Abstract
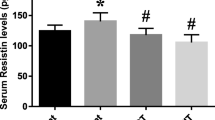
Inflammation plays an important role in the genesis and progression of diabetes. The purpose of this study was to investigate the effect of resistance training on serum levels of some inflammatory markers associated with diabetes mellitus. Twenty-four male Wistar rats (290 ± 19 g) were randomly divided into three groups: non-diabetic control (non-DC), diabetic control (DC), and diabetic trained (DT). Animals in DT group were subjected to a resistance training program with the use of a ladder (3 days/week, for 4 weeks). Body weight, serum high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hs-CRP), interleukin (IL)-6, tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α, fasting glucose, and insulin were measured. Four weeks of resistance training decreased serum levels of TNF-α, hs-CRP, and IL-6 in diabetic rats when compared with DC animals. We conclude that resistance training with appropriate intensity, duration, and recovery between exercise bouts has marked anti-inflammatory effects on diabetic rats. This may be an efficient strategy to protect against some diabetic complications.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
N.E. Gulcelik, A. Usman, A. Gürlek, Role of adipocytokines in predicting the development of diabetes and its late complications. Endocrine 36, 397–403 (2009)
K.I. Alexandraki, C. Piperi, P.D. Ziakas, N.V. Apostolopoulos, K. Makrilakis, V. Syriou, E. Diamanti-Kandarakis, G. Kaltsas, A. Kalofoutis, Cytokine secretion in long-standing diabetes mellitus type 1 and 2: associations with low-grade systemic inflammation. J. Clin. Immunol. 28, 314–321 (2008)
M. Brownlee, The pathobiology of diabetic complications: a unifying mechanism. Diabetes 54, 5–1615 (2005)
H. Tilg, A.R. Moschen, Inflammatory mechanisms in the regulation of insulin resistance. Mol. Med. 14, 222–231 (2008)
B.K. Pedersen, The anti-inflammatory effect of exercise: its role in diabetes and cardiovascular disease control. Essays Biochem. 42, 105–117 (2006)
C.J. Caspersen, J.E. Fulton, Epidemiology of walking and type 2 diabetes. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 40, 519–528 (2008)
P.T. Williams, Reduced diabetic, hypertensive, and cholesterol medication use with walking. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 40, 433–443 (2008)
C.R. Bruce, J.A. Hawley, Improvements in insulin resistance with aerobic exercise training: a lipocentric approach. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 36, 1–1196 (2004)
I.C. Ribeiro, R.T. Iborra, M.Q. Neves, S.A. Lottenberg, A.M. Charf, V.S. Nunes, C.E. Negrão, E.R. Nakandakare, E.C. Quintão, M. Passarelli, HDL atheroprotection by aerobic exercise training in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 40, 779–786 (2008)
K.R. Wilund, Is the anti-inflammatory effect of regular exercise responsible for reduced cardiovascular disease? Clin. Sci. (Lond) 112, 543–555 (2007)
Z.Z. Li, J.B. Liu, L. Jiao, L. Chen, Intensive therapy for diabetes through influence on innate immune system. Med. Hypotheses 72, 675–676 (2009)
N. Mathur, B.K. Pedersen, Exercise as a mean to control low-grade systemic inflammation. Mediators Inflamm. 2008, 109502 (2008)
N.E. Zanchi, F.S. Lira, M.A. de Siqueira Filho, J.C. Rosa, C.R. de Oliveira Carvalho, M. Seelaender, R.V. Santos, A.H. Lancha Jr, Chronic low frequency/low volume resistance training reduces pro-inflammatory cytokine protein levels and TLR4 mRNA in rat skeletal muscle. Eur. J. Appl. Physiol. 109(6), 1095–1102 (2010)
J. Peake, K. Nosaka, K. Suzuki, Characterization of inflammatory responses to eccentric exercise in humans. Exerc. Immunol. Rev. 11, 64–85 (2005)
J.Y. Yang, J.H. Nam, H. Park, Y.S. Cha, Effects of resistance exercise and growth hormone administration at low doses on lipid metabolism in middle-aged female rats. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 539, 99–107 (2006)
L. Pedersen, B.K. Hoffman-Goetz, Exercise and the immune system: regulation, integration, and adaptation. Physiol. Rev. 80, 1055–1081 (2000)
J. Hirosumi, G. Tuncman, L. Chang, C.Z. Görgün, K.T. Uysal, K. Maeda, M. Karin, G.S. Hotamisligil, A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 420, 333–336 (2002)
G.S. Hotamisligil, N.S. Shargill, B.M. Spiegelman, Adipose expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha: direct role in obesity-linked insulin resistance. Science 259, 87–91 (1993)
G.S. Hotamisligil, Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature 444, 860–867 (2006)
K.E. Wellen, G.S. Hotamisligil, Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J. Clin. Invest. 115, 1111–1119 (2005)
M.J. Puglisi, M.L. Fernandez, Modulation of C-reactive protein, tumor necrosis factor-alpha, and adiponectin by diet, exercise, and weight loss. J. Nutr. 138, 2293–2296 (2008)
B.J. Nicklas, F.C. Hsu, T.J. Brinkley, T. Church, B.H. Goodpaster, S.B. Kritchevsky, M. Pahor, Exercise training and plasma C-reactive protein and interleukin-6 in elderly people. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 56, 2045–2052 (2008)
N.P. Kadoglou, F. Iliadis, N. Angelopoulou, D. Perrea, G. Ampatzidis, C.D. Liapis, M. Alevizos, The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise training in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Eur. J. Cardiovasc. Prev. Rehabil. 14, 3–837 (2007)
G.Q. Chen, C.Y. Mou, Y.Q. Yang, S. Wang, Z.W. Zhao, Exercise training has beneficial anti-atrophy effects by inhibiting oxidative stress-induced MuRF1 upregulation in rats with diabetes. Life Sci. 89(1–2), 44–49 (2011)
L. Martín-Cordero, J.J. García, M.D. Hinchado, E. Ortega, The interleukin-6 and noradrenaline mediated inflammation-stress feedback mechanism is dysregulated in metabolic syndrome: effect of exercise. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 10, 42 (2011)
G. Howatson, K.A. van Someren, The prevention and treatment of exercise-induced muscle damage. Sports Med. 38, 483–503 (2008)
P. Liao, J. Zhou, L.L. Ji, Y. Zhang, Eccentric contraction induces inflammatory responses in rat skeletal muscle: role of tumor necrosis factor-α. Am. J. Physiol. Regul. Integr. Comp. Physiol. 298, 599–607 (2010)
A.M. Petersen, B.K. Pedersen, The anti-inflammatory effect of exercise. J. Appl. Physiol. 98, 1154–1162 (2005)
M.P. Miles, How do we solve the puzzle of unintended consequences of inflammation? Systematically. J. Appl. Physiol. 105, 1023–1025 (2008)
B. Zinman, N. Ruderman, B.N. Campaigne, J.T. Devlin, S.H. Schneider, American Diabetes Association, Physical activity/exercise and diabetes. Diabetes Care 27, S58–S62 (2004)
T. Enoki, Y. Yoshida, H. Hatta, A. Bonen, Exercise training alleviates MCT1 and MCT4 reductions in heart and skeletal muscles of STZ-induced diabetic rats. J. Appl. Physiol. 94, 2433–2438 (2003)
C. Mostarda, A. Rogow, I.C.M. Silva, R.N. De La Fuente, L. Jorge, B. Rodrigues, M.V. Heeren, E.G. Caldini, K. De Angelis, M.C. Irigoyen, Benefits of exercise training in diabetic rats persist after three weeks of detraining. Auton. Neurosci. 145(1–2), 11–16 (2009)
O. Coskun, A. Ocakci, T. Bayraktaroglu, M. Kanter, Exercise training prevents and protects streptozotocin-induced oxidative stress and beta-cell damage in rat pancreas. Tohoku J. Exp. Med. 203(3), 145–154 (2004)
D.M. Crespilho, J.A.C. de Almeida Leme, M.A.R. de Mello, E. Luciano, Effects of physical training on the immune system in diabetic rats. Int. J. Diabetes Dev. Ctries 30(1), 33–37 (2010)
M.D. Hordern, D.W. Dunstan, J.B. Prins, M.K. Baker, M.A. Singh, J.S. Coombes, Exercise prescription for patients with type 2 diabetes and pre-diabetes: a position statement from exercise and sport science Australia. J. Sci. Med. Sport 15(1), 25–31 (2012)
M. Brownlee, The pathobiology of diabetic complications: a unifying mechanism. Diabetes 54, 5–1615 (2005)
N. Kajitani, K. Shikata, A. Nakamura, T. Nakatou, M. Hiramatsu, H. Makino, Microinflammation is a common risk factor for progression of nephropathy and atherosclerosis in Japanese type 2 diabetes mellitus. Diab. Res. Clin. Pract. 88, 171–176 (2010)
M. Koulmanda, E. Budo, S. Bonner-Weir, A. Qipo, P. Putheti, N. Degauque, H. Shi, Z. Fan, J.S. Flier, H. Auchincloss Jr, X.X. Zheng, T.B. Strom, Modification of adverse inflammation is required to cure new-onset type 1 diabetic hosts. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 104(32), 13074–13079 (2007)
T.H. Reynolds 4th, M.A. Supiano, D.R. Dengel, Resistance training enhances insulin-mediated glucose disposal with minimal effect on the tumor necrosis factor-alpha system in older hypertensives. Metabolism 53, 397–402 (2004)
N. Brooks, J.E. Layne, P.L. Gordon, R. Roubenoff, M.E. Nelson, C. Castaneda- Sceppa, Strength training improves muscle quality and insulin sensitivity in Hispanic older adults with type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Med. Sci. 4, 19–27 (2007)
M.L. Kohut, D.A. McCann, D.W. Russell, D.N. Konopka, J.E. Cunnick, W.D. Franke, M.C. Castillo, A.E. Reighard, E. Vanderah, Aerobic exercise, but not flexibility/resistance exercise, reduces serum IL-18, CRP, and IL-6 independent of betablockers, BMI, and psychosocial factors in older adults. Brain Behav. Immun. 20, 201–209 (2006)
T.P. Olson, D.R. Dengel, A.S. Leon, K.H. Schmitz, Changes in inflammatory biomarkers following one-year of moderate resistance training in overweight women. Int. J. Obes. 31, 996–1003 (2007)
M. Shehab, E.K. Abd, Aerobic versus resistance exercise training in modulation of insulin resistance, adipocytokines and inflammatory cytokine levels in obese type 2 diabetic patients. J. Adv. Res. 2, 179–183 (2011)
S. Kang, J.H. Woo, K.O. Shin, D. Kim, H.J. Lee, Y.J. Kim, N.H. Yeo, Circuit resistance exercise improves glycemic control and adipokines in females with type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Sports Sci. Med. 8, 682–688 (2009)
M.L. Jorge, V.N. de Oliveira, N.M. Resende, L.F. Paraiso, A. Calixto, A.L. Diniz, E.S. Resende, E.R. Ropelle, J.B. Carvalheira, F.S. Espindola, P.T. Jorge, B. Geloneze, The effects of aerobic, resistance, and combined exercise on metabolic control, inflammatory markers, adipocytokines, and muscle insulin signaling in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Metabolism 60, 1244–1252 (2011)
I. Levinger, C. Goodman, J. Peake, A. Garnham, D.L. Hare, G. Jerums, S. Selig, Inflammation, hepatic enzymes and resistance training in individuals with metabolic risk factors. Diabet. Med. 26, 220–227 (2009)
K.D. Flack, K.P. Davy, M.W. Hulver, R.A. Winett, M.I. Frisard, B.M. Davy, Aging, resistance training and diabetes prevention. J. Aging Res. 2011, 127315 (2011)
S. Balducci, S. Zanuso, A. Nicolucci, F. Fernando, S. Cavallo, P. Cardelli, S. Fallucca, E. Alessi, C. Letizia, A. Jimenez, F. Fallucca, G. Pugliese, Anti-inflammatory effect of exercise training in subjects with type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome is dependent on exercise modalities and independent of weight loss. Nutr. Metab. Cardiovasc. Dis. 20, 608–617 (2010)
B.F. de Salles, R. Simão, S.J. Fleck, I. Dias, L.G. Kraemer-Aguiar, E. Bouskela, Effects of resistance training on cytokines. Int. J. Sports Med. 31, 441–450 (2010)
C. Kasapis, P.D. Thompson, The effects of physical activity on serum Creactive protein and inflammatory markers: a systematic review. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 45, 1563–1569 (2005)
M. Gleeson, N.C. Bishop, D.J. Stensel, M.R. Lindley, S.S. Mastana, M.A. Nimmo, The anti-inflammatory effects of exercise: mechanisms and implications for the prevention and treatment of disease. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 11, 607–615 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Talebi-Garakani, E., Safarzade, A. Resistance training decreases serum inflammatory markers in diabetic rats. Endocrine 43, 564–570 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-012-9786-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-012-9786-9