Abstract
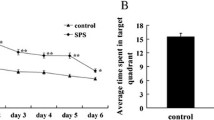
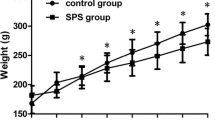
Apoptosis of hippocampal neurons is one of the mechanisms of hippocampal atrophy in posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD), and it is also an important cause of memory impairment in PTSD patients. Endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS) mediated by activated transcription factor 6α (ATF6α)/site 1 protease (S1P)/S2P is involved in cell apoptosis, but it is not clear whether it is involved in hippocampal neuron apoptosis caused by PTSD. A PTSD rat model was constructed by the single prolonged stress (SPS) method. The study was divided into three parts. Experiment 1 included the control group, SPS 1 d group, SPS 7 d group, and SPS 14 d group. Experiment 2 included the control group, SPS 7 d group, SPS 7 d + AEBSF group, and control + AEBSF group. (4-(2-Aminoethyl)benzenesulfonyl fluoride hydrochloride (AEBSF) is an ATF6α pathway inhibitor). Experiment 3 included the control group, SPS 4 d group, SPS 4 d + AEBSF group, and control + AEBSF group. The protein and mRNA expression levels of ATF6α, glucose-regulated protein (GRP78), S1P, S2P, C/EBP homologous protein (CHOP), and caspase-12 in the hippocampus of PTSD rats were detected by immunohistochemistry, Western blotting and qRT-PCR. Apoptosis of hippocampal neurons was detected by TUNEL staining. In experiment 1, the protein and mRNA expression of ATF6α and GRP78 increased gradually in the SPS 1 d group and the SPS 7 d group but decreased in the SPS 14 d group (P < 0.01). In experiment 2, compared with that in the control group, the protein and mRNA expression of ATF6α, GRP78, S1P, S2P, CHOP, and caspase-12 and the apoptosis rate were significantly increased in the SPS 7 d group (P < 0.01). However, the protein and mRNA expression of ATF6α, GRP78, S1P, S2P, CHOP, and caspase-12 and the apoptosis rate were significantly decreased after AEBSF pretreatment (P < 0.01). In experiment 3, compared with that in the control group, the protein and mRNA expression of ATF6α, GRP78, S1P, S2P, CHOP, and caspase-12 and the apoptosis rate were increased in the SPS 14 d group (P < 0.05). However, the protein and mRNA expression of ATF6α, GRP78, S1P, S2P, CHOP, and caspase-12 and the apoptosis rate were decreased after AEBSF pretreatment (P < 0.05). SPS induced apoptosis of hippocampal neurons by activating ERS mediated by ATF6α, suggesting that ERS-induced apoptosis is involved in the occurrence of PTSD.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Apfel BA, Ross J, Hlavin J, Meyerhoff DJ, Metzler TJ, Marmar CR, Weiner MW, Schuff N, Neylan TC (2011) Hippocampal volume differences in Gulf War veterans with current versus lifetime posttraumatic stress disorder symptoms. Biol Psychiatry 69(6):541–548. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2010.09.044
Ardic S, Gumrukcu A, Gonenc Cekic O, Erdem M, Reis Kose GD, Demir S, Kose B, Yulug E, Mentese A, Turedi S (2019) The value of endoplasmic reticulum stress markers (GRP78 and CHOP) in the diagnosis of acute mesenteric ischemia. Am J Emerg Med 37(4):596–602. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2018.06.033
Cassimeris L, Engiles JB, Galantino-Homer H (2019) Detection of endoplasmic reticulum stress and the unfolded protein response in naturally-occurring endocrinopathic equine laminitis. BMC Vet Res 15(1):24. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12917-018-1748-x
Chen F, Jin J, Hu J, Wang Y, Ma Z, Zhang J (2019) Endoplasmic reticulum stress cooperates in silica nanoparticles-induced macrophage apoptosis via activation of CHOP-mediated apoptotic signaling pathway. Int J Mol Sci 20(23):5846. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235846
Chen X, Jiang Y, Wang J, Liu Y, Xiao M, Song C, Bai Y, Yinuo Han N, Han F (2020) Synapse impairment associated with enhanced apoptosis in post-traumatic stress disorder. Synapse 74(2):e22134. https://doi.org/10.1002/syn.22134
Chung YW, Chung MW, Choi SK, Choi SJ, Choi SJN, Chung SY (2018) Tacrolimus-induced apoptosis is mediated by endoplasmic reticulum-derived calcium-dependent caspases-3,-12 in Jurkat cells. Transplant Proc 50(4):1172–1177. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2018.01.050
Fan F, Zhang Y, Yang Y, Mo L, Liu X (2011) Symptoms of posttraumatic stress disorder, depression, and anxiety among adolescents following the 2008 Wenchuan earthquake in China. J Trauma Stress 24(1):44–53. https://doi.org/10.1002/jts.20599
Fan H, Li M, Shen Z, Jiang C, Cui X, Wang M, Zhou J, Sun Y, Li S, Wang Y (2020) [Effects of curcumin on protein expression of glucose regulated protein 78 and caspase-12 of myocardial endoplasmic reticulum stress related factors in type 2 diabetes rats]. Wei Sheng Yan Jiu 49(1):98–131. https://doi.org/10.19813/j.cnki.weishengyanjiu.2020.01.017
Feng J, Chen Y, Lu B, Sun X, Zhu H, Sun X (2019) Autophagy activated via GRP78 to alleviate endoplasmic reticulum stress for cell survival in blue light-mediated damage of A2E-laden RPEs. BMC Ophthalmol 19(1):249. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12886-019-1261-4
Gao HH, Li JT, Liu JJ, Yang QA, Zhang JM (2017) Autophagy inhibition of immature oocytes during vitrification-warming and in vitro mature activates apoptosis via caspase-9 and -12 pathway. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 217:89–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejogrb.2017.08.029
Hetz C, Saxena S (2017) ER stress and the unfolded protein response in neurodegeneration. Nat Rev Neurol 13(8):477–491. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2017.99
Hines LA, Sundin J, Rona RJ, Wessely S, Fear NT (2014) Posttraumatic stress disorder post Iraq and Afghanistan: prevalence among military subgroups. Can J Psychiatry 59(9):468–479. https://doi.org/10.1177/070674371405900903
Ibrahim IM, Abdelmalek DH, Elfiky AA (2019) GRP78: A cell's response to stress. Life Sci 226:156–163. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2019.04.022
Joshi SA, Duval ER, Kubat B, Liberzon I (2020) A review of hippocampal activation in post-traumatic stress disorder. Psychophysiology 57(1):e13357. https://doi.org/10.1111/psyp.13357
Kim HS, Kim Y, Lim MJ, Park YG, Park SI, Sohn J (2019) The p38-activated ER stress-ATF6α axis mediates cellular senescence. FASEB J 33(2):2422–2434. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201800836R
La X, Zhang L, Li Z, Yang P, Wang Y (2017) Berberine-induced autophagic cell death by elevating GRP78 levels in cancer cells. Oncotarget 8(13):20909–20924. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.14959
Lee YS, Lee DH, Choudry HA, Bartlett DL, Lee YJ (2018) Ferroptosis-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress: cross-talk between ferroptosis and apoptosis. Mol Cancer Res 16(7):1073–1076. https://doi.org/10.1158/1541-7786.Mcr-18-0055
Lei Y, Wang S, Ren B, Wang J, Chen J, Lu J, Zhan S, Fu Y, Huang L, Tan J (2017) CHOP favors endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced apoptosis in hepatocellular carcinoma cells via inhibition of autophagy. PLoS One 12(8):e0183680. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0183680
Lisieski MJ, Eagle AL, Conti AC, Liberzon I, Perrine SA (2018) Single-prolonged stress: a review of two decades of progress in a rodent model of post-traumatic stress disorder. Front Psych 9:196. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyt.2018.00196
Lu HY, Chen XQ, Tang W, Wang QX, Zhang J (2017) GRP78 silencing enhances hyperoxia-induced alveolar epithelial cell apoptosis via CHOP pathway. Mol Med Rep 16(2):1493–1501. https://doi.org/10.3892/mmr.2017.6681
Martelli AM, Paganelli F, Chiarini F, Evangelisti C, McCubrey JA (2020) The unfolded protein response: a novel therapeutic target in acute leukemias. Cancers (Basel) 12(2). https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers12020333
Milani AC, Hoffmann EV, Fossaluza V, Jackowski AP, Mello MF (2017) Does pediatric post-traumatic stress disorder alter the brain? Systematic review and meta-analysis of structural and functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 71(3):154–169. https://doi.org/10.1111/pcn.12473
Moriguchi M, Watanabe T, Fujimuro M (2019) Capsaicin induces ATF4 translation with upregulation of CHOP, GADD34 and PUMA. Biol Pharm Bull 42(8):1428–1432. https://doi.org/10.1248/bpb.b19-00303
Moyer A (2016) Post-traumatic stress disorder and magnetic resonance imaging. Radiol Technol 87(6):649–667
Nisar S, Bhat AA, Hashem S, Syed N, Yadav SK, Uddin S, Fakhro K, Bagga P, Thompson P, Reddy R, Frenneaux MP, Haris M (2020) Genetic and neuroimaging approaches to understanding post-traumatic stress disorder. Int J Mol Sci 21(12). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21124503
Oka OB, van Lith M, Rudolf J, Tungkum W, Pringle M A, Bulleid NJ (2019) ERp18 regulates activation of ATF6α during unfolded protein response. Embo j 38(15):e100990. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.2018100990
Okada T, Haze K, Nadanaka S, Yoshida H, Seidah NG, Hirano Y, Sato R, Negishi M, Mori K (2003) A serine protease inhibitor prevents endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced cleavage but not transport of the membrane-bound transcription factor ATF6. J Biol Chem 278(33):31024–31032. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M300923200
Poone GK, Hasseldam H, Munkholm N, Rasmussen RS, Grønberg NV, Johansen FF (2015) The hypothermic influence on CHOP and Ero1-α in an endoplasmic reticulum stress model of cerebral ischemia. Brain Sci 5(2):178–187. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci5020178
Qi W, Gevonden M, Shalev A (2016) Prevention of post-traumatic stress disorder after trauma: current evidence and future directions. Curr Psychiatry Rep 18(2):20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11920-015-0655-0
Shan W, Han F, Xu Y, Shi Y (2020) Stathmin regulates spatiotemporal variation in the memory loop in single-prolonged stress rats. J Mol Neurosci 70(4):576–589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-019-01459-w
Sharma RB, Snyder JT, Alonso LC (2019) Atf6α impacts cell number by influencing survival, death and proliferation. Mol Metab 27s(Suppl):S69-s80. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molmet.2019.06.005
Sin J, Spain D, Furuta M, Murrells T, Norman I (2017) Psychological interventions for post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) in people with severe mental illness. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 1(1):Cd011464. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011464.pub2
Sisinni L, Pietrafesa M, Lepore S, Maddalena F, Condelli V, Esposito F, Landriscina M (2019) Endoplasmic reticulum stress and unfolded protein response in breast cancer: the balance between apoptosis and autophagy and its role in drug resistance. Int J Mol Sci 20(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20040857
Song J, Zhang Q, Wang S, Yang F, Chen Z, Dong Q, Ji Q, Yuan X, Ren D (2018) Cleavage of caspase-12 at Asp94, mediated by endoplasmic reticulum stress (ERS), contributes to stretch-induced apoptosis of myoblasts. J Cell Physiol 233(12):9473–9487. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26840
Stauffer WT, Arrieta A, Blackwood EA, Glembotski CC (2020) Sledgehammer to scalpel: broad challenges to the heart and other tissues yield specific cellular responses via transcriptional regulation of the ER-stress master regulator ATF6α. Int J Mol Sci 21(3). https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms21031134
Wan S, Jiang L (2016) Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress and the unfolded protein response (UPR) in plants. Protoplasma 253(3):753–764. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00709-015-0842-1
Xu W, Gao L, Li T, Zheng J, Shao A, Zhang J (2018a) Apelin-13 alleviates early brain injury after subarachnoid hemorrhage via suppression of endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated apoptosis and blood-brain barrier disruption: possible involvement of ATF6/CHOP pathway. Neuroscience 388:284–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.07.023
Xu W, Lu X, Zheng J, Li T, Gao L, Lenahan C, Shao A, Zhang J, Yu J (2018b) Melatonin protects against neuronal apoptosis via suppression of the ATF6/CHOP pathway in a rat model of intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Neurosci 12:638. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2018.00638
Xu X, Lai Y, Hua ZC (2019) Apoptosis and apoptotic body: disease message and therapeutic target potentials. Biosci Rep 39(1). https://doi.org/10.1042/bsr20180992
Yamamoto S, Morinobu S, Takei S, Fuchikami M, Matsuki A, Yamawaki S, Liberzon I (2009) Single prolonged stress: toward an animal model of posttraumatic stress disorder. Depress Anxiety 26(12):1110–1117. https://doi.org/10.1002/da.20629
Yu B, Wen L, Xiao B, Han F, Shi Y (2014) Single prolonged stress induces ATF6 alpha-dependent endoplasmic reticulum stress and the apoptotic process in medial frontal cortex neurons. BMC Neurosci 15:115. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12868-014-0115-5
Yu Y, Yu R, Men W, Zhang P, Zhang Y, Song L, Zhou K (2020) Psoralen induces hepatic toxicity through PERK and ATF6 related ER stress pathways in HepG2 cells. Toxicol Mech Methods 30(1):39–47. https://doi.org/10.1080/15376516.2019.1650150
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to all staff members of the China Medical University Experiment Center for their technical support.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the China National Natural Science Foundation (81571324) and the Science and Technology Project of Liao Ning Province, China (2017225011).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yanhao Xu and Yuxiu Shi contributed to the conception of the study and helped perform the analysis with constructive discussion. Liang han performed the experiment; contributed significantly to analysis and manuscript preparation; performed the data analyses, and wrote the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics Approval and Consent to Participate
The animal experiments were performed according to protocols approved by the Ethical Committee of Animal Research at the China Medical University, and all efforts were made to minimize the number of animals used and their suffering. All study participants provided informed consent, and the study design was approved by the appropriate ethics review board.
Competing Interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Han, L., Xu, Y. & Shi, Y. Molecular Mechanism of the ATF6α/S1P/S2P Signaling Pathway in Hippocampal Neuronal Apoptosis in SPS Rats. J Mol Neurosci 71, 2487–2499 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01823-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-021-01823-9