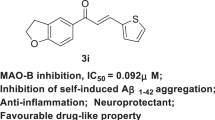
Abstract
Neurodegenerative disorders are one of the leading causes of death among the elderly. Therapeutic approaches with a single target have proven unsuccessful in treating these diseases. Structural combination of multi-functional compounds may lead to a molecule with multiple properties. In this study, we designed and synthesized T-006, a novel analog derived from two multi-functional neuroprotective chemicals, tetramethylpyrazine and J147. The methoxyphenyl group of J147 was replaced by tetramethylpyrazine. Bioactivity evaluation showed that T-006 at very low concentrations had multi-functional neuroprotective effects including rescuing iodoacetic acid-induced neuronal loss, preventing oxidative stress-induced neurotoxicity and reducing glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in vitro. Most importantly, T-006 significantly ameliorated memory impairments in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. These multiple functions of a single molecule suggest that T-006 is a promising novel neuroprotective agent for treating various neurodegenerative disorders, including and in particular Alzheimer’s disease.








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- TMP:
-
Tetramethylpyrazine
- CGNs:
-
Cerebellar granule neurons
- PC12:
-
Pheochromocytoma cell
- DIV:
-
Days in vitro
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- RNS:
-
Reactive nitrogen species
- IAA:
-
Iodoacetic acid
References
Aliev G, Obrenovich ME, Smith MA, Perry G (2003) Hypoperfusion, mitochondria failure, oxidative stress, and Alzheimer disease. J Biomed Biotechnol 2003:162–163
Ballard C, Gauthier S, Corbett A et al (2011) Alzheimer’s disease. Lancet 377:1019–1031
Cao K, Chen-Plotkin AS, Plotkin JB, Wang LS (2010) Age-correlated gene expression in normal and neurodegenerative human brain tissues. PLoS One 5:e13098
Chen Q, Prior M, Dargusch R et al (2011) A novel neurotrophic drug for cognitive enhancement and Alzheimer’s disease. PLoS One 6:e27865
Chiruta C, Zhao Y, Tang F, Wang T, Schubert D (2013) Metabolism of a potent neuroprotective hydrazide. Bioorg Med Chem 21:2733–2741
Citron M (2010) Alzheimer’s disease: strategies for disease modification. Nat Rev Drug Discov 9:387–398
Corbyn Z (2013) New set of Alzheimer’s trials focus on prevention. Lancet 381:614–615
Cui G, Shan L, Hung M et al (2013a) A novel Danshensu derivative confers cardioprotection via PI3K/Akt and Nrf2 pathways. Int J Cardiol 168:1349–1359
Cui W, Zhang Z, Li W et al (2013b) The anti-cancer agent SU4312 unexpectedly protects against MPP(+)-induced neurotoxicity via selective and direct inhibition of neuronal NOS. Br J Pharmacol 168:1201–1214
Fu H, Li W, Lao Y et al (2006) Bis(7)-tacrine attenuates beta amyloid-induced neuronal apoptosis by regulating L-type calcium channels. J Neurochem 98:1400–1410
Hu JZ, Huang JH, Xiao ZM et al (2013) Tetramethylpyrazine accelerates the function recovery of traumatic spinal cord in rat model by attenuating inflammation. J Neurol Sci 324:94–99
Jankowsky JL, Younkin LH, Gonzales V et al (2007) Rodent A beta modulates the solubility and distribution of amyloid deposits in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 282:22707–22720
Jove M, Portero-Otin M, Naudi A, Ferrer I, Pamplona R (2014) Metabolomics of human brain aging and age-related neurodegenerative diseases. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 73:640–657
Koehn FE, Carter GT (2005) The evolving role of natural products in drug discovery. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:206–220
Lin MT, Beal MF (2006) Mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. Nature 443:787–795
Liu Y, Dargusch R, Maher P, Schubert D (2008) A broadly neuroprotective derivative of curcumin. J Neurochem 105:1336–1345
Luo J, Li W, Zhao Y et al (2010) Pathologically activated neuroprotection via uncompetitive blockade of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors with fast off-rate by novel multifunctional dimer bis(propyl)-cognitin. J Biol Chem 285:19947–19958
Lv C, Liu X, Liu H, Chen T, Zhang W (2014) Geniposide attenuates mitochondrial dysfunction and memory deficits in APP/PS1 transgenic mice. Curr Alzheimer Res 11:580–587
Marx J (2006) Neurodegenerative diseases. Picking apart the causes of mysterious dementias. Science 314:42–43
Moreira PI, Nunomura A, Nakamura M et al (2008) Nucleic acid oxidation in Alzheimer disease. Free Radic Biol Med 44:1493–1505
Ng LF, Gruber J, Cheah IK et al (2014) The mitochondria-targeted antioxidant MitoQ extends lifespan and improves healthspan of a transgenic Caenorhabditis elegans model of Alzheimer disease. Free Radic Biol Med 71:390–401
Prior M, Dargusch R, Ehren JL, Chiruta C, Schubert D (2013) The neurotrophic compound J147 reverses cognitive impairment in aged Alzheimer’s disease mice. Alzheimers Res Ther 5:25
Radi E, Formichi P, Battisti C, Federico A (2014) Apoptosis and oxidative stress in neurodegenerative diseases. J Alzheimers Dis 42:S125–152
Sun Y, Jiang J, Zhang Z et al (2008) Antioxidative and thrombolytic TMP nitrone for treatment of ischemic stroke. Bioorg Med Chem 16:8868–8874
Suna H, Arai M, Tsubotani Y et al (2009) Dysideamine, a new sesquiterpene aminoquinone, protects hippocampal neuronal cells against iodoacetic acid-induced cell death. Bioorg Med Chem 17:3968–3972
Xu DP, Duan HW, Zhang ZJ et al (2014a) The novel tetramethylpyrazine bis-nitrone (TN-2) protects against MPTP/MPP+-induced neurotoxicity via inhibition of mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis. J Neuroimmune Pharmacol 9:245–258
Xu DP, Zhang K, Zhang ZJ et al (2014b) A novel tetramethylpyrazine bis-nitrone (TN-2) protects against 6-hydroxyldopamine-induced neurotoxicity via modulation of the NF-kappaB and the PKCalpha/PI3-K/Akt pathways. Neurochem Int 78C:76–85
Ye J, Lin H, Mu J et al (2010) Effect of basic fibroblast growth factor on hippocampal cholinergic neurons in a rodent model of ischaemic encephalopathy. Basic Clin Pharmacol Toxicol 107:931–939
Zhu X, Raina AK, Lee HG et al (2004) Oxidative stress signalling in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Res 1000:32–39
Zolezzi JM, Silva-Alvarez C, Ordenes D et al (2013) Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR) gamma and PPARalpha agonists modulate mitochondrial fusion-fission dynamics: relevance to reactive oxygen species (ROS)-related neurodegenerative disorders? PLoS One 8:e64019
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by grants from the China “12.5” Innovative Drug Project (2012ZX09103-101-055), the 2012 Hong Kong Scholars Program (122870), the China Postdoctoral Science Foundation (2012T50748 and 2013M531911), the Research Grants Council of Hong Kong (561011, 15101014), and the Hong Kong Polytechnic University (G-U952, G-YM32, G-SB10, and G-YZ15). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript. We sincerely thank Ms. Josephine Leung for proofreading our manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Hai-Yun Chen and Da-Ping Xu contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, HY., Xu, DP., Tan, GL. et al. A Potent Multi-functional Neuroprotective Derivative of Tetramethylpyrazine. J Mol Neurosci 56, 977–987 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0566-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-015-0566-x