Abstract
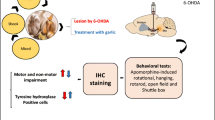
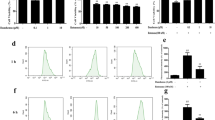
The effects of germinated brown rice (GBR) on the motor deficits and the dopaminergic (DA) cell death were investigated in Parkinson’s-like disease (PD) rats. Reactive oxidative species generated by chronic subcutaneous injection of rotenone (RT) lead to neuronal apoptosis particularly in the nigrostriatal DA system and produce many features of PD, bradykinesis, postural instability and rigidity. In this study, 4-phenylbutyric acid (4-PBA), previously reported to inhibit RT-induced DA cell death, was used as the positive control. Results show that pretreatment with GBR as well as 4-PBA significantly enhanced the motor activity after RT injection, and GBR affected significantly in open field test, only in the ambulation but not the mobility duration, and ameliorated the time to orient down (t-turn) and total time to descend the pole (t-total) in pole test as compared to RT group, but significantly lowered both t-turn and t-total only in 4-PBA group. The percentage of apoptotic cells in brain measured by flow cytometry and the inflammatory effect measured by ELISA of TNF-α showed significant increase in RT group as compared to the control (CT) group at P < 0.05. Apoptotic cells in RT group (85.98 %) showed a significant (P < 0.05) increase versus CT group (17.50 %), and this effect was attenuated in GBR+RT group by decreasing apoptotic cells (79.32 %), whereas, increased viable cells (17.94 %) versus RT group (10.79 %). GBR in GBR + RT group could decrease TNF-α both in the serum and in brain. In summary, GBR showed a neuroprotective effect in RT-induced PD rats, and it may be useful as a value-added functional food to prevent neurodegenerative disease or PD.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azmi, N. H., Ismail, N., Imam, M. U., & Ismail, M. (2013). Ethyl acetate extract of germinated brown rice attenuates hydrogen peroxide-induced oxidative stress in human SH-SY5Y neuroblastoma cells: role of anti-apoptotic, pro-survival and antioxidant genes. BMC Complement Altern Med, 13, 177.
Ballesteros, I., Cuartero, M. I., Moraga, A., de la Parra, J., Lizasoain, I., & Moro, M. A. (2014). Stereological and flow cytometry characterization of leukocyte subpopulations in models of transient or permanent cerebral ischemia. Journal of Visualized Experiments. doi:10.3791/52031.
Beal, M. F. (2001). Experimental models of Parkinson’s disease. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 2(5), 325–334.
Betarbet, R., Sherer, T. B., MacKenzie, G., Garcia-Osuna, M., Panov, A. V., & Greenamyre, J. T. (2000). Chronic systemic pesticide exposure reproduces features of Parkinson’s disease. Nature Neuroscience, 3(12), 1301–1306.
Carducci, M. A., Gilbert, J., Bowling, M. K., Noe, D., Eisenberger, M. A., Sinibaldi, V., et al. (2001). A Phase I clinical and pharmacological evaluation of sodium phenylbutyrate on an 120-h infusion schedule. Clinical Cancer Research, 7(10), 3047–3055.
Cho, D. H., & Lim, S. T. (2016). Germinated brown rice and its bio-functional compounds. Food Chemistry, 196, 259–271.
Collins, A. F., Pearson, H. A., Giardina, P., McDonagh, K. T., Brusilow, S. W., & Dover, G. J. (1995). Oral sodium phenylbutyrate therapy in homozygous beta thalassemia: A clinical trial. Blood, 85(1), 43–49.
de Jong, P. J., Lakke, J. P., & Teelken, A. W. (1984). CSF GABA levels in Parkinson’s disease. Advances in Neurology, 40, 427–430.
Gardian, G., Browne, S. E., Choi, D. K., Klivenyi, P., Gregorio, J., Kubilus, J. K., et al. (2005). Neuroprotective effects of phenylbutyrate in the N171-82Q transgenic mouse model of Huntington’s disease. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280(1), 556–563.
Gardian, G., Yang, L., Cleren, C., Calingasan, N. Y., Klivenyi, P., & Beal, M. F. (2004). Neuroprotective effects of phenylbutyrate against MPTP neurotoxicity. Neuromolecular Med, 5(3), 235–241.
Gorell, J. M., Johnson, C. C., Rybicki, B. A., Peterson, E. L., & Richardson, R. J. (1998). The risk of Parkinson’s disease with exposure to pesticides, farming, well water, and rural living. Neurology, 50(5), 1346–1350.
Hirata, Y., Suzuno, H., Tsuruta, T., Oh-hashi, K., & Kiuchi, K. (2008). The role of dopamine transporter in selective toxicity of manganese and rotenone. Toxicology, 244(2–3), 249–256.
Ho, J. N., Son, M. E., Lim, W. C., Lim, S. T., & Cho, H. Y. (2012). Anti-obesity effects of germinated brown rice extract through down-regulation of lipogenic genes in high fat diet-induced obese mice. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 76(6), 1068–1074.
Inden, M., Kitamura, Y., Takeuchi, H., Yanagida, T., Takata, K., Kobayashi, Y., et al. (2007). Neurodegeneration of mouse nigrostriatal dopaminergic system induced by repeated oral administration of rotenone is prevented by 4-phenylbutyrate, a chemical chaperone. Journal of Neurochemistry, 101(6), 1491–1504.
Inden, M., Taira, T., Kitamura, Y., Yanagida, T., Tsuchiya, D., Takata, K., et al. (2006). PARK7 DJ-1 protects against degeneration of nigral dopaminergic neurons in Parkinson’s disease rat model. Neurobiology of Diseases, 24(1), 144–158.
Ismail, N., Ismail, M., Fathy, S. F., Musa, S. N., Imam, M. U., Foo, J. B., et al. (2012). Neuroprotective effects of germinated brown rice against hydrogen peroxide induced cell death in human SH-SY5Y cells. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 13(8), 9692–9708.
Iwatsubo, T., Yamaguchi, H., Fujimuro, M., Yokosawa, H., Ihara, Y., Trojanowski, J. Q., et al. (1996). Purification and characterization of Lewy bodies from the brains of patients with diffuse Lewy body disease. American Journal of Pathology, 148(5), 1517–1529.
Kim, H. S., Lee, E. J., Lim, S. T., & Han, J. A. (2015). Self-enhancement of GABA in rice bran using various stress treatments. Food Chemistry, 172, 657–662.
Kitada, T., Asakawa, S., Hattori, N., Matsumine, H., Yamamura, Y., Minoshima, S., et al. (1998). Mutations in the parkin gene cause autosomal recessive juvenile parkinsonism. Nature, 392(6676), 605–608.
Leroy, E., Boyer, R., Auburger, G., Leube, B., Ulm, G., Mezey, E., et al. (1998). The ubiquitin pathway in Parkinson’s disease. Nature, 395(6701), 451–452.
Lin, Y. T., Pao, C. C., Wu, S. T., & Chang, C. Y. (2015). Effect of different germination conditions on antioxidative properties and bioactive compounds of germinated brown rice. Biomed Res Int, 2015, 608761.
Maestri, N. E., Brusilow, S. W., Clissold, D. B., & Bassett, S. S. (1996). Long-term treatment of girls with ornithine transcarbamylase deficiency. New England Journal of Medicine, 335(12), 855–859.
Mamiya, T., Kise, M., Morikawa, K., Aoto, H., Ukai, M., & Noda, Y. (2007). Effects of pre-germinated brown rice on depression-like behavior in mice. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 86(1), 62–67.
Marey-Semper, I., Gelman, M., & Levi-Strauss, M. (1995). A selective toxicity toward cultured mesencephalic dopaminergic neurons is induced by the synergistic effects of energetic metabolism impairment and NMDA receptor activation. Journal of Neuroscience, 15(9), 5912–5918.
Marino, M. J., Wittmann, M., Bradley, S. R., Hubert, G. W., Smith, Y., & Conn, P. J. (2001). Activation of group I metabotropic glutamate receptors produces a direct excitation and disinhibition of GABAergic projection neurons in the substantia nigra pars reticulata. Journal of Neuroscience, 21(18), 7001–7012.
Meissner, W., Leblois, A., Hansel, D., Bioulac, B., Gross, C. E., Benazzouz, A., et al. (2005). Subthalamic high frequency stimulation resets subthalamic firing and reduces abnormal oscillations. Brain, 128(Pt 10), 2372–2382.
Menegon, A., Board, P. G., Blackburn, A. C., Mellick, G. D., & Le Couteur, D. G. (1998). Parkinson’s disease, pesticides, and glutathione transferase polymorphisms. Lancet, 352(9137), 1344–1346.
Mercuri, E., Bertini, E., Messina, S., Pelliccioni, M., D’Amico, A., Colitto, F., et al. (2004). Pilot trial of phenylbutyrate in spinal muscular atrophy. Neuromuscular Disorders, 14(2), 130–135.
Mogi, M., Harada, M., Riederer, P., Narabayashi, H., Fujita, K., & Nagatsu, T. (1994). Tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) increases both in the brain and in the cerebrospinal fluid from parkinsonian patients. Neuroscience Letters, 165(1–2), 208–210.
Mogi, M., Togari, A., Ogawa, M., Ikeguchi, K., Shizuma, N., Fan, D., et al. (1998). Effects of repeated systemic administration of 1-methyl-4-phenyl-1,2,3,6-tetrahydropyridine (MPTP) to mice on interleukin-1beta and nerve growth factor in the striatum. Neuroscience Letters, 250(1), 25–28.
Mogi, M., Togari, A., Tanaka, K., Ogawa, N., Ichinose, H., & Nagatsu, T. (1999). Increase in level of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned striatum in rats without influence of systemic L-DOPA on the TNF-alpha induction. Neuroscience Letters, 268(2), 101–104.
Mohd Esa, N., Abdul Kadir, K. K., Amom, Z., & Azlan, A. (2013). Antioxidant activity of white rice, brown rice and germinated brown rice (in vivo and in vitro) and the effects on lipid peroxidation and liver enzymes in hyperlipidaemic rabbits. Food Chemistry, 141(2), 1306–1312.
Ng, L. T., Huang, S. H., Chen, Y. T., & Su, C. H. (2013). Changes of tocopherols, tocotrienols, gamma-oryzanol, and gamma-aminobutyric acid levels in the germinated brown rice of pigmented and nonpigmented cultivars. Journal of Agriculture and Food Chemistry, 61(51), 12604–12611.
Oh, C. H., & Oh, S. H. (2004). Effects of germinated brown rice extracts with enhanced levels of GABA on cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis. Journal of Medicinal Food, 7(1), 19–23.
Online document Mahmoud, S. M., Abdel Moneim, A. E. (2013). The Protective Effect of Pomegranate (Punica granatum) Juice against Carbon Tetrachloride-Induced Oxidative Stress in Brain Tissue of Adult Male Albino Rats. Resource document Life Science Journal, 10(1), 151-158. (ISSN:1097-8135), http://www.lifesciencesite.com. 22. doi:10.7537/marslsj100113.22.
Ono, K., Ikemoto, M., Kawarabayashi, T., Ikeda, M., Nishinakagawa, T., Hosokawa, M., et al. (2009). A chemical chaperone, sodium 4-phenylbutyric acid, attenuates the pathogenic potency in human alpha-synuclein A30P+A53T transgenic mice. Parkinsonism Relat Disord, 15(9), 649–654.
Ozcan, U., Yilmaz, E., Ozcan, L., Furuhashi, M., Vaillancourt, E., Smith, R. O., et al. (2006). Chemical chaperones reduce ER stress and restore glucose homeostasis in a mouse model of type 2 diabetes. Science, 313(5790), 1137–1140.
Park, H. J., Han, E. S., Park, D. K., Lee, C., & Lee, K. W. (2010). An extract of Phellinus linteus grown on germinated brown rice inhibits inflammation markers in RAW264.7 macrophages by suppressing inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and mediators and up-regulating antioxidant activity. Journal of Medicinal Food, 13(6), 1468–1477.
Parker, W. D, Jr., Boyson, S. J., & Parks, J. K. (1989). Abnormalities of the electron transport chain in idiopathic Parkinson’s disease. Ann Neurol, 26(6), 719–723.
Patil, S. B., & Khan, M. K. (2011). Germinated brown rice as a value added rice product: A review. Journal of Food Science and Technology, 48(6), 661–667.
Pober, Z., & Calhoun, W. K. (1975). Effect of oxethazaine HCl on control of food and water intake in the rat. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 3(1), 69–74.
Polymeropoulos, M. H., Lavedan, C., Leroy, E., Ide, S. E., Dehejia, A., Dutra, A., et al. (1997). Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science, 276(5321), 2045–2047.
Ren, Y., Liu, W., Jiang, H., Jiang, Q., & Feng, J. (2005). Selective vulnerability of dopaminergic neurons to microtubule depolymerization. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 280(40), 34105–34112.
Ryu, H., Smith, K., Camelo, S. I., Carreras, I., Lee, J., Iglesias, A. H., et al. (2005). Sodium phenylbutyrate prolongs survival and regulates expression of anti-apoptotic genes in transgenic amyotrophic lateral sclerosis mice. Journal of Neurochemistry, 93(5), 1087–1098.
Schapira, A. H. (1994). Mitochondrial function and neurotoxicity. Current Opinion in Neurology, 7(6), 531–534.
Schapira, A. H., Cooper, J. M., Dexter, D., Clark, J. B., Jenner, P., & Marsden, C. D. (1990). Mitochondrial complex I deficiency in Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurochemistry, 54(3), 823–827.
Sherer, T. B., Betarbet, R., Kim, J. H., & Greenamyre, J. T. (2003a). Selective microglial activation in the rat rotenone model of Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience Letters, 341(2), 87–90.
Sherer, T. B., Betarbet, R., Testa, C. M., Seo, B. B., Richardson, J. R., Kim, J. H., et al. (2003b). Mechanism of toxicity in rotenone models of Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neuroscience, 23(34), 10756–10764.
Sherer, T. B., Kim, J. H., Betarbet, R., & Greenamyre, J. T. (2003c). Subcutaneous rotenone exposure causes highly selective dopaminergic degeneration and alpha-synuclein aggregation. Experimental Neurology, 179(1), 9–16.
Shimohama, S., Sawada, H., Kitamura, Y., & Taniguchi, T. (2003). Disease model: Parkinson’s disease. Trends Mol Med, 9(8), 360–365.
Spillantini, M. G., Schmidt, M. L., Lee, V. M., Trojanowski, J. Q., Jakes, R., & Goedert, M. (1997). Alpha-synuclein in Lewy bodies. Nature, 388(6645), 839–840.
Swarnkar, S., Goswami, P., Kamat, P. K., Gupta, S., Patro, I. K., Singh, S., et al. (2012a). Rotenone-induced apoptosis and role of calcium: A study on Neuro-2a cells. Archives of Toxicology, 86(9), 1387–1397.
Swarnkar, S., Singh, S., Goswami, P., Mathur, R., Patro, I. K., & Nath, C. (2012b). Astrocyte activation: A key step in rotenone induced cytotoxicity and DNA damage. Neurochemical Research, 37(10), 2178–2189.
Taechowisan, T., Lu, C., Shen, Y., & Lumyong, S. (2007a). In vitro anti-inflammatory activity of 4-arylcoumarins from endophytic Streptomyces aureofaciens CMUAc130 in murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Natural Product Research, 21(12), 1104–1113.
Taechowisan, T., Tuntiwachwuttikul, P., Lu, C., Shen, Y., Lumyong, S., & Taylor, W. C. (2007b). Anti-inflammatory activity of 4-arylcoumarins from endophytic Streptomyces aureofaciens CMUAc130 in murine macrophage RAW 264.7 cells. Immunological Investigations, 36(2), 203–211.
Tansey, M. G., & Goldberg, M. S. (2010). Neuroinflammation in Parkinson’s disease: Its role in neuronal death and implications for therapeutic intervention. Neurobiology of Diseases, 37(3), 510–518.
Wu, F., Yang, N., Toure, A., Jin, Z., & Xu, X. (2013). Germinated brown rice and its role in human health. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition, 53(5), 451–463.
Yam, G. H., Gaplovska-Kysela, K., Zuber, C., & Roth, J. (2007). Sodium 4-phenylbutyrate acts as a chemical chaperone on misfolded myocilin to rescue cells from endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis. Investigative Ophthalmology and Visual Science, 48(4), 1683–1690.
Yamada, C., Izumi, H., Hirano, J., Mizukuchi, A., Kise, M., Matsuda, T., et al. (2005). Degradation of soluble proteins including some allergens in brown rice grains by endogenous proteolytic activity during germination and heat-processing. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 69(10), 1877–1883.
Zaitone, S. A., Abo-Elmatty, D. M., & Elshazly, S. M. (2012). Piracetam and vinpocetine ameliorate rotenone-induced Parkinsonism in rats. Indian J Pharmacol, 44(6), 774–779.
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge Miss Kanittar Srisook, Department of Pathology, Faculty of Medicine Siriraj Hospital, Mahidol University, for helping in the histopathological examination. We are very grateful for the generous providing of GBR from Institute of Nutrition, Mahidol University, Nakhon Pathom, Thailand.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no personal or professional conflicts of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chompoopong, S., Jarungjitaree, S., Punbanlaem, T. et al. Neuroprotective Effects of Germinated Brown Rice in Rotenone-Induced Parkinson’s-Like Disease Rats. Neuromol Med 18, 334–346 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-016-8427-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-016-8427-5