Abstract
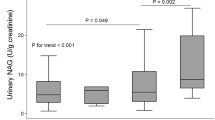
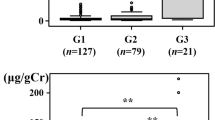
The aim of this study was to assess the relationship between urinary Smad1 and glomerular hyperfiltration (GHF) in type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM), and to explore the factors related to the urinary Smad1 in T2DM. The reference value of the estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR) was determined in 248 healthy individuals. 30 patients with GHF, 58 patients with norm-GFR T2DM, and 24 healthy patients who served as controls were recruited. Urinary Smad1, fasting plasma glucose (FPG), fasting serum C-Peptide (C-P), hemoglobin A1C (HbA1c), cystatin C, and other chemistry laboratory parameters of T2DM participants and controls were measured. Patients with GHF had higher levels of urinary Smad1 than the control group, and those with norm-GFR. For T2DM patients with body mass index, age, and gender adjustments, urinary Smad1 was positively correlated with FPG, HbA1C, and eGFR, but negatively correlated with fasting serum C-P. Multivariate linear regression analysis demonstrated that eGFR, HbA1C, and fasting serum C-P were independently associated with urinary Smad1. High levels of urinary Smad1 were found in GHF patients with T2DM, which may be another potential mechanism of GHF in relation to diabetic nephropathy.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
M. Krolewski, P.W. Eggers, J.H. Warram, Magnitude of end-stage renal disease in IDDM: a 35 year follow-up study. Kidney Int. 50, 2041–2046 (1996)
M. Bojestig, H.J. Arnqvist, G. Hermansson et al., Declining incidence of nephropathy in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N. Engl. J. Med. 330, 15–18 (1994)
B.M. Brenner, Hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury and the progressive nature of kidney disease. Kidney Int. 23, 647–655 (1983)
W.J. Fu, S.L. Xiong, Y.G. Fang et al., Urinary tubular biomarkers in short-term type 2 diabetes mellitus patients: a cross-sectional study. Endocrine 41, 82–88 (2012)
M. von Eynatten, M. Baumann, U. Heemann et al., Urinary L-FABP and anaemia: distinct roles of urinary markers in type diabetes. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 40, 95–102 (2010)
T. Matsubara, H. Abe, H. Arai et al., Expression of Smad1 is directly associated with mesangial matrix expansion in rat diabetic nephropathy. Lab. Investig. 86(4), 357–368 (2006)
P.A. Hoodless, T. Haerry, S. Abdollah et al., MADR1, a MAD-related protein that functions in BMP2 signaling pathways. Cell 85, 489–500 (1996)
M. Wang, H. Jin, D. Tang et al., Smad1 plays an essential role in bone development and postnatal bone formation. Osteoarthritis Cartil. 19(6), 751–762 (2011)
K.D. Tremblay, N.R. Dunn, E. Robertson, Mouse embryos lacking Smad1 signals display defects in extra-embryonic tissues and germ cell formation. Development 28, 3609–3621 (2001)
Rosolowsky ET, Niewczas MA, Ficociello LH, et al., Between hyperfiltration and impairment: demystifying early renal functional changes in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes. Res. Clin. Pract. 13(S1), S46–53 (2008)
B.M. Brenner, T.W. Meyer, T.H. Hostetter, Dietary protein intake and the progressive nature of kidney disease: the role of hemodynamically mediated glomerular injury in the pathogenesis of progressive glomerular sclerosis in aging, renal ablation, and intrinsic renal disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 307, 652–659 (1982)
M.P. O’Donnell, B.L. Kasiske, W.F. Keane, Glomerular hemodynamic and structural alterations in experimental diabetes mellitus. FASEB J. 2(8), 2339–2344 (1988)
G. Gruden, S. Thomas, D. Burt et al., Mechanical stretch induces vascular permeability factor in human mesangial cells: Mechanisms of signal transduction Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 94, 12112–12116 (1997)
W.J. Fu, B.L. Li, S.B. Wang et al., Changes of the tubular markers in type 2 diabetes mellitus with glomerular hyperfiltration. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 95(1), 105–109 (2012)
R.J. Macisaac, C. Tsalamandris, M.C. Thomas et al., Estimating glomerular filtration rate in diabetes: a comparison of cystatin-C- and creatinine-based methods. Diabetologia 49, 1686–1689 (2006)
L.H. Ficociello, B.A. Perkins, B. Roshan et al., Renal hyperfiltration and the development of microalbuminuria in type 1 diabetes. Diabetes Care 32, 889–893 (2009)
R. Bruce, M. Rutland, T. Cundy, Glomerular hyperfiltration in young Polynesians with type 2 diabetes. Diab. Res. Clin. Pract. 25, 155–160 (1994)
P. Vedel, J. Obel, F.S. Nielsen et al., Glomerular hyperfiltration in microalbuminuric NIDD patients. Diabetologia 39, 1584–1589 (1996)
C.K. Keller, K.H. Bergis, D. Fliser, E. Ritz, Renal findings in patients with short-term type 2 diabetes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 7, 2627–2635 (1996)
S.P. Silviero, R. Friedman, M.J. Azevedo et al., Five year prospective study of the glomerular filtration rate and albumin excretion rate in normofiltering and hyperfiltering normoalbuminuric NIDDM patients. Diabetes Care 19, 171–174 (1996)
G.D. Tan, A.V. Lewis, T.J. James et al., Clinical usefulness of cystatin C for the estimation of glomerular filtration rate in type 1 diabetes: reproducibility and accuracy compared with standard measures and iohexol clearance. Diabetes Care 25, 2004–2009 (2002)
Y. Jin, T. Moriya, K. Tanaka et al., Glomerular hyperfiltration in non-proteinuric and non-hypertensive Japanese type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 71, 264–271 (2006)
A. Mima, H. Arai, T. Matsubara et al., Urinary Smad1 is a novel marker to predict later on set of mesangial matrix expansion in diabetic nephropathy. Diabetes 57(6), 1712–1722 (2008)
G. Gruden, S. Zonca, A. Hayward et al., Mechanical stretch-induced fibronectin and transforming growth factor-beta1 production in human mesangial cells is p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase-dependent. Diabetes 49(4), 655–661 (2000)
S.W. Hong, M. Isono, S. Chen et al., Increased glomerular and tubular expression of transforming growth factor-beta1, its type II receptor, and activation of the Smad signaling pathway in the db/db mouse. Am. J. Pathol. 158(5), 1653–1663 (2001)
H. Jia, L. Yu, B. Gao, Q. Ji, Association between the T869C polymorphism of transforming growth factor-beta 1 and diabetic nephropathy: a meta-analysis. Endocrine 40(3), 372–378 (2011)
H. Abe, T. Matsubara, H. Arai et al., Role of Smad1 in diabetic nephropathy: molecular mechanisms and implications as a diagnostic marker. Histol. Histopathol. 26(4), 531–541 (2011)
C.E. Hills, N. Al-Rasheed, N. Al-Rasheed et al., C-peptide reverses TGF-beta1-induced changes in renal proximal tubular cells: implications for treatment of diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Physiol. Renal. Physiol. 296(3), F614–F621 (2009)
C.E. Hills, N.J. Brunskill, P.E. Squires, C-peptide as a therapeutic tool in diabetic nephropathy. Am. J. Nephrol. 31(5), 389–397 (2010)
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the funds from the Scientific and Technological Projects of Dongguan City, Guangdong Province, People’s Republic of China.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fu, WJ., Fang, YG., Deng, RT. et al. Correlation of high urinary Smad1 level with glomerular hyperfiltration in type 2 diabetes mellitus. Endocrine 43, 346–350 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-012-9741-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-012-9741-9