Abstract
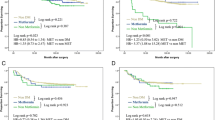
There was a contradictory data with metformin use on breast cancer risk, but there is growing evidence that the use of metformin in diabetic patients was associated with lower risks of breast cancer mortality and incidence. The effect of metformin on clinical and pathological properties of breast cancer was not known exactly, and we aimed to investigate the demographic and clinico-pathological characteristics of patients with metformin users at the time of breast cancer diagnosis. Patients with breast cancer diagnosed from 2000 to 2012 in our clinic were retrospectively analyzed. Patient’s demographics, including survival data and tumor characteristics were obtained from medical charts. Breast cancer patients who were taking metformin at the time of breast cancer diagnosis were enrolled as metformin users (n = 148), where the patients matched with the same age who were not taking metformin were included as a control group (n = 636). A total of 784 patients were included in this study. Median age of both metformin users and nonusers was 57 (23–87). There were no significant differences in baseline tumor size (P = 0.60), tumor stage (P = 0.76), and node positivity (P = 0.13) between the two groups. Metformin user patients compared to nonusers had significantly lower incidence of histological grade III tumor (P = 0.03). A similar significant trend for lower incidence of triple negative (P = 0.01) and higher incidence ER positivity (P = 0.008) and PR positivity (P = 0.01) was also seen in metformin users. In survival analysis, the estimated median disease-free survival was 118 months in metformin users, whereas 69 months in nonusers (P = 0.09). Median overall survival (OS) could not be obtained due to low events. In patients with metformin users, OS rate was 98.4, 97.1, and 93.8 %, and in nonusers was 99.6, 94.4, and 90.5 %, the first, third, and fifth years, respectively. The use of metformin at the time of breast cancer diagnosis was associated with better clinico-pathological properties and nonsignificantly improved disease-free survival in breast cancer patients.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Percik R, Stumvoll M. Obesity and cancer. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2009;117(10):563–6.
Hsu IR, Kim SP, Kabir M, Bergman RN. Metabolic syndrome, hyperinsulinemia, and cancer. Am J Clin Nutr. 2007;86(3):s867–71.
Warshamana-Greene GS, Litz J, Buchdunger E, Garcia-Echeverria C, Hofmann F, Krystal GW. The insulin-like growth factor-I receptor kinase inhibitor, NVP-ADW742, sensitizes small cell lung cancer cell lines to the effects of chemotherapy. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11(4):1563–71.
Pollak M. Insulin, insulin-like growth factors and neoplasia. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;22(4):625–38.
Wolf I, Sadetzki S, Catane R, Karasik A, Kaufman B. Diabetes mellitus and breast cancer. Lancet Oncol. 2005;6(2):103–11.
Larsson SC, Mantzoros CS, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of breast cancer: a meta-analysis. Int J Cancer. 2007;121(4):856–62.
Friberg E, Orsini N, Mantzoros CS, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of endometrial cancer: a meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2007;50(7):1365–74.
Larsson SC, Orsini N, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of colorectal cancer: a meta-analysis. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2005;97(22):1679–87.
Larsson SC, Orsini N, Brismar K, Wolk A. Diabetes mellitus and risk of bladder cancer: a meta-analysis. Diabetologia. 2006;49(12):2819–23.
El-Serag HB, Hampel H, Javadi F. The association between diabetes and hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review of epidemiologic evidence. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2006;4(3):369–80.
Everhart J, Wright D. Diabetes mellitus as a risk factor for pancreatic cancer. A meta-analysis. JAMA. 1995;273(20):1605–9.
Reeves GK, Pirie K, Beral V, Green J, Spencer E, Bull D. Cancer incidence and mortality in relation to body mass index in the Million Women Study: cohort study. BMJ. 2007;335(7630):1134.
Erickson K, Patterson RE, Flatt SW, Natarajan L, Parker BA, Heath DD, Laughlin GA, Saquib N, Rock CL, Pierce JP. Clinically defined type 2 diabetes mellitus and prognosis in early-stage breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(1):54–60.
Patterson RE, Flatt SW, Saquib N, Rock CL, Caan BJ, Parker BA, Laughlin GA, Erickson K, Thomson CA, Bardwell WA, et al. Medical comorbidities predict mortality in women with a history of early stage breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010;122(3):859–65.
Peairs KS, Barone BB, Snyder CF, Yeh HC, Stein KB, Derr RL, Brancati FL, Wolff AC. Diabetes mellitus and breast cancer outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(1):40–6.
Ali S, Fonseca V. Overview of metformin: special focus on metformin extended release. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2012;13(12):1797–805.
Nathan DM, Buse JB, Davidson MB, Ferrannini E, Holman RR, Sherwin R, Zinman B. Medical management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes mellitus: a consensus algorithm for the initiation and adjustment of therapy: a consensus statement from the American Diabetes Association and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes. Diabetologia. 2009;52(1):17–30.
Noto H, Tsujimoto T, Sasazuki T, Noda M. Significantly increased risk of cancer in patients with diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Endocr Pract. 2011;17(4):616–28.
Decensi A, Puntoni M, Goodwin P, Cazzaniga M, Gennari A, Bonanni B, Gandini S. Metformin and cancer risk in diabetic patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Prev Res (Phila). 2010;3(11):1451–61.
Bowker SL, Majumdar SR, Veugelers P, Johnson JA. Increased cancer-related mortality for patients with type 2 diabetes who use sulfonylureas or insulin. Diabetes Care. 2006;29(2):254–8.
Redaniel MT, Jeffreys M, May MT, Ben-Shlomo Y, Martin RM. Associations of type 2 diabetes and diabetes treatment with breast cancer risk and mortality: a population-based cohort study among British women. Cancer Causes Control. 2012;23(11):1785–95.
Col NF, Ochs L, Springmann V, Aragaki AK, Chlebowski RT. Metformin and breast cancer risk: a meta-analysis and critical literature review. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;135(3):639–46.
Chlebowski RT, McTiernan A, Wactawski-Wende J, Manson JE, Aragaki AK, Rohan T, Ipp E, Kaklamani VG, Vitolins M, Wallace R, et al. Diabetes, metformin, and breast cancer in postmenopausal women. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(23):2844–52.
Kahn BB, Alquier T, Carling D, Hardie DG. AMP-activated protein kinase: ancient energy gauge provides clues to modern understanding of metabolism. Cell Metab. 2005;1(1):15–25.
Zhou G, Myers R, Li Y, Chen Y, Shen X, Fenyk-Melody J, Wu M, Ventre J, Doebber T, Fujii N, et al. Role of AMP-activated protein kinase in mechanism of metformin action. J Clin Investig. 2001;108(8):1167–74.
Dowling RJ, Goodwin PJ, Stambolic V. Understanding the benefit of metformin use in cancer treatment. BMC Med. 2011;9:33.
Hadad SM, Fleming S, Thompson AM. Targeting AMPK: a new therapeutic opportunity in breast cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2008;67(1):1–7.
Hirsch HA, Iliopoulos D, Tsichlis PN, Struhl K. Metformin selectively targets cancer stem cells, and acts together with chemotherapy to block tumor growth and prolong remission. Cancer Res. 2009;69(19):7507–11.
Iliopoulos D, Hirsch HA, Struhl K. Metformin decreases the dose of chemotherapy for prolonging tumor remission in mouse xenografts involving multiple cancer cell types. Cancer Res. 2011;71(9):3196–201.
Currie CJ, Poole CD, Gale EA. The influence of glucose-lowering therapies on cancer risk in type 2 diabetes. Diabetologia. 2009;52(9):1766–77.
Libby G, Donnelly LA, Donnan PT, Alessi DR, Morris AD, Evans JM. New users of metformin are at low risk of incident cancer: a cohort study among people with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2009;32(9):1620–5.
Bodmer M, Meier C, Krahenbuhl S, Jick SS, Meier CR. Long-term metformin use is associated with decreased risk of breast cancer. Diabetes Care. 2010;33(6):1304–8.
Bonanni B, Puntoni M, Cazzaniga M, Pruneri G, Serrano D, Guerrieri-Gonzaga A, Gennari A, Trabacca MS, Galimberti V, Veronesi P, et al. Dual effect of metformin on breast cancer proliferation in a randomized presurgical trial. J Clin Oncol. 2012;30(21):2593–600.
Hadad S, Iwamoto T, Jordan L, Purdie C, Bray S, Baker L, Jellema G, Deharo S, Hardie DG, Pusztai L, et al. Evidence for biological effects of metformin in operable breast cancer: a pre-operative, window-of-opportunity, randomized trial. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;128(3):783–94.
Niraula S, Dowling RJ, Ennis M, Chang MC, Done SJ, Hood N, Escallon J, Leong WL, McCready DR, Reedijk M, et al. Metformin in early breast cancer: a prospective window of opportunity neoadjuvant study. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2012;135(3):821–30.
Jiralerspong S, Palla SL, Giordano SH, Meric-Bernstam F, Liedtke C, Barnett CM, Hsu L, Hung MC, Hortobagyi GN, Gonzalez-Angulo AM. Metformin and pathologic complete responses to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in diabetic patients with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27(20):3297–302.
Goodwin PJ, Stambolic V, Lemieux J, Chen BE, Parulekar WR, Gelmon KA, Hershman DL, Hobday TJ, Ligibel JA, Mayer IA, et al. Evaluation of metformin in early breast cancer: a modification of the traditional paradigm for clinical testing of anti-cancer agents. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2011;126(1):215–20.
Liu B, Fan Z, Edgerton SM, Deng XS, Alimova IN, Lind SE, Thor AD. Metformin induces unique biological and molecular responses in triple negative breast cancer cells. Cell Cycle. 2009;8(13):2031–40.
Stahlberg C, Pedersen AT, Andersen ZJ, Keiding N, Hundrup YA, Obel EB, Moller S, Rank F, Ottesen B, Lynge E. Breast cancer with different prognostic characteristics developing in Danish women using hormone replacement therapy. Br J Cancer. 2004;91(4):644–50.
Borgquist S, Anagnostaki L, Jirstrom K, Landberg G, Manjer J. Breast tumours following combined hormone replacement therapy express favourable prognostic factors. Int J Cancer. 2007;120(10):2202–7.
Berstein LM, Boyarkina MP, Tsyrlina EV, Turkevich EA, Semiglazov VF. More favorable progesterone receptor phenotype of breast cancer in diabetics treated with metformin. Med Oncol. 2011;28(4):1260–3.
Parulekar WCB, Elliott C, Shepherd LE, Gelmon KA, Pritchard KI, Whelan TJ, Ligibel JA, Hershman DL, Mayer IA, Hobday TJ, Rastogi P, Lemieux J, Ganz PA, Stambolic V, Goodwin PJ. A phase III randomized trial of metformin versus placebo on recurrence and survival in early-stage breast cancer (BC) (NCIC Clinical Trials Group MA.32). J Clin Oncol. 2011;29(suppl; abstr TPS103).
Conflict of interest
The authors indicated no potential conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Aksoy, S., Sendur, M.A.N. & Altundag, K. Demographic and clinico-pathological characteristics in patients with invasive breast cancer receiving metformin. Med Oncol 30, 590 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0590-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12032-013-0590-z