Abstract
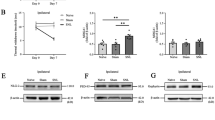
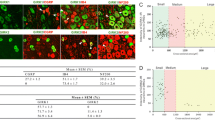
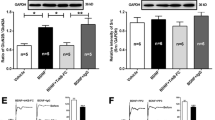
N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion (NSF) protein is a homohexameric ATPase that binds to the GluR2 subunit of α-amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazoleproprionic acid (AMPA) receptors. The stability and movement of AMPA receptors at synapses are important factors that control synaptic strength. NSF is involved in the surface expression regulation of AMPA receptors and consequently synaptic activity. Reduced expression of NSF or reduced interaction of NSF with GluR2 leads to a number of neurological disorders. Using a rat model of L5 spinal nerve ligation (SNL), we investigated the temporal and spatial expression of NSF in injured L5 and uninjured L4 dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons during mechanical allodynia. L5 SNL led to a significant decrease of NSF in both L4 and L5 DRGs observed at 3, 7, and 14 days after injury. In particular, NSF expression in calcitonin gene-related peptide (CGRP)-immunoreactive (IR) and IB4-IR neurons was reduced, whereas NSF expression in NF-200-IR neurons remained unaltered. These results indicate a role for NSF in CGRP-IR and IB4-IR neurons in SNL, with reduced NSF expression possibly contributing to SNL derived neuropathic pain.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry MF, Ziff EB (2002) Receptor trafficking and the plasticity of excitatory synapses. Curr Opin Neurobiol 12:279–286
Chaplan SR, Bach FW, Pogrel JW, Chung JM, Yaksh TL (1994) Quantitative assessment of tactile allodynia in the rat paw. J Neurosci Methods 53:55–63
Dixon WJ (1980) Efficient analysis of experimental observations. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 20:441–462
Engle MP, Gassman M, Sykes KT, Bettler B, Hammond DL (2006) Spinal nerve ligation does not alter the expression or function of GABA(B) receptors in spinal cord and dorsal root ganglia of the rat. Neuroscience 138:1277–1287
Engle MP, Merrill MA, Marquez De Prado B, Hammond DL (2012) Spinal nerve ligation decreases gamma-aminobutyric acidB receptors on specific populations of immunohistochemically identified neurons in L5 dorsal root ganglion of the rat. J Comp Neurol 520:1663–1677
Fukuoka T, Tokunaga A, Kondo E, Miki K, Tachibana T, Noguchi K (1998) Change in mRNAs for neuropeptides and the GABA(A) receptor in dorsal root ganglion neurons in a rat experimental neuropathic pain model. Pain 78:13–26
Fukuoka T, Kondo E, Dai Y, Hashimoto N, Noguchi K (2001) Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases in the uninjured dorsal root ganglion neurons in selective spinal nerve ligation model. J Neurosci 21:4891–4900
Garry EM, Moss A, Rosie R, Delaney A, Mitchell R, Fleetwood-Walker SM (2003) Specific involvement in neuropathic pain of AMPA receptors and adapter proteins for the GluR2 subunit. Mol Cell Neurosci 24:10–22
Ha SO, Kim JK, Hong HS, Kim DS, Cho HJ (2001) Expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rat dorsal root ganglia, spinal cord and gracile nuclei in experimental models of neuropathic pain. Neuroscience 107:301–309
Hartmann B, Ahmadi S, Heppenstall PA, Lewin GR, Schott C, Borchardt T, Seeburg PH, Zeilhofer HU, Sprengel R, Kuner R (2004) The AMPA receptor subunits GluR-A and GluR-B reciprocally modulate spinal synaptic plasticity and inflammatory pain. Neuron 44:637–650
Harvey SC, Koster A, Yu H, Skolnick P, Baumbarger P, Nisenbaum ES (2001) AMPA receptor function is altered in GLUR2-deficient mice. J Mol Neurosci 17:35–43
Hogan Q, Sapunar D, Modric-Jednacak K, McCallum JB (2004) Detection of neuropathic pain in a rat model of peripheral nerve injury. Anesthesiology 101:476–487
Hudson LJ, Bevan S, Wotherspoon G, Gentry C, Fox A, Winter J (2001) VR1 protein expression increases in undamaged DRG neurons after partial nerve injury. Eur J Neurosci 13:2105–2114
Jang JH, Lee BH, Nam TS, Kim JW, Kim DW, Leem JW (2010) Peripheral contributions to the mechanical hyperalgesia following a lumbar 5 spinal nerve lesion in rats. Neuroscience 165:221–232
Joels G, Lamprecht R (2010) Interaction between N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor and GluR2 is essential for fear memory formation in lateral amygdala. J Neurosci 30:15981–15986
Katano T, Furue H, Okuda-Ashitaka E, Tagaya M, Watanabe M, Yoshimura M, Ito S (2008) N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive fusion protein (NSF) is involved in central sensitization in the spinal cord through GluR2 subunit composition switch after inflammation. Eur J Neurosci 27:3161–3170
Kerr RC, Maxwell DJ, Todd AJ (1998) GluR1 and GluR2/3 subunits of the AMPA-type glutamate receptor are associated with particular types of neurone in laminae I-III of the spinal dorsal horn of the rat. Eur J Neurosci 10:324–333
Kim SH, Chung JM (1992) An experimental model for peripheral neuropathy produced by segmental spinal nerve ligation in the rat. Pain 50:355–363
Kuo LT, Tsai SY, Groves MJ, An SF, Scaravilli F (2011) Gene expression profile in rat dorsal root ganglion following sciatic nerve injury and systemic neurotrophin-3 administration. J Mol Neurosci 43:503–515
LaCroix-Fralish ML, Austin JS, Zheng FY, Levitin DJ, Mogil JS (2011) Patterns of pain: meta-analysis of microarray studies of pain. Pain 152:1888–1898
Li Y, Dorsi MJ, Meyer RA, Belzberg AJ (2000) Mechanical hyperalgesia after an L5 spinal nerve lesion in the rat is not dependent on input from injured nerve fibers. Pain 85:493–502
Li H, Zhou Y, Kang L, Ma L (2006) Single and repeated morphine administrations differently regulate expression of N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor gene in the rat brain. Neuroreport 17:71–74
Liu C, Hu B (2004) Alterations of N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive atpase following transient cerebral ischemia. Neuroscience 128:767–774
Lu W, Man H, Ju W, Trimble WS, MacDonald JF, Wang YT (2001) Activation of synaptic NMDA receptors induces membrane insertion of new AMPA receptors and LTP in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neuron 29:243–254
Lu CR, Hwang SJ, Phend KD, Rustioni A, Valtschanoff JG (2002) Primary afferent terminals in spinal cord express presynaptic AMPA receptors. J Neurosci 22:9522–9529
Luthi A, Chittajallu R, Duprat F, Palmer MJ, Benke TA, Kidd FL, Henley JM, Isaac JT, Collingridge GL (1999) Hippocampal LTD expression involves a pool of AMPARs regulated by the NSF-GluR2 interaction. Neuron 24:389–399
Noel J, Ralph GS, Pickard L, Williams J, Molnar E, Uney JB, Collingridge GL, Henley JM (1999) Surface expression of AMPA receptors in hippocampal neurons is regulated by an NSF-dependent mechanism. Neuron 23:365–376
Obara I, Goulding SP, Hu JH, Klugmann M, Worley PF, Szumlinski KK (2013) Nerve injury-induced changes in Homer/glutamate receptor signaling contribute to the development and maintenance of neuropathic pain. Pain 154:1932–1945
Osten P, Srivastava S, Inman GJ, Vilim FS, Khatri L, Lee LM, States BA, Einheber S, Milner TA, Hanson PI, Ziff EB (1998) The AMPA receptor GluR2 C terminus can mediate a reversible, ATP-dependent interaction with NSF and alpha- and beta-SNAPs. Neuron 21:99–110
Park JS, Voitenko N, Petralia RS, Guan X, Xu JT, Steinberg JP, Takamiya K, Sotnik A, Kopach O, Huganir RL, Tao YX (2009) Persistent inflammation induces GluR2 internalization via NMDA receptor-triggered PKC activation in dorsal horn neurons. J Neurosci 29:3206–3219
Sapunar D, Kostic S, Banozic A, Puljak L (2012) Dorsal root ganglion—a potential new therapeutic target for neuropathic pain. J Pain Res 5:31–38
Sato K, Kiyama H, Park HT, Tohyama M (1993) AMPA, KA and NMDA receptors are expressed in the rat DRG neurones. Neuroreport 4:1263–1265
Shi S, Hayashi Y, Esteban JA, Malinow R (2001) Subunit-specific rules governing AMPA receptor trafficking to synapses in hippocampal pyramidal neurons. Cell 105:331–343
Song I, Kamboj S, Xia J, Dong H, Liao D, Huganir RL (1998) Interaction of the N-ethylmaleimide-sensitive factor with AMPA receptors. Neuron 21:393–400
Wang W, Petralia RS, Takamiya K, Xia J, Li YQ, Huganir RL, Tao YX, Yaster M (2011) Preserved acute pain and impaired neuropathic pain in mice lacking protein interacting with C Kinase 1. Mol Pain 7:11
Willcockson H, Valtschanoff J (2008) AMPA and NMDA glutamate receptors are found in both peptidergic and non-peptidergic primary afferent neurons in the rat. Cell Tissue Res 334:17–23
Williams JT, Christie MJ, Manzoni O (2001) Cellular and synaptic adaptations mediating opioid dependence. Physiol Rev 81:299–343
Yamamoto W, Sugiura A, Nakazato-Imasato E, Kita Y (2008) Characterization of primary sensory neurons mediating static and dynamic allodynia in rat chronic constriction injury model. J Pharm Pharmacol 60:717–722
Yin S, Guan Z, Tang Y, Zhao J, Hong J, Zhang W (2005) Abnormal expression of epilepsy-related gene ERG1/NSF in the spontaneous recurrent seizure rats with spatial learning memory deficits induced by kainic acid. Brain Res 1053:195–202
Youn DH, Royle G, Kolaj M, Vissel B, Randic M (2008) Enhanced LTP of primary afferent neurotransmission in AMPA receptor GluR2-deficient mice. Pain 136:158–167
Yu W, Kawasaki F, Ordway RW (2011) Activity-dependent interactions of NSF and SNAP at living synapses. Mol Cell Neurosci 47:19–27
Zhang ET, Ossipov MH, Zhang DQ, Lai J, Porreca F (2007) Nerve injury-induced tactile allodynia is present in the absence of FOS labeling in retrogradely labeled post-synaptic dorsal column neurons. Pain 129:143–154
Acknowledgments
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81000478, 81171053) and Science and Technology Planning Project of Hunan Province, China (2012WK3019).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Zou, Y., Luo, H. et al. Spatiotemporal Changes in NSF Expression of DRG Neurons in a Rat Model of Spinal Nerve Ligation. J Mol Neurosci 53, 645–653 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0231-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-014-0231-9