Abstract
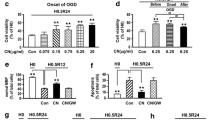
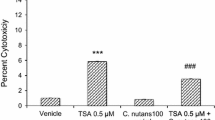
Many population-based epidemiological studies have unveiled an inverse correlation between intake of herbal plants and incidence of stroke. C. nutans is a traditional herbal medicine widely used for snake bite, viral infection and cancer in Asian countries. However, its role in protecting stroke damage remains to be studied. Despite of growing evidence to support epigenetic regulation in the pathogenesis and recovery of stroke, a clear understanding of the underlying molecular mechanisms is still lacking. In the present study, primary cortical neurons were subjected to in vitro oxygen–glucose deprivation (OGD)–reoxygenation and hypoxic neuronal death was used to investigate the interaction between C. nutans and histone deacetylases (HDACs). Using pharmacological agents (HDAC inhibitor/activator), loss-of-function (HDAC siRNA) and gain-of-function (HDAC plasmid) approaches, we demonstrated an early induction of HDAC1/2/3/8 and HDAC6 in neurons after OGD insult. C. nutans extract selectively inhibited HDAC1 and HDAC6 expression and attenuated neuronal death. Results of reporter analysis further revealed that C. nutans suppressed HDAC1 and HDAC6 transcription. Besides ameliorating neuronal death, C. nutans also protected astrocytes and endothelial cells from hypoxic-induced cell death. In summary, results support ability for C. nutans to suppress post-hypoxic HDACs activation and mitigate against OGD-induced neuronal death. This study further opens a new avenue for the use of herbal medicines to regulate epigenetic control of brain injury.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aune, S. E., Herr, D. J., Kutz, C. J., & Menick, D. R. (2015). Histone deacetylases exert class-specific roles in conditioning the brain and heart against acute ischemic injury. Frontiers Neurology, 6, 145.
Bellenguez, C., Bevan, S., Gschwendtner, A., & ISGC, WTCCC2. (2012). Genome-wide association study identifies a variant in HDAC9 associated with large vessel ischemic stroke. Nature Genetics, 44(3), 328–333.
Borghi, S. M., Carvalho, T. T., Staurengo-Ferrari, L., Hohmann, M. S., Pinge-Filho, P., Casagrande, R., et al. (2013). Vitexin inhibits inflammatory pain in mice by targeting TRPV1, oxidative stress, and cytokines. Journal of Natural Products, 76(6), 1141–1149.
Chen, Y. C., Wu, J. S., Yang, S. T., Huang, C. Y., Chang, C., Sun, G. Y., & Lin, T. N. (2012a). Stroke, angiogenesis and phytochemicals. Frontiers in Bioscience (Schol Ed)., 4, 599–610.
Chen, Y. T., Zang, X. F., Pan, J., Zhu, X. L., Chen, F., Chen, Z. B., & Xu, Y. (2012b). Expression patterns of histone deacetylases in experimental stroke and potential targets for neuroprotection. Clinical and Experimental Pharmacology and Physiology, 39(9), 751–758.
Daduang, S., Sattayasai, N., Sattayasai, J., Tophrom, P., Thammathaworn, A., Chaveerach, A., et al. (2005). Screening of plants containing Naja Naja siamensis cobra venom inhibitory activity using modified ELISA technique. Analytical Biochemistry, 341(2), 316–325.
Fessler, E. B., Chibane, F. L., Wang, Z., & Chuang, D. M. (2013). Potential roles of HDAC inhibitors in mitigating ischemia-induced brain damage and facilitating endogenous regeneration and recovery. Current Pharmaceutical Design, 19(28), 5105–5120.
Goldberg, M. P., & Choi, D. W. (1993). Combined oxygen and glucose deprivation in cortical cell culture: Calcium-dependent and calcium-independent mechanisms of neuronal injury. The Journal of neuroscience: The official journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 13(8), 3510–3524.
He, M., Zhang, B., Wei, X., Wang, Z., Fan, B., et al. (2013). HDAC4/5-HMGB1 signaling mediated by NADPH oxidase activity contributes to cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 17(4), 531–542.
Hu, C. J., Chen, S. D., Yang, D. I., Lin, T. N., Chen, C. M., Huang, T. H., & Hsu, C. Y. (2006). Promoter region methylation and reduced expression of thrombospondin-1 after oxygen-glucose deprivation in murine cerebral endothelial cells. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 26(12), 1519–1526.
Huang, C. Y., Chen, J. J., Wu, J. S., Tsai, H. D., Lin, H., Yan, Y. T., et al. (2015). Novel Link of Anti-apoptotic ATF3 with Pro-apoptotic CTMP in the Ischemic Brain. Molecular Neurobiology, 51(2), 543–557.
Ito, K., Lim, S., Caramori, G., Cosio, B., Chung, K. F., Adcock, I. M., & Barnes, P. J. (2002). A molecular mechanism of action of theophylline: induction of histone deacetylase activity to decrease inflammatory gene expression. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 99(13), 8921–8926.
Loizou, S., Lekakis, I., Chrousos, G. P., & Moutsatsou, P. (2010). Beta-sitosterol exhibits anti-inflammatory activity in human aortic endothelial cells. Molecular Nutrition and Food Research, 54(4), 551–558.
Mandal, A., Ojha, D., Lalee, A., Kaity, S., Das, M., Chattopadhyay, D., et al. (2015). Bioassay directed isolation of a novel anti-inflammatory cerebroside from the leaves of Aerva sanguinolenta. Medicinal Chemistry Research, 24, 1952–1963.
Mehta, S. L., Manhas, N., & Raghubir, R. (2007). Molecular targets in cerebral ischemia for developing novel therapeutics. Brain Research Reviews, 54(1), 34–66.
Pongphasuk, N., & Khunkitti, W. (1996). Anti-inflammatory and analgesic activities of the extract from Garcinia mangostana Linn. Traditional Medicine and Nutraceuticals, 6, 125–130.
Sakdarat, S., Shuyprom, A., Ayudhya, T., Waterman, P. G., & Karagianis, G. (2006). Chemical composition investigation of the Clinacanthus nutans Lindau leaves. Thai Journal of Phytopharmacy, 13(2), 14–24.
Saleem, M. (2009). Lupeol, a novel anti-inflammatory and anti-cancer dietary triterpene. Cancer Letters, 285(2), 109–115.
Schweizer, S., Meisel, A., & Märschenz, S. (2013). Epigenetic mechanisms in cerebral ischemia. Journal of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism, 33(9), 1335–1346.
Tan, C. S., Ng, Y. K., & Ong, W. Y. (2015). Epigenetic regulation of cytosolic phospholipase A in SH-SY5Y human neuroblastoma cells. Molecular Neurobiology. doi:10.1007/s12035-015-9314-z.
Tan, C. S, Ho, C. F, Heng, S. S, Wu, J. S, Tan, B. K, Ng, Y. K, Sun, G. Y, Lin, T. N, Ong, W. Y. Clinacanthus nutans extracts modulate epigenetic link to cytosolic phospholipase A2 expression in SH-SY5Y cells and primary neurons (submitted).
Thiagalingam, S., Cheng, K. H., Lee, H. J., Mineva, N., Thiagalingam, A., & Ponte, J. F. (2003). Histone deacetylases: Unique players in shaping the epigenetic histone code. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 983, 84–100.
Tou, L., Liu, Q., & Shivdasani, R. A. (2004). Regulation of mammalian epithelial differentiation and intestine development by class I histone deacetylases. Molecular and Cellular Biology, 24(8), 3132–3139.
Uawonggul, N., Chaveerach, A., Thammasirirak, S., Arkaravichien, T., Chuachan, C., & Daduang, S. (2006). Screening of plants acting against Heterometrus laoticus scorpion venom activity on fibroblast cell lysis. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 103(2), 201–207.
Wang, Z., Leng, Y., Wang, J., Liao, H. M., Bergman, J., Leeds, P., et al. (2016). Tubastatin A, an HDAC6 inhibitor, alleviates stroke-induced brain infarction and functional deficits: Potential roles of α-tubulin acetylation and FGF-21 up-regulation. Sci Rep., 6, 19626.
Wu, J. S., Cheung, W. M., Tsai, Y. S., Chen, Y. T., Fong, W. H., Tsai, H. D., et al. (2009). Ligand-activated PPAR-γ protects against ischemic cerebral infarction and neuronal apoptosis by 14-3-3ε upregulation. Circulation, 119(8), 1124–1134.
Wu, J. S, Tsai, H. D, Cheung, W. M, Hsu, C. Y, Lin, T. N. (2015). PPAR-γ ameliorates neuronal apoptosis and ischemic brain injury via suppressing NF-κB-driven p22phox transcription. Molecular Neurobiology (Epub) PMID: 26108185.
Wu, J. S., Tsai, H. D., Huang, C. Y., Chen, J. J., & Lin, T. N. (2014). 15-deoxy-∆12,14-PGJ2 via activating peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma suppresses p22phox transcription to protect brain endothelial cells against hypoxia-induced apoptosis. Molecular Neurobiology, 50(1), 221–238.
Yin, K. J., Cirrito, J. R., Yan, P., Hu, X., Xiao, Q., Pan, X., et al. (2006). Matrix metalloproteinases expressed by astrocytes mediate extracellular amyloid-beta peptide catabolism. Journal of Neuroscience, 26(43), 10939–10948.
Yong, Y. K., Tan, J. J., Teh, S. S., Mah, S. H., Ee, G. C., Chiong, H. S., et al. (2013). Clinacanthus nutans extracts are antioxidant with antiproliferative effect on cultured human cancer cell lines. Evidence Based Complementary Alternative Med, 2013, 462751. doi:10.1155/2013/462751.
Zhou, X., Gan, P., Hao, L., Tao, L., Jia, J., Gao, B., et al. (2014). Antiinflammatory effects of orientin-2″-O-galactopyranoside on lipopolysaccharide-stimulated microglia. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 37(8), 1282–1294.
Ziemka-Nalecz, M., & Zalewska, T. (2014). Neuroprotective effects of histone deacetylase inhibitors in brain ischemia. Acta Neurobiology Express (Wars)., 74(4), 383–395.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from Academia Sinica, and Minister of Science and Technology ROC (MOST 104-2320-B-001-006-MY3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Wei-Yi Ong and Teng-Nan Lin have equally contributed to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tsai, HD., Wu, JS., Kao, MH. et al. Clinacanthus nutans Protects Cortical Neurons Against Hypoxia-Induced Toxicity by Downregulating HDAC1/6. Neuromol Med 18, 274–282 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-016-8401-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-016-8401-2