Abstract
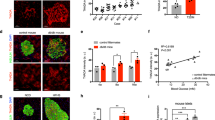
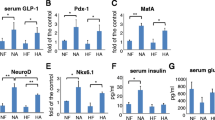
Reg family proteins have long been implicated in islet β-cell proliferation, survival, and regeneration. In our previous study, we reported that Reg3β overexpression did not increase islet growth but prevented streptozotocin-induced islet damage by inducing specific genes. In order to explore its role in type 2 diabetes (T2D), we established high-fat diet (HFD)-induced obesity and diabetes in RIP-I/Reg3β mice. Glucose and insulin tolerance tests, immunofluorescence for insulin, eIF2α, and GLUT2 in islets, Western blots on phosphorylated AMPKα and hepatic histology were performed. Both RIP-I/Reg3β and wild-type mice gained weight rapidly and became hyperglycemic after 10 weeks on the HFD. However, the transgenic mice exhibited more significant acceleration in blood glucose levels, further deterioration of glucose intolerance and insulin resistance, and a lower intensity of insulin staining. Immunofluorescence revealed similar magnitude of islet compensation to a wild-type HFD. The normal GLUT2 distribution in the transgenic β-cells was disrupted and the staining was obviously diminished on the cell membrane. HFD feeding also caused a further decrease in the level of AMPKα phosphorylation in the transgenic islets. Our results suggest that unlike its protective effect against T1D, overexpressed Reg3β was unable to protect the β-cells against HFD-induced damage.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
K. Terazono, H. Yamamoto, S. Takasawa, K. Shiga, Y. Yonemura, Y. Tochino, H. Okamoto, A novel gene activated in regenerating islets. J. Biol. Chem. 263(5), 2111–2114 (1988)
T. Watanabe, H. Yonekura, K. Terazono, H. Yamamoto, H. Okamoto, Complete nucleotide sequence of human reg gene and its expression in normal and tumoral tissues. The reg protein, pancreatic stone protein, and pancreatic thread protein are one and the same product of the gene. J. Biol. Chem. 265(13), 7432–7439 (1990)
H. Miyashita, K. Nakagawara, M. Mori, Y. Narushima, N. Noguchi, S. Moriizumi, S. Takasawa, H. Yonekura, T. Takeuchi, H. Okamoto, Human REG family genes are tandemly ordered in a 95-kilobase region of chromosome 2p12. FEBS Lett. 377(3), 429–433 (1995)
Y. Narushima, M. Unno, K. Nakagawara, M. Mori, H. Miyashita, Y. Suzuki, N. Noguchi, S. Takasawa, T. Kumagai, H. Yonekura, H. Okamoto, Structure, chromosomal localization and expression of mouse genes encoding type III Reg, RegIII alpha, RegIII beta, RegIII γ. Gene 185(2), 159–168 (1997)
M. Abe, K. Nata, T. Akiyama, N.J. Shervani, S. Kobayashi, T. Tomioka-Kumagai, S. Ito, S. Takasawa, H. Okamoto, Identification of a novel Reg family gene, Reg IIIδ, and mapping of all three types of Reg family gene in a 75 kilobase mouse genomic region. Gene 246(1–2), 111–122 (2000)
H. Okamoto, The Reg gene family and Reg proteins: with special attention to the regeneration of pancreatic beta-cells. J. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Surg. 6(3), 254–262 (1999)
Q. Li, X. Xiong, J.L. Liu, The contribution of Reg family proteins to cell growth and survival in pancreatic islets, in The Islets of Langerhans. Advances in Experimental Medicine and Biology, vol. 654, ed. by M.S. Islam (Springer, Berlin, 2014), pp. 955–988
J.L. Liu, W. Cui, B. Li, Y. Lu, Possible roles of reg family proteins in pancreatic islet cell growth. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 8(1), 1–10 (2008)
L. Christa, F. Carnot, M.T. Simon, F. Levavasseur, M.G. Stinnakre, C. Lasserre, D. Thepot, B. Clement, E. Devinoy, C. Brechot, HIP/PAP is an adhesive protein expressed in hepatocarcinoma, normal Paneth, and pancreatic cells. Am. J. Physiol. 271(6 Pt 1), G993–G1002 (1996)
H.T. Lieu, F. Batteux, M.T. Simon, A. Cortes, C. Nicco, F. Zavala, A. Pauloin, J.G. Tralhao, O. Soubrane, B. Weill, C. Brechot, L. Christa, HIP/PAP accelerates liver regeneration and protects against acetaminophen injury in mice. Hepatology 42(3), 618–626 (2005)
S. Takasawa, T. Ikeda, T. Akiyama, K. Nata, K. Nakagawa, N.J. Shervani, N. Noguchi, S. Murakami-Kawaguchi, A. Yamauchi, I. Takahashi, T. Tomioka-Kumagai, H. Okamoto, Cyclin D1 activation through ATF-2 in Reg-induced pancreatic beta-cell regeneration. FEBS Lett. 580(2), 585–591 (2006)
L. Rosenberg, M. Lipsett, J.W. Yoon, M. Prentki, R. Wang, H.S. Jun, G.L. Pittenger, D. Taylor-Fishwick, A.I. Vinik, A pentadecapeptide fragment of islet neogenesis-associated protein increases beta-cell mass and reverses diabetes in C57BL/6 J mice. Ann. Surg. 240(5), 875–884 (2004)
D.A. Taylor-Fishwick, A. Bowman, N. Hamblet, P. Bernard, D.M. Harlan, A.I. Vinik, Islet neogenesis associated protein transgenic mice are resistant to hyperglycemia induced by streptozotocin. J. Endocrinol. 190(3), 729–737 (2006). doi:10.1677/joe.1.06698
T.J. Chang, J.R. Weaver, A. Bowman, K. Leone, R. Raab, A.I. Vinik, G.L. Pittenger, D.A. Taylor-Fishwick, Targeted expression of INGAP to beta cells enhances glucose tolerance and confers resistance to streptozotocin-induced hyperglycemia. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 335(2), 104–109 (2011). doi:10.1016/j.mce.2010.12.026
L. Liu, J.L. Liu, C.B. Srikant, Reg2 protects mouse insulinoma cells from streptozotocin-induced mitochondrial disruption and apoptosis. Growth Factors 28(5), 370–378 (2010). doi:10.3109/08977194.2010.504721
L. Liu, S. Chowdhury, X. Fang, J.L. Liu, C.B. Srikant, Attenuation of unfolded protein response and apoptosis by mReg2 induced GRP78 in mouse insulinoma cells. FEBS Lett. 588(11), 2016–2024 (2014). doi:10.1016/j.febslet.2014.04.030
W. Cui, K. De Jesus, H. Zhao, S. Takasawa, B. Shi, C.B. Srikant, J.L. Liu, Overexpression of Reg3alpha increases cell growth and the levels of cyclin D1 and CDK4 in insulinoma cells. Growth Factors 27(3), 195–202 (2009). doi:10.1080/08977190902863548
C. Lasserre, M.T. Simon, H. Ishikawa, S. Diriong, V.C. Nguyen, L. Christa, P. Vernier, C. Brechot, Structural organization and chromosomal localization of a human gene (HIP/PAP) encoding a C-type lectin overexpressed in primary liver cancer. Eur. J. Biochem. 224(1), 29–38 (1994)
J.C. Hartupee, H. Zhang, M.F. Bonaldo, M.B. Soares, B.K. Dieckgraefe, Isolation and characterization of a cDNA encoding a novel member of the human regenerating protein family: reg IV. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1518(3), 287–293 (2001)
R. Graf, M. Schiesser, A. Lussi, P. Went, G.A. Scheele, D. Bimmler, Coordinate regulation of secretory stress proteins (PSP/reg, PAP I, PAP II, and PAP III) in the rat exocrine pancreas during experimental acute pancreatitis. J. Surg. Res. 105(2), 136–144 (2002)
B. Zhong, P. Strnad, D.M. Toivola, G.Z. Tao, X. Ji, H.B. Greenberg, M.B. Omary, Reg-II is an exocrine pancreas injury-response product that is up-regulated by keratin absence or mutation. Mol. Biol. Cell 18(12), 4969–4978 (2007). doi:10.1091/mbc.E07-02-0180
Y. Lu, A. Ponton, H. Okamoto, S. Takasawa, P.L. Herrera, J.L. Liu, Activation of the Reg family genes by pancreatic-specific IGF-I gene deficiency and after streptozotocin-induced diabetes in mouse pancreas. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 291(1), E50–E58 (2006). doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00596.2005
Y. Wang, C. Jacovetti, B. Li, T. Siddique, X. Xiong, H. Yin, M. Wang, H. Zhao, J.L. Liu, Coordinated age-dependent and pancreatic-specific expression of mouse Reg2Reg3alpha, and Reg3beta genes. Growth Factors 29(2–3), 72–81 (2011). doi:10.3109/08977194.2011.562866
M. Gironella, E. Folch-Puy, A. LeGoffic, S. Garcia, L. Christa, A. Smith, L. Tebar, S.P. Hunt, R. Bayne, A.J. Smith, J.C. Dagorn, D. Closa, J.L. Iovanna, Experimental acute pancreatitis in PAP/HIP knock-out mice. Gut 56(8), 1091–1097 (2007). doi:10.1136/gut.2006.116087
N. Baeza, D. Sanchez, L. Christa, O. Guy-Crotte, B. Vialettes, C. Figarella, Pancreatitis-associated protein (HIP/PAP) gene expression is upregulated in NOD mice pancreas and localized in exocrine tissue during diabetes. Digestion 64(4), 233–239 (2001)
X. Xiong, X. Wang, B. Li, S. Chowdhury, Y. Lu, C.B. Srikant, G. Ning, J.L. Liu, Pancreatic islet-specific overexpression of Reg3β protein induced the expression of pro-islet genes and protected mice against streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 300, E669–E680 (2011)
Y. Lu, P.L. Herrera, Y. Guo, D. Sun, Z. Tang, D. LeRoith, J.L. Liu, Pancreatic-specific inactivation of IGF-I gene causes enlarged pancreatic islets and significant resistance to diabetes. Diabetes 53(12), 3131–3141 (2004)
S.H. Back, R.J. Kaufman, Endoplasmic reticulum stress and type 2 diabetes. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 81, 767–793 (2012). doi:10.1146/annurev-biochem-072909-095555
D.R. Clemmons, A.C. Moses, A. Sommer, W. Jacobson, A.D. Rogol, M.R. Sleevi, G. Allan, Rh/IGF-I/rhIGFBP-3 administration to patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus reduces insulin requirements while also lowering fasting glucose. Growth Horm. IGF Res. 15(4), 265–274 (2005)
P. Zhang, B. McGrath, S. Li, A. Frank, F. Zambito, J. Reinert, M. Gannon, K. Ma, K. McNaughton, D.R. Cavener, The PERK eukaryotic initiation factor 2 alpha kinase is required for the development of the skeletal system, postnatal growth, and the function and viability of the pancreas. Mol. Cell. Biol. 22(11), 3864–3874 (2002)
C.R. Lindholm, R.L. Ertel, J.D. Bauwens, E.G. Schmuck, J.D. Mulligan, K.W. Saupe, A high-fat diet decreases AMPK activity in multiple tissues in the absence of hyperglycemia or systemic inflammation in rats. J. Physiol. Biochem. 69(2), 165–175 (2013). doi:10.1007/s13105-012-0199-2
F. Schuit, D. Flamez, A. De Vos, D. Pipeleers, Glucose-regulated gene expression maintaining the glucose-responsive state of beta-cells. Diabetes 51(suppl 3), S326–S332 (2002). doi:10.2337/diabetes.51.2007.S326
R. Jacob, E. Barrett, G. Plewe, K.D. Fagin, R.S. Sherwin, Acute effects of insulin-like growth factor I on glucose and amino acid metabolism in the awake fasted rat. Comparison with insulin. J. Clin. Invest. 83(5), 1717–1723 (1989)
K. Ohtsubo, S. Takamatsu, M.T. Minowa, A. Yoshida, M. Takeuchi, J.D. Marth, Dietary and genetic control of glucose transporter 2 glycosylation promotes insulin secretion in suppressing diabetes. Cell 123(7), 1307–1321 (2005). doi:10.1016/j.cell.2005.09.041
M.S. Lipkowitz, E. Leal-Pinto, B.E. Cohen, R.G. Abramson, Galectin 9 is the sugar-regulated urate transporter/channel UAT. Glycoconj. J. 19(7–9), 491–498 (2004). doi:10.1023/B:GLYC.0000014078.65610.2f
D.R. Clemmons, Involvement of insulin-like growth factor-I in the control of glucose homeostasis. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 6(6), 620–625 (2006). doi:10.1016/j.coph.2006.08.006
S.G. Laychock, J. Duzen, C.O. Simpkins, Metallothionein induction in islets of Langerhans and insulinoma cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 165(1–2), 179–187 (2000)
X. Li, H. Chen, P.N. Epstein, Metallothionein and catalase sensitize to diabetes in nonobese diabetic mice: reactive oxygen species may have a protective role in pancreatic {beta}-cells. Diabetes 55(6), 1592–1604 (2006)
C.L. Acerini, C.M. Patton, M.O. Savage, A. Kernell, O. Westphal, D.B. Dunger, Randomised placebo-controlled trial of human recombinant insulin-like growth factor I plus intensive insulin therapy in adolescents with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. The Lancet 350(9086), 1199–1204 (1997)
B. Viollet, L. Lantier, J. Devin-Leclerc, S. Hebrard, C. Amouyal, R. Mounier, M. Foretz, F. Andreelli, Targeting the AMPK pathway for the treatment of type 2 diabetes. Front. Biosci. J. Virtual Libr. 14, 3380–3400 (2009)
G.R. Steinberg, B.E. Kemp, AMPK in health and disease. Physiol. Rev. 89(3), 1025–1078 (2009). doi:10.1152/physrev.00011.2008
K.M. Utzschneider, S.E. Kahn, Review: the role of insulin resistance in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 91(12), 4753–4761 (2006). doi:10.1210/jc.2006-0587
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dr. Louise Larose for her instructions on ER stress tests and Carolynna Olha for the English revision and editing of this manuscript. This work was supported by the Canadian Institutes of Health Research (Grant MOP-84389), Canadian Diabetes Association (OG-3-11-3469-JL) and a bridge fund from the Research Institute of the McGill University Health Centre (RI-MUHC) to JLL. QL received support from the China Scholarship Council (201208370055). ZHG was supported by the RI-MUHC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
All authors declared there were no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Xiaoquan Xiong and Qing Li have contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
12020_2016_998_MOESM1_ESM.tif
Supplemental Figure 1. Interlobular fat deposition within the pancreatic tissues of HFD- but not Chow-fed mice. At the end of the 10-week HFD feeding, pancreatic sections were stained with HE, the brown arrows indicate fat deposition in the form of bubbles. Representative images of N=5. Supplementary material 1 (TIFF 1345 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiong, X., Li, Q., Cui, W. et al. Deteriorated high-fat diet-induced diabetes caused by pancreatic β-cell-specific overexpression of Reg3β gene in mice. Endocrine 54, 360–370 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-0998-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-016-0998-2