Abstract
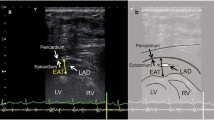
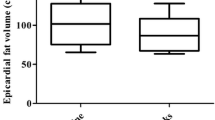
The aim of the study was to assess the effect of sitagliptin addition on the epicardial adipose tissue (EAT) thickness in subjects with type 2 diabetes mellitus inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy. This was a 24-week interventional pilot study in 26 consecutive type 2 diabetic patients, 14 females and 12 males average age of 43.8 ± 9.0 years, with Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) ≥7 % on metformin monotherapy. Subjects who met the inclusion criteria were added on sitagliptin and started on sitagliptin/metformin combination at the dosage of 50 mg/1000 mg twice daily. EAT and visceral and total body fat were measured, respectively, with echocardiography and bioelectrical impedance analysis at baseline and after 24 weeks of sitagliptin/metformin treatment in each subject. HbA1c and plasma lipids were also measured. EAT decreased significantly from 9.98 ± 2.63 to 8.10 ± 2.11 mm, p = 0.001, accounting for a percentage of reduction (∆ %) of −15 % after 24 weeks of sitagliptin addition, whereas total body fat percentage, visceral fat, and body mass index (BMI), decreased by 8, 12, and 7 %, respectively (p = 0.001 for all). After 6 month, EAT ∆ % was significantly correlated with ∆ % of visceral fat (r = 0.456; p = 0.01), whereas no correlation with either BMI ∆ % (r = 0.292; p = 0.147) or HbA1c ∆ % was found. The addition of Sitagliptin produced a significant and rapid reduction of EAT, marker of organ-specific visceral fat, in overweight/obese individuals with type 2 diabetes inadequately controlled on metformin monotherapy. EAT as measured with ultrasound can serve as no invasive and accurate marker of visceral fat changes during pharmaceutical interventions targeting the fat.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
G. Iacobellis, A.M. Sharma, Epicardial adipose tissue as new cardio-metabolic risk marker and potential therapeutic target in the metabolic syndrome. Curr. Pharm. Des. 13, 2180–2184 (2007)
A. Gastaldelli, G. Basta, Ectopic fat and cardiovascular disease: what is the link? Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 20, 481–490 (2010)
G. Iacobellis, D. Corradi, A.M. Sharma, Epicardial adipose tissue: anatomical, biomolecular and clinical relation to the heart. Nat. Clin. Pract. Cardiovasc. Med. 2, 536–543 (2005)
G. Iacobellis, Epicardial adipose tissue in endocrine and metabolic diseases. Endocrine 46, 8–15 (2014)
M.M. Lima-Martínez, C. Blandenier, G. Iacobellis, Epicardial adipose tissue: more than a simple fat deposit? Endocrinol. Nutr. 60, 320–328 (2013)
G. Iacobellis, Local and systemic effects of the multifaceted epicardial adipose tissue depot. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 11, 363–371 (2015)
G. Iacobellis, H.J. Willens, Echocardiographic epicardial fat: a review of research and clinical applications. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 22, 1311–1319 (2009)
A.E. Malavazos, G. Di Leo, F. Secchi, E.N. Lupo, G. Dogliotti, C. Coman, L. Morricone, M.M. Corsi, F. Sardanelli, G. Iacobellis, Relation of echocardiographic epicardial fat thickness and myocardial fat. Am. J. Cardiol. 105, 1831–1835 (2010)
G. Iacobellis, M.C. Ribaudo, F. Assael, E. Vecci, C. Tiberti, A. Zappaterreno, U. Di Mario, F. Leonetti, Echocardiographic epicardial adipose tissue is related to anthropometric and clinical parameters of metabolic syndrome: a new indicator of cardiovascular risk. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 88, 5163–5168 (2003)
M.M. Lima-Martínez, G. López-Mendez, R. Odreman, J.H. Donis, M. Paoli, Epicardial adipose tissue thickness and its association with adiponectin in metabolic syndrome patients from Mérida, Venezuela. Arq. Bras. Endocrinol. Metab. 58, 352–361 (2014)
S.D. Pierdomenico, A.M. Pierdomenico, F. Cuccurullo, G. Iacobellis, Meta-analysis of the relation of echocardiographic epicardial adipose tissue thickness and the metabolic syndrome. Am. J. Cardiol. 111, 73–78 (2013)
G. Iacobellis, E. Lonn, A. Lamy, N. Singh, A.M. Sharma, Epicardial fat thickness and coronary artery disease correlate independently of obesity. Int. J. Cardiol. 146, 452–454 (2011)
Y. Xu, X. Cheng, K. Hong, C. Huang, L. Wan, How to interpret epicardial adipose tissue as a cause of coronary artery disease: a meta-analysis. Coron. Artery Dis. 23, 227–233 (2012)
H.S. Sacks, J.N. Fain, P. Cheema, S.W. Bahouth, E. Garrett, R.Y. Wolf, D. Wolford, J. Samaha, Inflammatory genes in epicardial fat contiguous with coronary atherosclerosis in the metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes: changes associated with pioglitazone. Diabetes Care 34, 730–733 (2011)
J.T. Jonker, H.J. Lamb, R.W. van der Meer, L.J. Rijzewijk, L.J. Menting, M. Diamant, J.J. Bax, A. de Roos, J.A. Romijn, J.W. Smit, Pioglitazone compared with metformin increases pericardial fat volume in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 95, 456–460 (2010)
J.H. Park, Y.S. Park, Y.J. Kim, I.S. Lee, J.H. Kim, J.H. Lee, S.W. Choi, J.O. Jeong, I.W. Seong, Effects of statins on the epicardial fat thickness in patients with coronary artery stenosis underwent percutaneous coronary intervention: comparison of atorvastatin with simvastatin/ezetimibe. J. Cardiovasc. Ultrasound. 18, 121–126 (2010)
G. Iacobellis, N. Singh, S. Wharton, A.M. Sharma, Substantial changes in epicardial fat thickness after weight loss in severely obese subjects. Obesity 16, 1693–1697 (2008)
H.J. Willens, P. Byers, J.A. Chirinos, E. Labrador, J.M. Hare, E. de Marchena, Effects of weight loss after bariatric surgery on epicardial fat measured using echocardiography. Am. J. Cardiol. 99, 1242–1245 (2007)
A.J. Scheen, Cardiovascular effects of dipeptidyl peptidase-4 inhibitors: from risk factors to clinical outcomes. Postgrad. Med. 125, 7–20 (2013)
A. Mikada, T. Narita, H. Yokoyama, R. Yamashita, Y. Horikawa, K. Tsukiyama, Y. Yamada, Effects of miglitol, sitagliptin, and initial combination therapy with both on plasma incretin responses to a mixed meal and visceral fat in over-weight Japanese patients with type 2 diabetes. “The MASTER randomized, controlled trial”. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 106, 538–547 (2014)
R. Scott, T. Loeys, M.J. Davies, S.S. Engel, Sitagliptin Study 801 Group, Efficacy and safety of sitagliptin when added to ongoing metformin therapy in patients with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. Obes. Metab. 10, 959–969 (2008)
American Diabetes Association, Classification and diagnosis of diabetes. Diabetes Care 38(Suppl), S8–S16 (2015)
American Diabetes Association, Foundations of care: education, nutrition, physical activity, smoking cessation, psychosocial care, and immunization. Diabetes Care 38(Suppl), S20–S30 (2015)
D.R. Matthews, J.P. Hosker, A.S. Rudenski, B.A. Naylor, D.F. Treacher, R.C. Turner, Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28, 412–419 (1985)
G. Iacobellis, F. Assael, M.C. Ribaudo, A. Zappaterreno, G. Alessi, U. Di Mario, F. Leonetti, Epicardial fat from echocardiography: a new method for visceral adipose tissue prediction. Obes. Res. 11, 304–310 (2003)
T.B. Nguyen-Duy, M.Z. Nichaman, T.S. Church, S.N. Blair, R. Ross, Visceral fat and liver fat are independent predictors of metabolic risk factors in men. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 284, E1065–E1071 (2003)
M.M. Lima-Martínez, M. Paoli, J.H. Donis, R. Odreman, C. Torres, G. Iacobellis, Cut-off point of epicardial adipose tissue thickness for predicting metabolic syndrome in Venezuelan population. Endocrinol. Nutr. 60, 570–576 (2013)
G. Iacobellis, G. Barbaro, H.C. Gerstein, Relationship of epicardial fat thickness and fasting glucose. Int. J. Cardiol. 128, 424–426 (2008)
G. Iacobellis, F. Leonetti, Epicardial adipose tissue and insulin resistance in obese subjects. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 90, 6300–6302 (2005)
G. Iacobellis, S. Diaz, A. Mendez, R. Goldberg, Increased epicardial fat and plasma leptin in type 1 diabetes independently of obesity. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 24, 725–729 (2014)
S.W. Rabkin, H. Campbell, Comparison of reducing epicardial fat by exercise, diet or bariatric surgery weight loss strategies: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 16, 406–415 (2015)
Y. Yilmaz, O. Yonal, O. Deyneli, C.A. Celikel, C. Kalayci, D.G. Duman, Effects of sitagliptin in diabetic patients with nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Acta Gastroenterol. Belg. 75, 240–244 (2012)
M. Itou, T. Kawaguchi, E. Taniguchi, T. Oriishi, M. Sata, Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor improves insulin resistance and steatosis in a refractory nonalcoholic fatty liver disease patient: a case report. Case Rep. Gastroenterol. 6, 538–544 (2012)
G. Iacobellis, G. Barbarini, C. Letizia, G. Barbaro, Epícardial fat thickness and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in obese subjects. Obesity (Silver Spring) 22, 332–336 (2014)
J. Vendrell, R. El Bekay, B. Peral, E. García-Fuentes, A. Megia, M. Macias-Gonzalez, J. Fernández-Real, Y. Jimenez-Gomez, X. Escoté, G. Pachón, R. Simó, D.M. Selva, M.M. Malagón, F.J. Tinahones, Study of the potential association of adipose tissue GLP-1 receptor with obesity and insulin resistance. Endocrinology 152, 4072–4079 (2011)
S. Morano, E. Romagnoli, T. Filardi, L. Nieddu, E. Mandosi, M. Fallarino, I. Turinese, M.P. Dagostino, A. Lenzi, V. Carnevale, Short-term effects of glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) receptor agonist on fat distribution in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: an ultrasonography study. Acta Diabetol. 52, 727–732 (2015)
A.R. Baker, A.L. Harte, N. Howell, D.C. Pritlove, A.M. Ranasinghe, N.F. da Silva, E.M. Youssef, K. Khunti, M.J. Davies, R.S. Bonser, S. Kumar, D. Pagano, P.G. McTernan, Epicardial adipose tissue as a source of nuclear factor-kappaB and c-Jun N-terminal kinase mediated inflammation in patients with coronary artery disease. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 94, 261–267 (2009)
Z. Shah, T. Kampfrath, J.A. Deiuliis, J. Zhong, C. Pineda, Z. Ying, X. Xu, B. Lu, S. Moffatt-Bruce, R. Durairaj, Q. Sun, G. Mihai, A. Maiseyeu, S. Rajagopalan, Long-term dipeptidyl-peptidase 4 inhibition reduces atherosclerosis and inflammation via effects on monocyte recruitment and chemotaxis. Circulation 124, 2338–2349 (2011)
A. Aroor, S. McKarns, R. Nistala, V. DeMarco, M. Gardner, M. Garcia-Touza, A. Whaley-Connell, J.R. Sowers, DPP-4 inhibitors as therapeutic modulators of immune cell function and associated cardiovascular and renal insulin resistance in obesity and diabetes. Cardiorenal. Med. 3, 48–56 (2013)
M.M. Lima-Martínez, E. Guerra-Alcalá, M. Contreras, J. Nastasi, J.A. Noble, C. Polychronakos, One year remission of type 1 diabetes mellitus in a patient treated with sitagliptin. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2014, 140072 (2014)
M.M. Lima-Martínez, E. Campo, J. Salazar, M. Paoli, I. Maldonado, C. Acosta, M. Rodney, M. Contreras, J.O. Cabrera-Rego, G. Iacobellis, Epicardial fat thickness as cardiovascular risk factor and therapeutic target in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with biological and nonbiological therapies. Arthritis 2014, 782850 (2014)
D. Lamers, S. Famulla, N. Wronkowitz, S. Hartwig, S. Lehr, D.M. Ouwens, K. Eckardt, J.M. Kaufman, M. Ryden, S. Müller, F.G. Hanisch, J. Ruige, P. Arner, H. Sell, J. Eckel, Dipeptidyl peptidase 4 is a novel adipokine potentially linking obesity to the metabolic syndrome. Diabetes 60, 1917–1925 (2011)
A.D. Dobrian, Q. Ma, J.W. Lindsay, K.A. Leone, K. Ma, J. Coben, E.V. Galkina, J.L. Nadler, Dipeptidyl peptidase IV inhibitor sitagliptin reduces local inflammation in adipose tissue and in pancreatic islets of obese mice. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 300, E410–E421 (2011)
R. Verovská, Z. Lacnák, D. Haluziková, P. Fábin, P. Hájek, L. Horák, M. Haluzík, S. Svacina, M. Matoulek, Comparison of various methods of body fat analysis in overweight and obese women. Vnitr. Lek. 55, 455–461 (2009)
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Ana Pensa and José Ledezma for their support, and Prof. Carlos Mota for his valuable comments to the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts to disclose.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lima-Martínez, M.M., Paoli, M., Rodney, M. et al. Effect of sitagliptin on epicardial fat thickness in subjects with type 2 diabetes and obesity: a pilot study. Endocrine 51, 448–455 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0710-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-015-0710-y