficits in a 22q11-deletion mouse model. Nat Genet 2008
Perkins DO, Jeffries CD, Jarskog LF, Thomson JM, Woods K, Newman MA, Parker JS, Jin J, Hammond SM (2007) microRNA expression in the prefrontal cortex of individuals with schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder. Genome Biol 8(2):R27
Beveridge NJ, Tooney PA, Carroll AP, Gardiner E, Bowden N, Scott RJ, Tran N, Dedova I, Cairns MJ (2008) Dysregulation of miRNA 181b in the temporal cortex in schizophrenia. Hum Mol Genet 17(8):1156–1168
Kocerha J, Faghihi MA, Lopez-Toledano MA, Huang J, Ramsey AJ, Caron MG, Sales N, Willoughby D, Elmen J, Hansen HF et al (2009) MicroRNA-219 modulates NMDA receptor-mediated neurobehavioral dysfunction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(9):3507–3512
Abu-Elneel K, Liu T, Gazzaniga FS, Nishimura Y, Wall DP, Geschwind DH, Lao K, Kosik KS (2008) Heterogeneous dysregulation of microRNAs across the autism spectrum. Neurogenetics 9(3):153–161
Sarachana T, Zhou R, Chen G, Manji HK, Hu VW (2010) Investigation of post-transcriptional gene regulatory networks associated with autism spectrum disorders by microRNA expression profiling of lymphoblastoid cell lines. Genome Med 2(4):23
Seno MM, Hu P, Gwadry FG, Pinto D, Marshall CR, Casallo G, Scherer SW (2011) Gene and miRNA expression profiles in autism spectrum disorders. Brain Res 1380:85–97
Lukiw WJ (2007) Micro-RNA speciation in fetal, adult and Alzheimer's disease hippocampus. Neuroreport 18(3):297–300
Sethi P, Lukiw WJ (2009) Micro-RNA abundance and stability in human brain: specific alterations in Alzheimer's disease temporal lobe neocortex. Neurosci Lett 459(2):100–104
Wang WX, Rajeev BW, Stromberg AJ, Ren N, Tang G, Huang Q, Rigoutsos I, Nelson PT (2008) The expression of microRNA miR-107 decreases early in Alzheimer's disease and may accelerate disease progression through regulation of beta-site amyloid precursor protein-cleaving enzyme 1. J Neurosci 28(5):1213–1223
Hebert SS, Horre K, Nicolai L, Papadopoulou AS, Mandemakers W, Silahtaroglu AN, Kauppinen S, Delacourte A, De Strooper B (2008) Loss of microRNA cluster miR-29a/b-1 in sporadic Alzheimer's disease correlates with increased BACE1/beta-secretase expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105(17):6415–6420
Hebert SS, Papadopoulou AS, Smith P, Galas MC, Planel E, Silahtaroglu AN, Sergeant N, Buee L, De Strooper B (2010) Genetic ablation of Dicer in adult forebrain neurons results in abnormal tau hyperphosphorylation and neurodegeneration. Hum Mol Genet 19(20):3959–3969
Boissonneault V, Plante I, Rivest S, Provost P (2009) MicroRNA-298 and microRNA-328 regulate expression of mouse beta-amyloid precursor protein-converting enzyme 1. J Biol Chem 284(4):1971–1981
Vilardo E, Barbato C, Ciotti M, Cogoni C, Ruberti F (2010) MicroRNA-101 regulates amyloid precursor protein expression in hippocampal neurons. J Biol Chem 285(24):18344–18351
Lukiw WJ, Zhao Y, Cui JG (2008) An NF-kappaB-sensitive micro RNA-146a-mediated inflammatory circuit in Alzheimer disease and in stressed human brain cells. J Biol Chem 283(46):31315–31322
Lee ST, Chu K, Im WS, Yoon HJ, Im JY, Park JE, Park KH, Jung KH, Lee SK, Kim M et al (2011) Altered microRNA regulation in Huntington's disease models. Exp Neurol 227(1):172–179
Johnson R, Buckley NJ (2009) Gene dysregulation in Huntington's disease: REST, microRNAs and beyond. Neuromolecular Med 11(3):183–199
Conaco C, Otto S, Han JJ, Mandel G (2006) Reciprocal actions of REST and a microRNA promote neuronal identity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(7):2422–2427
Packer AN, Xing Y, Harper SQ, Jones L, Davidson BL (2008) The bifunctional microRNA miR-9/miR-9* regulates REST and CoREST and is downregulated in Huntington's disease. J Neurosci 28(53):14341–14346
Gaughwin PM, Ciesla M, Lahiri N, Tabrizi SJ, Brundin P, Bjorkqvist M (2011) Hsa-miR-34b is a plasma-stable microRNA that is elevated in pre-manifest Huntington's disease. Hum Mol Genet 20(11):2225–2237
Doxakis E (2010) Post-transcriptional regulation of alpha-synuclein expression by mir-7 and mir-153. J Biol Chem 285(17):12726–12734
Junn E, Lee KW, Jeong BS, Chan TW, Im JY, Mouradian MM (2009) Repression of alpha-synuclein expression and toxicity by microRNA-7. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(31):13052–13057
Wang G, van der Walt JM, Mayhew G, Li YJ, Zuchner S, Scott WK, Martin ER, Vance JM (2008) Variation in the miRNA-433 binding site of FGF20 confers risk for Parkinson disease by overexpression of alpha-synuclein. Am J Hum Genet 82(2):283–289
Saba R, Goodman CD, Huzarewich RL, Robertson C, Booth SA (2008) A miRNA signature of prion induced neurodegeneration. PLoS One 3(11):e3652
Pogue AI, Dua P, Eicken C, Hill JM, Lukiw WJ: Up-regulation of microRNA-146a (miRNA-146a), a marker for inflammatory neurodegeneration, in sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (sCJD) and Gerstmann–Straussler Scheinker (GSS) syndrome. Journal of Toxicology and Environmental Health 2011, in press
Roizen NJ, Patterson D (2003) Down's syndrome. Lancet 361(9365):1281–1289
Kuhn DE, Nuovo GJ, Martin MM, Malana GE, Pleister AP, Jiang J, Schmittgen TD, Terry AV Jr, Gardiner K, Head E et al (2008) Human chromosome 21-derived miRNAs are overexpressed in down syndrome brains and hearts. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 370(3):473–477
Elton TS, Sansom SE, Martin MM (2010) Trisomy-21 gene dosage over-expression of miRNAs results in the haploinsufficiency of specific target proteins. RNA Biol 7(5):540–547
Kuhn DE, Nuovo GJ, Terry AV Jr, Martin MM, Malana GE, Sansom SE, Pleister AP, Beck WD, Head E, Feldman DS et al (2010) Chromosome 21-derived microRNAs provide an etiological basis for aberrant protein expression in human Down syndrome brains. J Biol Chem 285(2):1529–1543
Pogue AI, Cui JG, Li YY, Zhao Y, Culicchia F, Lukiw WJ (2010) Micro RNA-125b (miRNA-125b) function in astrogliosis and glial cell proliferation. Neurosci Lett 476(1):18–22
Tan KS, Armugam A, Sepramaniam S, Lim KY, Setyowati KD, Wang CW, Jeyaseelan K (2009) Expression profile of MicroRNAs in young stroke patients. PLoS One 4(11):e7689
Buller B, Liu X, Wang X, Zhang RL, Zhang L, Hozeska-Solgot A, Chopp M, Zhang ZG (2010) MicroRNA-21 protects neurons from ischemic death. FEBS J 277(20):4299–4307
Liu XS, Chopp M, Zhang RL, Tao T, Wang XL, Kassis H, Hozeska-Solgot A, Zhang L, Chen C, Zhang ZG (2011) MicroRNA profiling in subventricular zone after stroke: MiR-124a regulates proliferation of neural progenitor cells through Notch signaling pathway. PLoS One 6(8):e23461
Aronica E, Fluiter K, Iyer A, Zurolo E, Vreijling J, van Vliet EA, Baayen JC, Gorter JA (2010) Expression pattern of miR-146a, an inflammation-associated microRNA, in experimental and human temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur J Neurosci 31(6):1100–1107
Saus E, Soria V, Escaramis G, Vivarelli F, Crespo JM, Kagerbauer B, Menchon JM, Urretavizcaya M, Gratacos M, Estivill X (2010) Genetic variants and abnormal processing of pre-miR-182, a circadian clock modulator, in major depression patients with late insomnia. Hum Mol Genet 19(20):4017–4025
Xu Y, Liu H, Li F, Sun N, Ren Y, Liu Z, Cao X, Wang Y, Liu P, Zhang K (2010) A polymorphism in the microRNA-30e precursor associated with major depressive disorder risk and P300 waveform. J Affect Disord 127(1–3):332–336
Kim AH, Reimers M, Maher B, Williamson V, McMichael O, McClay JL, van den Oord EJ, Riley BP, Kendler KS, Vladimirov VI (2010) MicroRNA expression profiling in the prefrontal cortex of individuals affected with schizophrenia and bipolar disorders. Schizophr Res 124(1–3):183–191
Rong H, Liu TB, Yang KJ, Yang HC, Wu DH, Liao CP, Hong F, Yang HZ, Wan F, Ye XY et al (2011) MicroRNA-134 plasma levels before and after treatment for bipolar mania. J Psychiatr Res 45(1):92–95
Baudry A, Mouillet-Richard S, Schneider B, Launay JM, Kellermann O (2010) miR-16 targets the serotonin transporter: a new facet for adaptive responses to antidepressants. Science 329(5998):1537–1541
Zhou R, Yuan P, Wang Y, Hunsberger JG, Elkahloun A, Wei Y, Damschroder-Williams P, Du J, Chen G, Manji HK (2009) Evidence for selective microRNAs and their effectors as common long-term targets for the actions of mood stabilizers. Neuropsychopharmacology 34(6):1395–1405
Ponjavic J, Oliver PL, Lunter G, Ponting CP (2009) Genomic and transcriptional co-localization of protein-coding and long non-coding RNA pairs in the developing brain. PLoS Genet 5(8):e1000617
Price M, Lazzaro D, Pohl T, Mattei MG, Ruther U, Olivo JC, Duboule D, Di Lauro R (1992) Regional expression of the homeobox gene Nkx-2.2 in the developing mammalian forebrain. Neuron 8(2):241–255
Kohtz JD, Fishell G (2004) Developmental regulation of EVF-1, a novel non-coding RNA transcribed upstream of the mouse Dlx6 gene. Gene Expr Patterns 4(4):407–412
Zerucha T, Stuhmer T, Hatch G, Park BK, Long Q, Yu G, Gambarotta A, Schultz JR, Rubenstein JL, Ekker M (2000) A highly conserved enhancer in the Dlx5/Dlx6 intergenic region is the site of cross-regulatory interactions between Dlx genes in the embryonic forebrain. J Neurosci 20(2):709–721
Wang Y, Dye CA, Sohal V, Long JE, Estrada RC, Roztocil T, Lufkin T, Deisseroth K, Baraban SC, Rubenstein JL (2010) Dlx5 and Dlx6 regulate the development of parvalbumin-expressing cortical interneurons. J Neurosci 30(15):5334–5345
Bond AM, Vangompel MJ, Sametsky EA, Clark MF, Savage JC, Disterhoft JF, Kohtz JD (2009) Balanced gene regulation by an embryonic brain ncRNA is critical for adult hippocampal GABA circuitry. Nat Neurosci 12(8):1020–1027
Pevny L, Placzek M (2005) SOX genes and neural progenitor identity. Curr Opin Neurobiol 15(1):7–13
Amaral PP, Neyt C, Wilkins SJ, Askarian-Amiri ME, Sunkin SM, Perkins AC, Mattick JS (2009) Complex architecture and regulated expression of the Sox2ot locus during vertebrate development. RNA 15(11):2013–2027
Blackshaw S, Harpavat S, Trimarchi J, Cai L, Huang H, Kuo WP, Weber G, Lee K, Fraioli RE, Cho SH et al (2004) Genomic analysis of mouse retinal development. PLoS Biol 2(9):E247
Rapicavoli NA, Poth EM, Blackshaw S (2010) The long noncoding RNA RNCR2 directs mouse retinal cell specification. BMC Dev Biol 10:49
Arisi I, D'Onofrio M, Brandi R, Felsani A, Capsoni S, Drovandi G, Felici G, Weitschek E, Bertolazzi P, Cattaneo A (2011) Gene expression biomarkers in the brain of a mouse model for Alzheimer's disease: mining of microarray data by logic classification and feature selection. J Alzheimers Dis 24(4):721–738
Tiedge H, Chen W, Brosius J (1993) Primary structure, neural-specific expression, and dendritic location of human BC200 RNA. J Neurosci 13(6):2382–2390
Wang H, Iacoangeli A, Popp S, Muslimov IA, Imataka H, Sonenberg N, Lomakin IB, Tiedge H (2002) Dendritic BC1 RNA: functional role in regulation of translation initiation. J Neurosci 22(23):10232–10241
Mus E, Hof PR, Tiedge H (2007) Dendritic BC200 RNA in aging and in Alzheimer's disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104(25):10679–10684
Lukiw WJ, Handley P, Wong L, Crapper McLachlan DR (1992) BC200 RNA in normal human neocortex, non-Alzheimer dementia (NAD), and senile dementia of the Alzheimer type (AD). Neurochem Res 17(6):591–597
Pollard KS, Salama SR, Lambert N, Lambot MA, Coppens S, Pedersen JS, Katzman S, King B, Onodera C, Siepel A et al (2006) An RNA gene expressed during cortical development evolved rapidly in humans. Nature 443(7108):167–172
Johnson R, Richter N, Jauch R, Gaughwin PM, Zuccato C, Cattaneo E, Stanton LW (2010) The Human Accelerated Region 1 noncoding RNA is repressed by REST in Huntington's disease. Physiol Genomics 41:269–274
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Dolores Malaspina, Dr. Rajiv Ratan, and Dr. Quanhong Ma for critical reading of the manuscript and providing thoughtful comments. Owing to space limitations, we apologize for being unable to cite many excellent papers in this field. This work was supported by Ellison Medical Foundation (T. S.), an award from Hirschl/Weill-Caulier Trust (T. S.), and an R01-MH083680 grant from NIH/NIMH (T. S.).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bian, S., Sun, T. Functions of Noncoding RNAs in Neural Development and Neurological Diseases. Mol Neurobiol 44, 359–373 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-011-8211-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12035-011-8211-3