Abstract
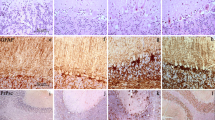
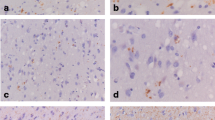
αB-crystallin is a member of the small heat shock protein family constitutively presenting in brains at a relatively low level. To address the alteration of αB-crystallin in prion disease, the αB-crystallin levels in the brains of scrapie agent 263 K-infected hamsters were analyzed. The levels of αB-crystallin were remarkably increased in the brains of 263 K-infected hamsters, showing a time-dependent manner along with incubation time. Immunohistochemical (IHC) and immunofluorescent (IFA) assays illustrated more αB-crystallin-positive signals in the regions of the cortex and thalamus containing severe astrogliosis. Double-stained IFA verified that the αB-crystallin signals colocalized with the enlarged glial fibrillary acidic protein-positive astrocytes, but not with neuronal nuclei-positive cells. IHC and IFA of the serial brain sections of infected hamsters showed no colocalization and correlation between PrPSc deposits and αB-crystallin increase. Moreover, increased αB-crystallin deposits were observed in the brain sections of parietal lobe of a sporadic Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease (sCJD) case, parietal lobe and thalamus of a G114V genetic CJD case, and thalamus of a fatal family insomnia (FFI) case, but not in a parietal lobe of FFI where only very mild astrogliosis was addressed. Additionally, the molecular interaction between αB-crystallin and PrP was only observed in the reactions of recombinant proteins purified from Escherichia coli, but not either in that of brain homogenates or in that of the cultured cell lysates expressing human PrP and αB-crystallin. Our data indicate that brain αB-crystallin is abnormally upregulated in various prion diseases, which is coincidental with astrogliosis. Direct interaction between αB-crystallin and PrP seems not to be essential during the pathogenesis of prion infection.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aoyama A, Steiger RH, Frohli E, Schafer R, von Deimling A, Wiestler OD, Klemenz R (1993) Expression of alpha B-crystallin in human brain tumors. Int J Cancer 55:760–764
Aquilina JA, Benesch JL, Ding LL, Yaron O, Horwitz J, Robinson CV (2004) Phosphorylation of alphaB-crystallin alters chaperone function through loss of dimeric substructure. J Biol Chem 279:28675–28680
Benarroch EE (2011) Heat shock proteins: multiple neuroprotective functions and implications for neurologic disease. Neurology 76:660–667
Ciechanover A, Brundin P (2003) The ubiquitin proteasome system in neurodegenerative diseases: sometimes the chicken, sometimes the egg. Neuron 40:427–446
Collinge J (2001) Prion diseases of humans and animals: their causes and molecular basis. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:519–550
Dehle FC, Ecroyd H, Musgrave IF, Carver JA (2010) alphaB-Crystallin inhibits the cell toxicity associated with amyloid fibril formation by kappa-casein and the amyloid-beta peptide. Cell Stress Chaperones 15:1013–1026
Dong CF, Wang XF, Wang X, Shi S, Wang GR, Shan B, An R, Li XL, Zhang BY, Han J, Dong XP (2008) Molecular interaction between prion protein and GFAP both in native and recombinant forms in vitro. Med Microbiol Immunol 197:361–368
Duguid JR, Rohwer RG, Seed B (1988) Isolation of cDNAs of scrapie-modulated RNAs by subtractive hybridization of a cDNA library. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 85:5738–5742
Ecroyd H, Carver JA (2009) Crystallin proteins and amyloid fibrils. Cell Mol Life Sci 66:62–81
Ecroyd H, Meehan S, Horwitz J, Aquilina JA, Benesch JL, Robinson CV, Macphee CE, Carver JA (2007) Mimicking phosphorylation of alphaB-crystallin affects its chaperone activity. Biochem J 401:129–141
Eng LF, Ghirnikar RS, Lee YL (2000) Glial fibrillary acidic protein: GFAP-thirty-one years (1969–2000). Neurochem Res 25:1439–1451
Hagemann TL, Boelens WC, Wawrousek EF, Messing A (2009) Suppression of GFAP toxicity by alphaB-crystallin in mouse models of Alexander disease. Hum Mol Genet 18:1190–1199
Hilton GR, Lioe H, Stengel F, Baldwin AJ, Benesch JL (2013) Small heat-shock proteins: paramedics of the cell. Top Curr Chem 328:69–98
Iwaki T, Iwaki A, Tateishi J, Goldman JE (1994) Sense and antisense modification of glial alpha B-crystallin production results in alterations of stress fiber formation and thermoresistance. J Cell Biol 125:1385–1393
Iwaki T, Kume-Iwaki A, Goldman JE (1990) Cellular distribution of alpha B-crystallin in non-lenticular tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 38:31–39
Iwaki T, Wisniewski T, Iwaki A, Corbin E, Tomokane N, Tateishi J, Goldman JE (1992) Accumulation of alpha B-crystallin in central nervous system glia and neurons in pathologic conditions. Am J Pathol 140:345–356
Jing YY, Li XL, Shi Q, Wang ZY, Guo Y, Pan MM, Tian C, Zhu SY, Chen C, Gong HS, Han J, Gao C, Dong XP (2011) A novel PrP partner HS-1 associated protein X-1 (HAX-1) protected the cultured cells against the challenge of H(2)O(2). J Mol Neurosci 45:216–228
Kato K, Ito H, Kamei K, Inaguma Y, Iwamoto I, Saga S (1998) Phosphorylation of alphaB-crystallin in mitotic cells and identification of enzymatic activities responsible for phosphorylation. J Biol Chem 273:28346–28354
Kato S, Hirano A, Umahara T, Llena JF, Herz F, Ohama E (1992) Ultrastructural and immunohistochemical studies on ballooned cortical neurons in Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease: expression of alpha B-crystallin, ubiquitin and stress-response protein 27. Acta Neuropathol 84:443–448
Lanneau D, Wettstein G, Bonniaud P, Garrido C (2010) Heat shock proteins: cell protection through protein triage. ScientificWorldJournal 10:1543–1552
Li P, Dong C, Lei Y, Shan B, Xiao X, Jiang H, Wang X, Gao C, Shi Q, Xu K, Tian C, Han J, Dong X (2009) Doppel-induced cytotoxicity in human neuronal SH-SY5Y cells is antagonized by the prion protein. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin (Shanghai) 41:42–53
Lin DI, Barbash O, Kumar KG, Weber JD, Harper JW, Klein-Szanto AJ, Rustgi A, Fuchs SY, Diehl JA (2006) Phosphorylation-dependent ubiquitination of cyclin D1 by the SCF (FBX4-alphaB crystallin) complex. Mol Cell 24:355–366
Markossian KA, Yudin IK, Kurganov BI (2009) Mechanism of suppression of protein aggregation by alpha-crystallin. Int J Mol Sci 10:1314–1345
Meade-White KD, Barbian KD, Race B, Favara C, Gardner D, Taubner L, Porcella S, Race R (2009) Characteristics of 263K scrapie agent in multiple hamster species. Emerg Infect Dis 15:207–215
Mignot C, Boespflug-Tanguy O, Gelot A, Dautigny A, Pham-Dinh D, Rodriguez D (2004) Alexander disease: putative mechanisms of an astrocytic encephalopathy. Cell Mol Life Sci 61:369–385
Mounier N, Arrigo AP (2002) Actin cytoskeleton and small heat shock proteins: how do they interact? Cell Stress Chaperones 7:167–176
Parchi P, Castellani R, Cortelli P, Montagna P, Chen SG, Petersen RB, Manetto V, Vnencak-Jones CL, McLean MJ, Sheller JR et al (1995) Regional distribution of protease-resistant prion protein in fatal familial insomnia. Ann Neurol 38:21–29
Raman B, Ban T, Sakai M, Pasta SY, Ramakrishna T, Naiki H, Goto Y, Rao Ch M (2005) AlphaB-crystallin, a small heat-shock protein, prevents the amyloid fibril growth of an amyloid beta-peptide and beta2-microglobulin. Biochem J 392:573–581
Renkawek K, de Jong WW, Merck KB, Frenken CW, van Workum FP, Bosman GJ (1992) alpha B-crystallin is present in reactive glia in Creutzfeldt–Jakob disease. Acta Neuropathol 83:324–327
Renkawek K, Voorter CE, Bosman GJ, van Workum FP, de Jong WW (1994) Expression of alpha B-crystallin in Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol 87:155–160
Seifert G, Schilling K, Steinhauser C (2006) Astrocyte dysfunction in neurological disorders: a molecular perspective. Nat Rev Neurosci 7:194–206
Strom A, Diecke S, Hunsmann G, Stuke AW (2006) Identification of prion protein binding proteins by combined use of far-Western immunoblotting, two dimensional gel electrophoresis and mass spectrometry. Proteomics 6:26–34
Sun G, Guo M, Shen A, Mei F, Peng X, Gong R, Guo D, Wu J, Tien P, Xiao G (2005) Bovine PrPC directly interacts with alphaB-crystalline. FEBS Lett 579:5419–5424
Tseng WC, Lu KS, Lee WC, Chien CL (2006) Redistribution of GFAP and alphaB-crystallin after thermal stress in C6 glioma cell line. J Biomed Sci 13:681–694
van Rijk AF, Bloemendal H (2000) Alpha-B-crystallin in neuropathology. Ophthalmologica 214:7–12
Wang SB, Shi Q, Xu Y, Xie WL, Zhang J, Tian C, Guo Y, Wang K, Zhang BY, Chen C, Gao C, Dong XP (2012) Protein disulfide isomerase regulates endoplasmic reticulum stress and the apoptotic process during prion infection and PrP mutant-induced cytotoxicity. PLoS One 7:e38221
Xu Y, Tian C, Wang SB, Xie WL, Guo Y, Zhang J, Shi Q, Chen C, Dong XP (2012) Activation of the macroautophagic system in scrapie-infected experimental animals and human genetic prion diseases. Autophagy 8:1604–1620
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Chinese National Natural Science Foundation Grant (81100980, 81101302, and 31100117), the China Mega-Project for Infectious Disease (2011ZX10004-101 and 2012ZX10004215), and the SKLID Development Grant (2012SKLID102, 2011SKLID302, 2011SKLID204, and 2011SKLID211).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Ke Wang and Jin Zhang contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, K., Zhang, J., Xu, Y. et al. Abnormally Upregulated αB-crystallin Was Highly Coincidental with the Astrogliosis in the Brains of Scrapie-Infected Hamsters and Human Patients with Prion Diseases. J Mol Neurosci 51, 734–748 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0057-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0057-x