Abstract
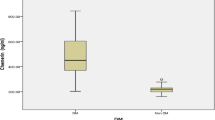
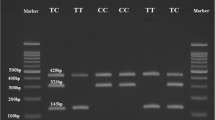
Serum retinal binding protein 4 (RBP4) was recently described as a new liver- and adipocyte-derived signal that may contribute to Type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and insulin resistance. The aim of this study was to test whether the RBP4 gene could be used as a genetic marker to predict the development of T2DM amongst the Chinese population of Han. For this study, a normal control group of 115 healthy subjects and an experimental group of 107 patients with T2DM were examined. A combined method of denaturing high-performance liquid chromatography (DHPLC) and sequencing was applied to the detection of the RBP4 gene variants. Two SNPs, rs17484721 and rs36035572, were analyzed. Phenotypes and biochemical indicators related to the metabolism of glucose and lipid were measured. We found that there are significant differences between the control group and the patients group in terms of their respective distributions of genotype and allele frequency. The TG levels of the TT and II genotype was significantly higher than that of the TC + CC and ID + DD, respectively, in both patient group and control group. These findings suggest that the variations in the RBP4 gene may be associated with T2DM and serum triglyeride levels in the Han Chinese.


Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Electronic version of Diabetes Atlas. Executive summary, 2nd ed. International Diabetes Federation. (2003). http://www.eatlas.idf.org/webdata/docs/Atlas%202003-Summary.pdf
M. Stumvoll, B.J. Goldstein, T.W. van Haeften, Lancet 365, 1333–1346 (2005)
S.K. Das, S.C. Elbein, Cell Sci. Rev. 2, 1–32 (2006)
L. Hutley, J.B. Prins, Am. J. Med. Sci. 330, 280–289 (2005)
Q. Yang, T.E. Graham, N. Mody, F. Preitner, O.D. Peroni, J.M. Zabolotny, K. Kotani, L. Quadro, B.B. Kahn, Nature 436, 356–362 (2005)
Y. Tamori, H. Sakaue, M. Kasuga, Nat. Med. 12(1), 30–31 (2006)
Y.M. Cho, B.S. Youn, H. Lee, N. Lee, S.S. Min, S.H. Kwak, H.K. Lee, K.S. Park, Diabetes Care 29, 2457–2461 (2006)
M. Broch, J. Vendrell, W. Ricart, C. Richart, J.M. Fernandez Real, Diabetes Care 30, 1802–1806 (2007)
T.E. Graham, Q. Yang, M. Bluher, A. Hammarstedt, T.P. Ciaraldi, R.R. Henry, C.J. Wason, A. Oberbach, P.A. Jansson, U. Smith, B.B.N. Kahn, Engl. J. Med. 354(24), 2552–2563 (2006)
Q. Qi, Z. Yu, X. Ye, F. Zhao, P. Huang, F.B. H u, O.H. Franco, J. Wang, H. Li, Y. Liu, Lin X. Elevated, J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 92(12), 4827–4834 (2007)
A. Ost, A. Danielsson, M. Lidén, FASEB J. 21(13), 3696–3704 (2007)
K.S. Polonsky, N. Engl. J. Med. 354, 2596–2598 (2006)
J.B. Meigs, C.I. Panhuysen, R.H. Myers, P.W. Wilson, L.A. Cupples, Diabetes 51, 833–840 (2002)
R. Duggirala, J. Blangero, L. Almasy, T.D. Dyer, K.L. Williams, R.J. Leach, P. O’Connell, M.P. Stern(1999). Am. J. Hum. Genet. 64:1127–1140.
R.L. Craig, W.S. Chu, S.C. Elbein, Mol. Genet. Metab. 90(3), 338–344 (2007)
L. Munkhtulga, K. Nakayama, N. Utsumi, Y. Yanagisawa, T. Gotoh, T. Omi, M. Kumada, B. Erdenebulgan, K. Zolzaya, T. Lkhagvasuren, S. Iwamoto, Hum. Genet. 120(6), 879–888 (2007)
P. Zimmet, Diabetes Care 2, 144–153 (1979)
A.K. Diehl, M.P. Stern, Adv. Intern. Med. 34, 73–96 (1989)
P.M. McKeigue, B. Shah, M.G. Marmot, Lancet 337, 382–386 (1991)
M.A. Banerji, H.E. Lebovitz, Diabetes 38, 784–792 (1989)
P. Arner, T. Pollare, H. Lithell, Diabetologia 34, 483–487 (1991)
A. Taniguchi, Y. Nakai, M. Fukushima, H. Kawamura, H. Imura, I. Nagata, K. Tokuyama, Diabetes 41, 1540–1546 (1992)
A. Hirasawa, K. Tsumaya, T. Awaji, S. Katsuma, T. Adachi, M. Yamada, Y. Sugimoto, S. Miyazaki, G. Tsujimoto, Nat. Med. 11(1), 90–94 (2005)
R. Perfetti, P. Merkel, Eur. J. Endocrinol. 143, 717–725 (2000)
M. Dong, Y.H. Gong , L. Wang, Hereditas (Bejing) 25(2), 205–207 (2003)
Acknowledgments
Supported by the grant of National Natural Science Foundation of China (30571014), the grant of platform of Genetic resource of Chinese people project from Ministry of Science and Technology of People’s Republic of China (2003DEA3N026), Program for New Century Excellent Talents in University from Ministry of Education of People’s Republic of China (NCET-05-0885), and the Key project of Science and Technology of Gansu Province (grant No. 2GS064-A43-020-25).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Gao, Jy., Zhang, Jp. et al. Evaluation of the association between retinal binding protein 4 polymorphisms and type 2 diabetes in Chinese by DHPLC. Endocr 34, 23–28 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-008-9097-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12020-008-9097-3