Abstract
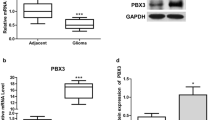
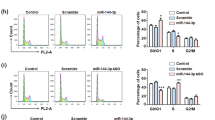
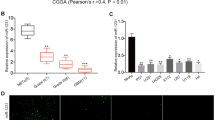
Substantial evidence indicates that the human ether-a-go-go-related gene potassium channel (hERG, Kv11.1, KCNH2) is overexpressed in human glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) specimens and plays an essential role in the malignant proliferation of glioma cells. However, its upstream regulator in glioma cells is not fully elucidated. The present study was designed to determine whether the expression of hERG gene is regulated by miR-133b or miR-34a, thereby contributing to the anti-proliferation effect of arsenic trioxide (ATO) in U251 human glioma cells. Real-time polymerase chain reactions (qRT-PCR) and Western blot results demonstrated that hERG mRNA and protein levels were dramatically upregulated in clinical GBM specimens. Conversely, both miR-133b and miR-34a were markedly downregulated in clinical GBM specimens by qRT-PCR. The hERG gene was a direct target of miR-133b and miR-34a by bioinformatics analyses and luciferase reporter assays. Moreover, ATO, which is an emerging chemotherapy drug for glioma disease, remarkably elevated the level of miR-133b, but not miR-34a in U251 glioma cells. The level of miR-133b upstream transactivator serum response factor (SRF) was also suppressed by ATO. The transfection of anti-miR-133b oligonucleotide (AMO-133b) remarkably prevented the decrease of hERG protein by 5 μM ATO treatment for 24 h in U251 cells, whereas anti-miR-34a oligonucleotide (AMO-34a) did not exhibit recuperated effect. Finally, the transient overexpression by miR-133b mimics and treatment with the hERG channel-specific blocker E4031 markedly facilitated the ATO inhibition of proliferation of and induced apoptosis in U251 cells, whereas AMO-miR-133b attenuated these changes. Our study provided the evidence for the pathological role of miR-133b and miR-34a in the development of GBM and thus expanded our understanding of the hERG gene expression and ATO chemotherapeutic roles of miRNAs. Targeting miR-133b/hERG pathway may be a new strategy for chemotherapy of malignant gliomas.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asher V, Sowter H, Shaw R, Bali A, Khan R (2010) Eag and HERG potassium channels as novel therapeutic targets in cancer. World J Surg Oncol 8:113
Asher V, Warren A, Shaw R, Sowter H, Bali A, Khan R (2011) The role of Eag and HERG channels in cell proliferation and apoptotic cell death in SK-OV-3 ovarian cancer cell line. Cancer Cell Int 11:6
Bai Y, Liao H, Liu T, Zeng X, Xiao F, Luo L, Guo H, Guo L (2013) MiR-296-3p regulates cell growth and multi-drug resistance of human glioblastoma by targeting ether-a-go-go (EAG1). Eur J Cancer 49:710–724
Chu W, Li C, Qu X, Zhao D, Wang X, Yu X, Cai F, Liang H, Zhang Y, Zhao X, Li B, Qiao G, Dong D, Lu Y, Du Z, Yang B (2012) Arsenic-induced interstitial myocardial fibrosis reveals a new insight into drug-induced long QT syndrome. Cardiovasc Res 96:90–98
Cohen KJ, Gibbs IC, Fisher PG, Hayashi RJ, Macy ME, Gore L (2013) A phase I trial of arsenic trioxide chemoradiotherapy for infiltrating astrocytomas of childhood. Neuro Oncol 15:783–787
Ficker E, Kuryshev YA, Dennis AT, Obejero-Paz C, Wang L, Hawryluk P, Wible BA, Brown AM (2004) Mechanisms of arsenic-induced prolongation of cardiac repolarization. Mol Pharmacol 66:33–44
Gonzalez-Juanatey JR, Iglesias MJ, Alcaide C, Pineiro R, Lago F (2003) Doxazosin induces apoptosis in cardiomyocytes cultured in vitro by a mechanism that is independent of alpha1-adrenergic blockade. Circulation 107:127–131
Grimm SA, Marymont M, Chandler JP, Muro K, Newman SB, Levy RM, Jovanovic B, McCarthy K, Raizer JJ (2012) Phase I study of arsenic trioxide and temozolomide in combination with radiation therapy in patients with malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol 110:237–243
He JH, Li YM, Li YG, Xie XY, Wang L, Chun SY, Cheng WJ (2013) hsa-miR-203 enhances the sensitivity of leukemia cells to arsenic trioxide. Exp Ther Med 5:1315–1321
Ivey KN, Muth A, Arnold J, King FW, Yeh RF, Fish JE, Hsiao EC, Schwartz RJ, Conklin BR, Bernstein HS, Srivastava D (2008) MicroRNA regulation of cell lineages in mouse and human embryonic stem cells. Cell Stem Cell 2:219–229
Kanzawa T, Zhang L, Xiao L, Germano IM, Kondo Y, Kondo S (2005) Arsenic trioxide induces autophagic cell death in malignant glioma cells by upregulation of mitochondrial cell death protein BNIP3. Oncogene 24:980–991
Koshkin PA, Chistiakov DA, Chekhonin VP (2013) Role of microRNAs in mechanisms of glioblastoma resistance to radio- and chemotherapy. Biochemistry (Mosc) 78:325–334
Li Y, Guessous F, Zhang Y, Dipierro C, Kefas B, Johnson E, Marcinkiewicz L, Jiang J, Yang Y, Schmittgen TD, Lopes B, Schiff D, Purow B, Abounader R (2009) MicroRNA-34a inhibits glioblastoma growth by targeting multiple oncogenes. Cancer Res 69:7569–7576
Lin H, Li Z, Chen C, Luo X, Xiao J, Dong D, Lu Y, Yang B, Wang Z (2011) Transcriptional and post-transcriptional mechanisms for oncogenic overexpression of ether a go-go K + channel. PLoS One 6:e20362
Liu L, Shao X, Gao W, Zhang Z, Liu P, Wang R, Huang P, Yin Y, Shu Y (2012) MicroRNA-133b inhibits the growth of non-small-cell lung cancer by targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor. FEBS J 279:3800–3812
Luan S, Sun L, Huang F (2010) MicroRNA-34a: a novel tumor suppressor in p53-mutant glioma cell line U251. Arch Med Res 41:67–74
Masi A, Becchetti A, Restano-Cassulini R, Polvani S, Hofmann G, Buccoliero AM, Paglierani M, Pollo B, Taddei GL, Gallina P, Di Lorenzo N, Franceschetti S, Wanke E, Arcangeli A (2005) hERG1 channels are overexpressed in glioblastoma multiforme and modulate VEGF secretion in glioblastoma cell lines. Br J Cancer 93:781–792
Patil SA, Hosni-Ahmed A, Jones TS, Patil R, Pfeffer LM, Miller DD (2013) Novel approaches to glioma drug design and drug screening. Expert Opin Drug Discov 8:1135–1151
Patron JP, Fendler A, Bild M, Jung U, Muller H, Arntzen MO, Piso C, Stephan C, Thiede B, Mollenkopf HJ, Jung K, Kaufmann SH, Schreiber J (2012) MiR-133b targets antiapoptotic genes and enhances death receptor-induced apoptosis. PLoS One 7:e35345
Primon M, Huszthy PC, Motaln H, Talasila KM, Torkar A, Bjerkvig R, Lah Turnsek T (2013) Cathepsin L silencing enhances arsenic trioxide mediated in vitro cytotoxicity and apoptosis in glioblastoma U87MG spheroids. Exp Cell Res 319:2637–2648
Qin W, Dong P, Ma C, Mitchelson K, Deng T, Zhang L, Sun Y, Feng X, Ding Y, Lu X, He J, Wen H, Cheng J (2012) MicroRNA-133b is a key promoter of cervical carcinoma development through the activation of the ERK and AKT1 pathways. Oncogene 31:4067–4075
Shan H, Zhang Y, Cai B, Chen X, Fan Y, Yang L, Chen X, Liang H, Zhang Y, Song X, Xu C, Lu Y, Yang B, Du Z (2013) Upregulation of microRNA-1 and microRNA-133 contributes to arsenic-induced cardiac electrical remodeling. Int J Cardiol 167:2798–2805
Silber J, Lim DA, Petritsch C, Persson AI, Maunakea AK, Yu M, Vandenberg SR, Ginzinger DG, James CD, Costello JF, Bergers G, Weiss WA, Alvarez-Buylla A, Hodgson JG (2008) miR-124 and miR-137 inhibit proliferation of glioblastoma multiforme cells and induce differentiation of brain tumor stem cells. BMC Med 6:14
Villar AV, Merino D, Wenner M, Llano M, Cobo M, Montalvo C, Garcia R, Martin-Duran R, Hurle JM, Hurle MA, Nistal JF (2011) Myocardial gene expression of microRNA-133a and myosin heavy and light chains, in conjunction with clinical parameters, predict regression of left ventricular hypertrophy after valve replacement in patients with aortic stenosis. Heart 97:1132–1137
Wang Y, Jiang T (2013) Understanding high grade glioma: molecular mechanism, therapy and comprehensive management. Cancer Lett 331:139–146
Wu Y, Li XF, Yang JH, Liao XY, Chen YZ (2012) microRNAs expression profile in acute promyelocytic leukemia cell differentiation induced by all-trans retinoic acid and arsenic trioxide. Zhonghua Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi 33:546–551
Xin H, Li Y, Buller B, Katakowski M, Zhang Y, Wang X, Shang X, Zhang ZG, Chopp M (2012) Exosome-mediated transfer of miR-133b from multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells to neural cells contributes to neurite outgrowth. Stem Cells 30:1556–1564
Xin H, Li Y, Liu Z, Wang X, Shang X, Cui Y, Gang Zhang Z, Chopp M (2013) Mir-133b Promotes Neural Plasticity and Functional Recovery after Treatment of Stroke with Multipotent Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Rats Via Transfer of Exosome-Enriched Extracellular Particles. Stem Cells
Zhang Y, Xiao J, Wang H, Luo X, Wang J, Villeneuve LR, Zhang H, Bai Y, Yang B, Wang Z (2006) Restoring depressed HERG K + channel function as a mechanism for insulin treatment of abnormal QT prolongation and associated arrhythmias in diabetic rabbits. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 291:H1446–H1455
Zhao H, Lai F, Nonn L, Brooks JD, Peehl DM (2005) Molecular targets of doxazosin in human prostatic stromal cells. Prostate 62:400–410
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 Program, 2012AA02A508) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81372700).
Conflict of Interest
The authors have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, J., Li, Y. & Jiang, C. MiR-133b Contributes to Arsenic-Induced Apoptosis in U251 Glioma Cells by Targeting the hERG Channel. J Mol Neurosci 55, 985–994 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0455-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0455-8