Abstract
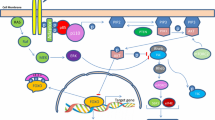
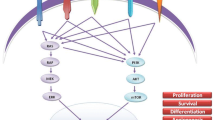
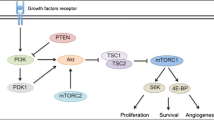
The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt/mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) pathway is a central hub for the regulation of cell proliferation, apoptosis, cell cycle, metabolism, and angiogenesis. Several studies have recently suggested that the PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathway is implicated in the pathogenesis and progression of neuroendocrine tumors. Medullary thyroid cancer (MTC) is a neuroendocrine tumor developing from the C cells of the thyroid. Mutations in the RET proto-oncogene are involved in the pathogenesis of several forms of MTC. The deregulation of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway seems to contribute to the tumorigenic activity of RET proto-oncogene mutations. Targeting this pathway through specific inhibitors at simple or multiple sites may represent an attractive potential therapeutic approach for patients with advanced MTCs. The aim of this review is to examine the role of the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway in the development and progression of MTC and the new therapeutic options that target this signaling pathway.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
C. Eng, D. Clayton, I. Schuffenecker, G. Lenoir, G. Cote, R.F. Gagel, H.K. van Amstel, C.J. Lips, I. Nishisho, S.I. Takai, D.J. Marsh, B.G. Robinson, K. Frank-Raue, F. Raue, F. Xue, W.W. Noll, C. Romei, F. Pacini, M. Fink, B. Niederle, J. Zedenius, M. Nordenskjöld, P. Komminoth, G.N. Hendy, L.M. Mulligan et al., The relationship between specific RET proto-oncogene mutations and disease phenotype in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2. International RET mutation consortium analysis. JAMA 276(19), 1575–1579 (1996)
C. Eng, L.M. Mulligan, Mutations of the RET protooncogene in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2, related sporadic tumours and Hirschsprung diseases. Hum. Mutat. 9, 97–109 (1997)
B. Pasini, M.G. Borrello, A. Greco, I. Bongarzone, Y. Luo, P. Mondellini, L. Alberti, C. Miranda, E. Arighi, R. Bocciardi et al., Loss of function effect of RET mutations causing Hirschsprung disease. Nature Genet. 10, 35–40 (1995)
L. Mulligan, C. Eng, C.S. Healey, D. Clayton, J.B. Kwok, E. Gardner, M.A. Ponder, A. Frilling, C.E. Jackson, H. Lehnert et al., Specific mutations of the RET proto-oncogene are related to disease phenotype in MEN 2A and FMTC. Nature Genet. 6, 70–74 (1994)
M.G. Borrello, D.P. Smith, B. Pasini, I. Bongarzone, A. Greco, M.J. Lorenzo, E. Arighi, C. Miranda, C. Eng, L. Alberti et al., RET activation by germline MEN2A and MEN2B mutations. Oncogene 11, 2419–2427 (1995)
G. Vitale, M. Caraglia, A. Ciccarelli, G. Lupoli, A. Abbruzzese, P. Tagliaferri, G. Lupoli, Current approaches and perspectives in the therapy of medullary thyroid carcinoma. Cancer 91(9), 1797–1808 (2001)
C. Puppin, C. Durante, M. Sponziello, A. Verrienti, V. Pecce, E. Lavarone, F. Baldan, A.F. Campese, A. Boichard, L. Lacroix, D. Russo, S. Filetti, G. Damante, Overexpression of genes involved in miRNA biogenesis in medullary thyroid carcinomas with RET mutation. Endocrine (2014). doi:10.1007/s12020-014-0204-3
A. Cerrato, V. De Falco, M. Santoro, Molecular genetics of medullary thyroid carcinoma: the quest for novel therapeutic targets. J. Mol. Endocrinol. 43, 143–155 (2009)
C. Durante, A. Paciaroni, K. Plasmati, F. Trulli, S. Filetti, Vandetanib: opening a new treatment practice in advanced medullary thyroid carcinoma. Endocrine 44(2), 334–342 (2013)
S. Wullschleger, R. Loewith, M.N. Hall, TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell 124, 471–484 (2006)
D.M. Sabatini, MTOR and cancer: insights into a complex relationship. Nat. Rev. Cancer 6, 729–734 (2006)
T. Schmeizle, M.N. Hall, TOR, a central controller of cell growth. Cell 103, 253–262 (2000)
Y. Samuels, Z. Wang, A. Bardelli, N. Silliman, J. Ptak, S. Szabo, H. Yan, A. Gazdar, S.M. Powell, G.J. Riggins, J.K. Willson, S. Markowitz, K.W. Kinzler, B. Vogelstein, V.E. Velculescu, High frequency of mutations of the PIK3CA gene in human cancers. Science 304, 554 (2004)
I. Vivanco, C.L. Sawyers, The phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2, 489–501 (2002)
A. De Benedetti, J.R. Graff, EIF-4E expression and its role in malignancies and metastases. Oncogene 23, 3189–3199 (2004)
J.A. Engelman, Targeting PI3K signaling in cancer: opportunities, challenges and limitations. Nat. Rev. Cancer 9, 550–562 (2009)
J. Li, C. Yen, D. Liaw, K. Podsypanina, S. Bose, S.I. Wang, J. Puc, C. Miliaresis, L. Rodgers, R. McCombie, S.H. Bigner, B.C. Giovanella, M. Ittmann, B. Tycko, H. Hibshoosh, M.H. Wigler, R. Parsons, PTEN, a putative protein tyrosine phosphatase gene mutated in human brain, breast, and prostate cancer. Science 275, 1943–1947 (1997)
T. Gagliano, M. Bellio, E. Gentilin, D. Molè, F. Tagliati, M. Schiavon, N.G. Cavallesco, L.G. Andriolo, M.R. Ambrosio, F. Rea, E. Degli Uberti, M.C. Zatelli, mTOR, p70S6K, AKT, and ERK1/2 levels predict sensitivity to mTOR and PI3K/mTOR inhibitors in human bronchial carcinoids. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 20(4), 463–475 (2013)
K.L. Yim, Role of biological targeted therapies in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumours. Endocrine 40(2), 181–186 (2011)
J. Capdevila, J. Tabernero, A shining light in the darkness for the treatment of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer Discov. 1, 213–221 (2011)
M.C. Zatelli, M. Minoia, C. Martini, F. Tagliati, M.R. Ambrosio, M. Schiavon, M. Buratto, F. Calabrese, E. Gentilin, G. Cavallesco, L. Berdondini, F. Rea, E.C. degli Uberti, Everolimus as a new potential antiproliferative agent in aggressive human bronchial carcinoids. Endocr. Relat. Cancer. 17(3), 719–729 (2010)
K.I. Alexandraki, G. Kaltsas, Gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors: new insights in the diagnosis and therapy. Endocrine 41(1), 40–52 (2012)
E. Missaglia, I. Dalai, S. Barbi, S. Beghelli, M. Falconi, M. della Peruta, L. Piemonti, G. Capurso, A. Di Florio, G. delle Fave, P. Pederzoli, C.M. Croce, A. Scarpa, Pancreatic endocrine tumors: expression profiling evidences a role for Akt-mTOR pathway. J. Clin. Oncol. 28, 245–255 (2010)
Y. Jiao, C. Shi, B.H. Edil, R.F. de Wilde, D.S. Klimstra, A. Maitra, R.D. Schulick, L.H. Tang, C.L. Wolfgang, M.A. Choti, V.E. Velculescu, L.A. Diaz Jr, B. Vogelstein, K.W. Kinzler, R.H. Hruban, N. Papadopoulos, DAXX/ATRX, MEN1 and mTOR pathway genes are frequently altered in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Science 331, 1199–1203 (2011)
T. Shida, T. Kishimoto, M. Furuya, T. Nikaido, K. Koda, S. Takano, F. Kimura, H. Shimizu, H. Yoshidome, M. Ohtsuka, T. Tanizawa, Y. Nakatani, M. Miyazaki, Expression of an activated mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) in gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 65, 889–893 (2010)
F. Meric-Bernstam, A.M. Gonzalez-Angulo, Targeting the mTOR signaling network for cancer therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 27, 2278–2287 (2009)
K.G. Foster, D.C. Fingar, Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR): conducting the cellular signaling symphony. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 14071–14077 (2010)
J.C. Yao, M.H. Shah, T. Ito, C.L. Bohas, E.M. Wolin, E. Van Cutsem, T.J. Hobday, T. Okusaka, J. Capdevila, E.G. de Vries, P. Tomassetti, M.E. Pavel, S. Hoosen, T. Haas, J. Lincy, D. Lebwohl, K. Öberg, RAD001 in Advanced Neuroendocrine Tumors, Third Trial (RADIANT-3) Study Group: everolimus for advanced pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 364(6), 514–523 (2011)
R.M. Melillo, F. Carlomagno, G. De Vita, P. Formisano, G. Vecchio, A. Fusco, M. Billaud, M. Santoro, The insulin receptor substrate (IRS)-1 recruits phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase to Ret: evidence for a competition between Shc and IRS-1 for the binding to Ret. Oncogene 20, 209–218 (2001)
I. Rapa, E. Saggiorato, D. Giachino, N. Palestini, F. Orlandi, M. Papotti, M. Volante, Mammalian target of rapamycin pathway activation is associated to RET mutation status in medullary thyroid carcinoma. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 96, 2146–2153 (2011)
A. Tamburrino, A.A. Molinolo, P. Salerno, R.D. Chernock, M. Raffeld, L. Xi, J.S. Gutkind, J.F. Moley, S.A. Wells Jr, M. Santoro, Activation of the mTOR pathway in primary medullary thyroid carcinoma and lymph node metastases. Clin. Cancer Res. 18, 3532–3540 (2012)
S.A. Wells, M. Santoro, Targeting the RET pathway in thyroid cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 15, 7119–7123 (2009)
M. Mazumdar, A. Adhikary, S. Chakraborty, S. Mukherjee, A. Manna, S. Saha, S. Mohanty, A. Dutta, P. Bhattacharjee, P. Ray, S. Chattopadhyay, S. Banerjee, J. Chakraborty, A.K. Ray, G. Sa, T. Das, Targeting RET to induce medullary thyroid cancer cell apoptosis: an antagonistic interplay between PI3K/Akt and p38MAPK/caspase-8 pathways. Apoptosis 18, 589–604 (2013)
A. Samadi, J. Bazzill, X. Zhang, R. Gallagher, H. Zhang, R. Gollapudi, K. Kindscher, B. Timmermann, M.S. Cohen, Novel withanolides target medullary thyroid cancer through inhibition of both RET phosphorylation and the mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. Surgery. 152(6), 1238–1247 (2012)
H.D. Skinner, J.Z. Zheng, J. Fang, F. Agani, B.H. Jiang, Vascular endothelial growth factor transcriptional activation is mediated by hypoxia inducible factor 1alpha, HDM2, and p70S6K1 in response to phosphatidylinositol 3kinase/AKT signaling. J. Biol. Chem. 279, 45643–45651 (2004)
A. Sekulic, C.C. Hudson, J.L. Homme, P. Yin, D.M. Otterness, L.M. Karnitz, R.T. Abraham, A direct linkage between the phosphoinositide 3-kinase-AKT signaling pathway and the mammalian target of rapamycin in mitogen-stimulated and transformed cells. Cancer Res. 60, 3504–3513 (2000)
G. Vitale, S. Zappavigna, M. Marra, A. Dicitore, S. Meschini, M. Condello, G. Arancia, S. Castiglioni, P. Maroni, P. Bendinelli, R. Piccoletti, P.M. van Koetsveld, F. Cavagnini, A. Budillon, A. Abbruzzese, L.J. Hofland, M. Caraglia, The PPAR-γ agonist troglitazone antagonizes survival pathways induced by STAT-3 in recombinant interferon-β treated pancreatic cancer cells. Biotechnol. Adv. 30(1), 169–184 (2012)
S. Isotani, K. Hara, C. Tokunaga, H. Inoue, J. Avruch, K. Yonezawa, Immunopurified mammalian target of rapamycin phosphorylates and activates p70 S6 kinase alpha in vitro. J. Biol. Chem. 274(48), 34493–34498 (1999)
R. Zoncu, A. Efeyan, D.M. Sabatini, mTOR: from growth signal integration to cancer, diabetes and ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 12(1), 21–35 (2011)
E. Jacinto, V. Facchinetti, D. Liu, N. Soto, S. Wei, S.Y. Jung, Q. Huang, J. Qin, B. Su, SIN1/MIP1 maintains rictor-mTOR complex integrity and regulates Akt phosphorylation and substrate specificity. Cell 127, 125–137 (2006)
J. Martin, J. Masri, A. Bernath, R.N. Nishimura, J. Gera, Hsp70 associates with rictor and is required for mTORC2 formation and activity. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 372, 578–583 (2008)
D.D. Sarbassov, S.M. Ali, D.H. Kim, D.A. Guertin, R.R. Latek, H. Erdjument-Bromage, P. Tempst, D.M. Sabatini, Rictor, a novel binding partner of mTOR, defines a rapamycin-insensitive and raptor-independent pathway that regulates the cytoskeleton. Curr. Biol. 14, 1296–1302 (2004)
P.C. McDonald, A. Oloumi, J. Mills, I. Dobreva, M. Maidan, V. Gray, E.D. Wederell, M.B. Bally, L.J. Foster, S. Dedhar, Rictor and integrin-linked kinase interact and regulate Akt phosphorylation and cancer cell survival. Cancer Res. 68, 1618–1624 (2008)
I. Hernandez-Negrete, J. Carretero-Ortega, H. Rosenfeldt, R. Hernández-García, J.V. Calderón-Salinas, G. Reyes-Cruz, J.S. Gutkind, J. Vázquez-Prado, P-Rex1 links mammalian target of rapamycin signaling to Rac activation and cell migration. J. Biol. Chem. 282, 23708–23715 (2007)
Y. Samuels, V.E. Velculescu, Oncogenic mutations of PIK3CA in human cancers. Cell Cycle 3, 1221–1224 (2004)
R. Bianco, I. Shin, C.A. Ritter, F.M. Yakes, A. Basso, N. Rosen, J. Tsurutani, P.A. Dennis, G.B. Mills, C.L. Arteaga, Loss of PTEN/MMAC1/TEP in EGF receptor-expressing tumor cells counteracts the antitumor action of EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Oncogene 22, 2812–2822 (2003)
S.L. Moulder, F.M. Yakes, S.K. Muthuswamy, R. Bianco, J.F. Simpson, C.L. Arteaga, Epidermal growth factor receptor (HER1) tyrosine kinase inhibitor ZD1839 (Iressa) inhibits HER2/neu (erbB2)-overexpressing breast cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Res. 61, 8887–8895 (2001)
F.M. Yakes, W. Chinratanalab, C.A. Ritter, W. King, S. Seelig, C.L. Arteaga, Herceptin-induced inhibition of phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase and Akt is required for antibody-mediated effects on p27, cyclin D1, and antitumor action. Cancer Res. 62, 4132–4141 (2002)
I.K. Mellinghoff, M.Y. Wang, I. Vivanco, D.A. Haas-Kogan, S. Zhu, E.Q. Dia, K.V. Lu, K. Yoshimoto, J.H. Huang, D.J. Chute, B.L. Riggs, S. Horvath, L.M. Liau, W.K. Cavenee, P.N. Rao, R. Beroukhim, T.C. Peck, J.C. Lee, W.R. Sellers, D. Stokoe, M. Prados, T.F. Cloughesy, C.L. Sawyers, P.S. Mischel, Molecular determinants of the response of glioblastomas to EGFR kinase inhibitors. N. Engl. J. Med. 353, 2012–2024 (2005)
C. Eng, D. Clayton, I. Schuffenecker, G. Lenoir, G. Cote, R.F. Gagel, H.K. van Amstel, C.J. Lips, I. Nishisho, S.I. Takai, D.J. Marsh, B.G. Robinson, K. Frank-Raue, F. Raue, F. Xue, W.W. Noll, C. Romei, F. Pacini, M. Fink, B. Niederle, J. Zedenius, M. Nordenskjöld, P. Komminoth, G.N. Hendy, L.M. Mulligan et al., The relationship between specific RET proto-oncogene mutations and disease phenotype in multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2. International RET mutation consortium analysis. JAMA. 276(19), 1575–1579 (1996)
N. Hay, N. Sonenberg, Upstream and downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 18, 1926–1945 (2004)
S. Schubbert, K. Shannon, G. Bollag, Hyperactive Ras in developmental disorders and cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer 7, 295–308 (2007)
C. Segouffin-Cariou, M. Billaud, Transforming ability of MEN2A-RET requires activation of the phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/Akt signaling pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 3568–3576 (2000)
M. Drosten, G. Hilken, M. Böckmann, F. Rödicker, N. Mise, A.N. Cranston, U. Dahmen, B.A. Ponder, B.M. Pützer, Role of MEN2Aderived RET in maintenance and proliferation of medullary thyroid cancer. J. Natl Cancer Inst. 96, 1231–1239 (2004)
M.A. Kouvaraki, C. Liakou, A. Paraschi, K. Dimas, E. Patsouris, S. Tseleni-Balafouta, G.Z. Rassidakis, D. Moraitis, Activation of mTOR signaling in medullary and aggressive papillary thyroid carcinomas. Surgery. 150, 1258–1265 (2011)
M. Gild, I. Landa, M. Ryder, R.A. Ghossein, J.A. Knauf, J.A. Fagin, Targeting mTOR in RET mutant medullary and differentiated thyroid cancer cells. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 20, 659–667 (2013)
J.F. Burke, L. Schlosser, A.D. Harrison, M. Kunnimalaiyaan, H. Chen, MK-2206 causes growth suppression and reduces neuroendocrine tumor marker production in medullary thyroid cancer through Akt inhibition. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 20(12), 3862–3868 (2013)
S. Grozinsky-Glasberg, H. Rubinfeld, Y. Nordenberg, A. Gorshtein, M. Praiss, E. Kendler, R. Feinmesser, A.B. Grossman, I. Shimon, The rapamycin derivative RAD001 (everolimus) inhibits cell viability and interacts with the Akt-mTOR-p70S6K pathway in human medullary thyroid carcinoma cells. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 315, 87–94 (2010)
A. Faggiano, V. Ramundo, A. Dicitore, S. Castiglioni, M.O. Borghi, R. Severino, P. Ferolla, L. Crinò, A. Abbruzzese, P. Sperlongano, M. Caraglia, D. Ferone, L. Hofland, A. Colao, G. Vitale, Everolimus is an active agent in medullary thyroid cancer: a clinical and in vitro study. J. Cell Mol. Med. 16, 1563–1572 (2012)
S. Wang, R.V. Lloyd, M.J. Hutzler, M.S. Safran, N.A. Patwardhan, A. Khan, The role of cell cycle regulatory protein, cyclin D1, in the progression of thyroid cancer. Mod. Pathol. 13, 882–887 (2000)
S.M. Jafarmejad, G. Li, Regulation of p53 by ING family members in suppression of tumor initiation and progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 31(1–2), 55–73 (2012)
M. Kunnimayalaan, M. Ndiaye, H. Chen, Apoptosis-mediated medullary thyroid cancer growth suppression by the PI3K inhibitor LY294002. Surgery 140(6), 1009–1015 (2006)
R. Frédérick, C. Mawson, J.D. Kendall, C. Chaussade, G.W. Rewcastle, P.R. Shepherd, W.A. Denny, Phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K) inhibitors: identification of new scaffolds using virtual screening. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 19(20), 5842–5847 (2009)
S.F. Lin, Y.Y. Huang, J.D. Lin, T.C. Chou, C. Hsueh, R.J. Wong, Utility of a PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor (NVP-BEZ235) for Thyroid Cancer Therapy. PLoS One 7(10), e46726 (2012)
M.L. Gild, I. Landa, M. Ryder, R.A. Ghossein, J.A. Knauf, J.A. Fagin, Targeting mTOR in RET mutant medullary and differentiated thyroid cancer cells. Endocr. Relat. Cancer 20(5), 659–667 (2013)
C.D. Britten, PI3K and MEK inhibitor combinations: examining the evidence in selected tumor types. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 71(6), 1395–1409 (2013)
N. Jin, T. Jiang, D.M. Rosen, B.D. Nelkin, D.W. Ball, Synergistic Action of a RAF Inhibitor and a Dual PI3K/mTOR Inhibitor in Thyroid Cancer. Clin. Cancer Res. 17, 6482–6489 (2011)
M. Druce, T.T. Chung, S. Grozinsky-Glasberg, D.J. Gross, A.B. Grossman, Preliminary report of the use of everolimus in a patient with progressive medullary thyroid carcinoma. Clin. Endocrinol. 77(1), 154–155 (2012)
S.M. Lim, H. Chang, M.J. Yoon, Y.K. Hong, H. Kim, W.Y. Chung, C.S. Park, K.H. Nam, S.W. Kang, M.K. Kim, S.B. Kim, S.H. Lee, H.G. Kim, I.I. Na, Y.S. Kim, M.Y. Choi, J.G. Kim, K.U. Park, H.J. Yun, J.H. Kim, B.C. Cho, A multicenter, phase II trial of everolimus in locally advanced or metastatic thyroid cancer of all histologic subtypes. Ann. Oncol. 24(12), 3089–3094 (2013)
http://www.clinicaltrials.gov/. Accessed 8 Aug 2014
Acknowledgments
This work was partially supported by the Italian Ministry of Education, Research and University (FIRB RBAP11884 M).
Conflict of interest
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manfredi, G.I., Dicitore, A., Gaudenzi, G. et al. PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling in medullary thyroid cancer: a promising molecular target for cancer therapy. Endocrine 48, 363–370 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0380-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-014-0380-1