Abstract
Purpose
Patients with diabetes retinopathy appear to show increased susceptibility to periodontal disease. This study was performed to assess the relationship between periodontitis and the prevalence of diabetic retinopathy in a large probability sample of the Korean population. A subgroup analysis was performed using body mass index <25 kg/m2 as the criterion to evaluate the effect of obesity on this relationship.
Methods
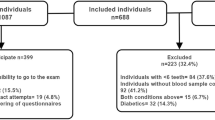
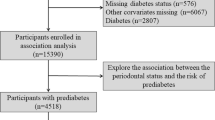
This study is based on data from the Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey of the Korean population, conducted between 2008 and 2010. The presence of diabetic retinopathy in relation to demographic variables and anthropometric characteristics of the participants is presented as means with their standard errors. The presence of periodontitis and presence of retinopathy categorized by body mass index (<25 and ≥25 kg/m2) were evaluated. Multiple logistic regression analyses were used to assess the associations between periodontitis and diabetic retinopathy after adjustment with variables, including age, sex, smoking, drinking, exercise, hypertension, metabolic syndrome, HbA1c, and duration of diabetes mellitus.
Results
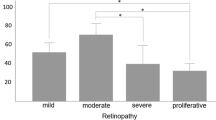
There was a statistically significant increase in the prevalence of periodontitis in individuals who had proliferative diabetic retinopathy. The odds ratios [95% confidence intervals] of prevalence of diabetic retinopathy were 1.193 [0.757–1.881] for the whole population after adjustments with confounding factors. Subgroup analysis after adjustments with confounding factors showed that the odds ratios [95% confidence intervals] of prevalence were 2.206 [1.114–4.366] and 0.588 [0.326–1.061] among participants with body mass index <25 kg/m2 and body mass index 37 ≥25 kg/m2, respectively.
Conclusions
The diabetic retinopathy was positively associated with the presence of periodontitis in non-obese diabetic Korean adults after adjustment with confounding variables. Our findings suggest that when a periodontist finds the presence of periodontitis in non-obese diabetic patients, timely evaluation of the patient’s ophthalmic evaluation should be 44 recommended.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
F. Lakschevitz, G. Aboodi, H. Tenenbaum, M. Glogauer, Diabetes and periodontal diseases: interplay and links. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 7, 433–439 (2011)
H. Thorstensson, J. Kuylenstierna, A. Hugoson, Medical status and complications in relation to periodontal disease experience in insulin-dependent diabetics. J. Clin. Periodontol. 23, 194–202 (1996)
J.B. Saaddine, A.A. Honeycutt, K.M. Narayan, X. Zhang, R. Klein, J.P. Boyle, Projection of diabetic retinopathy and other major eye diseases among people with diabetes mellitus: United States, 2005–2050. Arch. Ophthalmol. 126, 1740–1747 (2008)
J.W. Yau, S.L. Rogers, R. Kawasaki, E.L. Lamoureux, J.W. Kowalski, T. Bek, S.J. Chen, J.M. Dekker, A. Fletcher, J. Grauslund, S. Haffner, R.F. Hamman, M.K. Ikram, T. Kayama, B.E. Klein, R. Klein, S. Krishnaiah, K. Mayurasakorn, J.P. O’Hare, T.J. Orchard, M. Porta, M. Rema, M.S. Roy, T. Sharma, J. Shaw, H. Taylor, J.M. Tielsch, R. Varma, J.J. Wang, N. Wang, S. West, L. Xu, M. Yasuda, X. Zhang, P. Mitchell, T.Y. Wong, Global prevalence and major risk factors of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes Care 35, 556–564 (2012)
A.A. Amiri, A. Maboudi, A. Bahar, A. Farokhfar, F. Daneshvar, H.R. Khoshgoeian, M. Nasohi, A. Khalilian, Relationship between type 2 diabetic retinopathy and periodontal disease in Iranian adults. N. Am. J. Med. Sci. 6, 139–144 (2014)
A. Vaag, S.S. Lund, Non-obese patients with type 2 diabetes and prediabetic subjects: distinct phenotypes requiring special diabetes treatment and (or) prevention? Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 32, 912–920 (2007)
G.E. Nam, H. Kim do, K.H. Cho, Y.G. Park, K.D. Han, Y.S. Choi, S.M. Kim, B.J. Ko, Y.H. Kim, K.S. Lee, Estimate of a predictive cut-off value for serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D reflecting abdominal obesity in Korean adolescents. Nutr. Res. 32, 395–402 (2012)
T.M. Wallace, J.C. Levy, D.R. Matthews, Use and abuse of HOMA modeling. Diabetes Care 27, 1487–1495 (2004)
W.J. Lee, L. Sobrin, M.J. Lee, M.H. Kang, M. Seong, H. Cho, The relationship between diabetic retinopathy and diabetic nephropathy in a population-based study in Korea (KNHANES V-2, 3). Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 55, 6547–6553 (2014)
J.Y. Jeon, S.H. Ko, H.S. Kwon, N.H. Kim, J.H. Kim, C.S. Kim, K.H. Song, J.C. Won, S. Lim, S.H. Choi, M.J. Jang, Y. Kim, K. Oh, D.J. Kim, B.Y. Cha, Prevalence of diabetes and prediabetes according to fasting plasma glucose and HbA1c. Diabetes Metab. J. 37, 349–357 (2013)
Y.H. Chun, H.R. Kim, K. Han, Y.G. Park, H.J. Song, K.S. Na, Total cholesterol and lipoprotein composition are associated with dry eye disease in Korean women. Lipids Health Dis. 12, 84 (2013)
Y.H. Kim, K.H. Cho, Y.S. Choi, S.M. Kim, G.E. Nam, S.H. Lee, B.J. Ko, Y.G. Park, K.D. Han, K.S. Lee, D.H. Kim, Low bone mineral density is associated with metabolic syndrome in South Korean men but not in women: the 2008–2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination survey. Arch. Osteoporos. 8, 142 (2013)
M.A. Weber, S. Julius, S.E. Kjeldsen, H.R. Brunner, S. Ekman, L. Hansson, T. Hua, J.H. Laragh, G.T. McInnes, L. Mitchell, F. Plat, M.A. Schork, B. Smith, A. Zanchetti, Blood pressure dependent and independent effects of antihypertensive treatment on clinical events in the value trial. Lancet 363, 2049–2051 (2004)
J.H. Ahn, J.H. Yu, S.H. Ko, H.S. Kwon, D.J. Kim, J.H. Kim, C.S. Kim, K.H. Song, J.C. Won, S. Lim, S.H. Choi, K. Han, B.Y. Cha, N.H. Kim, Prevalence and determinants of diabetic nephropathy in Korea: Korea national health and nutrition examination survey. Diabetes Metab. J. 38, 109–119 (2014)
Y.H. Kim, D.H. Kim, K.S. Lim, B.J. Ko, B.D. Han, G.E. Nam, Y.G. Park, K.D. Han, J.H. Kim, K.H. Cho. Oral health behaviors and metabolic syndrome: the 2008–2010 Korean National Health and Nutrition Examination survey. Clin. Oral Investig. 18, 1517–1524 (2014)
Y. Lim, S. Chun, J.H. Lee, K.H. Baek, W.K. Lee, H.W. Yim, M.I. Kang. Association of bone mineral density and diabetic retinopathy in diabetic subjects: the 2008–2011 Korea national health and nutrition examination survey. Osteoporos. Int. 27, 2249–2257 (2016)
R. Banthia, S. Raje, P. Banthia, S.K. Saral, P. Singh, S. Gupta, Evaluation of the association between periodontal disease and diabetic retinopathy. Gen. Dent. 62, e28–e32 (2014)
I.M. Rosenthal, H. Abrams, A. Kopczyk, The relationship of inflammatory periodontal disease to diabetic status in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus patients. J. Clin. Periodontol. 15, 425–429 (1988)
R. Sadzeviciene, P. Paipaliene, G. Zekonis, J. Zilinskas, The influence of microvascular complications caused by diabetes mellitus on the inflammatory pathology of periodontal tissues. Stomatologija 7, 121–124 (2005)
J. Negishi, M. Kawanami, Y. Terada, C. Matsuhashi, E. Ogami, K. Iwasaka, T. Hongo, Effect of lifestyle on periodontal disease status in diabetic patients. J. Int. Acad. Periodontol. 6, 120–124 (2004)
W. Nesse, A. Linde, F. Abbas, F.K. Spijkervet, P.U. Dijkstra, E.C. de Brabander, I. Gerstenbluth, A. Vissink, Dose-response relationship between periodontal inflamed surface area and HbA1c in type 2 diabetics. J. Clin. Periodontol. 36, 295–300 (2009)
The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group, The relationship of glycemic exposure (HbA1c) to the risk of development and progression of retinopathy in the diabetes control and complications trial. Diabetes 44, 968–983 (1995)
J. Perayil, N. Suresh, A. Fenol, R. Vyloppillil, A. Bhaskar, S. Menon, Comparison of glycated hemoglobin levels in individuals without diabetes and with and without periodontitis before and after non-surgical periodontal therapy. J. Periodontol. 85, 1658–1666 (2014)
S.G. Grossi, R.J. Genco, Periodontal disease and diabetes mellitus: a two-way relationship. Ann. Periodontol. 3, 51–61 (1998)
L. Casanova, F.J. Hughes, P.M. Preshaw, Diabetes and periodontal disease: a two-way relationship. Br. Dent. J. 217, 433–437 (2014)
N. Braun, F. Gomes, P. Schutz, “The obesity paradox” in disease—is the protective effect of obesity true? Swiss Med. Wkly. 145, w14265 (2015)
D.E. Amundson, S. Djurkovic, G.N. Matwiyoff, The obesity paradox. Crit. Care Clin. 26, 583–596 (2010)
S.H. Preston, A. Stokes, Obesity paradox: conditioning on disease enhances biases in estimating the mortality risks of obesity. Epidemiology 25, 454–461 (2014)
M.R. Carnethon, P.J. De Chavez, M.L. Biggs, C.E. Lewis, J.S. Pankow, A.G. Bertoni, S.H. Golden, K. Liu, K.J. Mukamal, B. Campbell-Jenkins, A.R. Dyer, Association of weight status with mortality in adults with incident diabetes. J. Am. Med. Assoc. 308, 581–590 (2012)
A. Oreopoulos, R. Padwal, C.M. Norris, J.C. Mullen, V. Pretorius, K. Kalantar-Zadeh, Effect of obesity on short- and long-term mortality postcoronary revascularization: a meta-analysis. Obesity 16, 442–450 (2008)
S. Stenholm, T.B. Harris, T. Rantanen, M. Visser, S.B. Kritchevsky, L. Ferrucci, Sarcopenic obesity: definition, cause and consequences. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 11, 693–700 (2008)
M. Sandini, D.P. Bernasconi, D. Fior, M. Molinelli, D. Ippolito, L. Nespoli, R. Caccialanza, L. Gianotti. A high visceral adipose tissue-to-skeletal muscle ratio as a determinant of major complications after pancreatoduodenectomy for cancer. Nutrition 32, 1231–1237 (2016)
N.H. Kim, J. Lee, T.J. Kim, K.M. Choi, S.H. Baik, D.S. Choi, R. Pop-Busui, Y. Park, S.G. Kim, Body mass index and mortality in the general population and in subjects with chronic disease in Korea: a nationwide cohort study (2002–2010). PLoS ONE 10, e0139924 (2015)
R. Prando, V. Cheli, P. Melga, R. Giusti, E. Ciuchi, P. Odetti, Is type 2 diabetes a different disease in obese and nonobese patients? Diabetes Care 21, 1680–1685 (1998)
A. Lukich, D. Gavish, M. Shargorodsky, Normal weight diabetic patients versus obese diabetics: relation of overall and abdominal adiposity to vascular health. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 13, 141 (2014)
P. Arner, T. Pollare, H. Lithell, Different aetiologies of type 2 (non-insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus in obese and non-obese subjects. Diabetologia 34, 483–487 (1991)
K. Han, Y. Ko, Y.G. Park, J.B. Park, Associations between the number of natural teeth in postmenopausal women and duration of lactation: the 2010–2012 Korea national health and nutrition examination survey. Maturitas 85, 73–78 (2016)
A. Kingman, C. Susin, J.M. Albandar, Effect of partial recording protocols on severity estimates of periodontal disease. J. Clin. Periodontol. 35, 659–667 (2008)
C. Susin, A. Kingman, J.M. Albandar, Effect of partial recording protocols on estimates of prevalence of periodontal disease. J. Periodontol. 76, 262–267 (2005)
J.B. Park, K. Han, Y.G. Park, Y. Ko, Association between alcohol consumption and periodontal disease: the 2008 to 2010 Korea national health and nutrition examination survey. J. Periodontol. 85, 1521–1528 (2014)
K. Han, Y. Ko, Y.G. Park, J.B. Park, Associations between the periodontal disease in women before menopause and menstrual cycle irregularity: the 2010–2012 Korea national health and nutrition examination survey. Medicine 95, e2791 (2016)
H.M. Choi, K. Han, Y.G. Park, J.B. Park, Associations among oral hygiene behavior and hypertension prevalence and control: the 2008 to 2010 Korea national health and nutrition examination survey. J. Periodontol. 86, 866–873 (2015)
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the Korea Centers for Disease Control and Prevention for providing the data.
Funding
This work was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT & Future Planning (NRF-2014R1A1A1003106).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Su Jeong Song and Seong-su Lee have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, S.J., Lee, Ss., Han, K. et al. Periodontitis is associated with diabetic retinopathy in non-obese adults. Endocrine 56, 82–89 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-1215-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-1215-z