Abstract
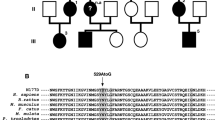
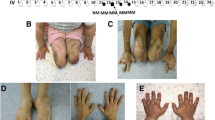
Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy 1 (HSAN1) is an autosomal dominant disorder that can be caused by variants in SPTLC1 or SPTLC2, encoding subunits of serine palmitoyl-CoA transferase. Disease variants alter the enzyme’s substrate specificity and lead to accumulation of neurotoxic 1-deoxysphingolipids. We describe two families with autosomal dominant HSAN1C caused by a new variant in SPTLC2, c.547C>T, p.(Arg183Trp). The variant changed a conserved amino acid and was not found in public variant databases. All patients had a relatively mild progressive distal sensory impairment, with onset after age 50. Small fibers were affected early, leading to abnormalities on quantitative sensory testing. Sural biopsy revealed a severe chronic axonal neuropathy with subtotal loss of myelinated axons, relatively preserved number of non-myelinated fibers and no signs for regeneration. Skin biopsy with PGP9.5 labeling showed lack of intraepidermal nerve endings early in the disease. Motor manifestations developed later in the disease course, but there was no evidence of autonomic involvement. Patients had elevated serum 1-deoxysphingolipids, and the variant protein produced elevated amounts of 1-deoxysphingolipids in vitro, which proved the pathogenicity of the variant. Our results expand the genetic spectrum of HSAN1C and provide further detail about the clinical characteristics. Sequencing of SPTLC2 should be considered in all patients presenting with mild late-onset sensory-predominant small or large fiber neuropathy.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- 1-deoxySL:
-
1-Deoxysphingolipid
- DML:
-
Distal motor latency
- ENMG:
-
Electroneuromyography
- HbA1C :
-
Glycated hemoglobin
- HSAN:
-
Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy
- NCV:
-
Nerve conduction velocity
- QST:
-
Quantitative sensory testing
- SA:
-
Sphinganine
- SISu:
-
Sequencing Initiative Suomi
- SO:
-
Sphingosine
- SPT:
-
Serine palmitoyl-CoA transferase
References
Adzhubei, I. A., Schmidt, S., Peshkin, L., Ramensky, V. E., Gerasimova, A., Bork, P., et al. (2010). A method and server for predicting damaging missense mutations. Nature Methods, 7, 248–249. doi:10.1038/nmeth0410-248.
Bejaoui, K., Wu, C., Scheffler, M. D., Haan, G., Ashby, P., Wu, L., et al. (2001). SPTLC1 is mutated in hereditary sensory neuropathy, type 1. Nature Genetics, 27, 261–262. doi:10.1038/85817.
Dawkins, J. L., Hulme, D. J., Brahmbhatt, S. B., Auer-Grumbach, M., & Nicholson, G. A. (2001). Mutations in SPTLC1, encoding serine palmitoyltransferase, long chain base subunit-1, cause hereditary sensory neuropathy type I. Nature Genetics, 27, 309–312. doi:10.1038/85879.
Ernst, D., Murphy, S. M., Sathiyanadan, K., Wei, Y., Othman, A., Laura, M., et al. (2015). Novel HSAN1 mutation in serine palmitoyltransferase resides at a putative phosphorylation site that is involved in regulating substrate specificity. NeuroMolecular Medicine, 17, 47–57. doi:10.1007/s12017-014-8339-1.
Fridman, V., Oaklander, A. L., David, W. S., Johnson, E. A., Pan, J., Novak, P., et al. (2015). Natural history and biomarkers in hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1. Muscle and Nerve, 51, 489–495. doi:10.1002/mus.24336.
Garofalo, K., Penno, A., Schmidt, B. P., Lee, H. J., Frosch, M. P., von Eckardstein, A., et al. (2011). Oral l-serine supplementation reduces production of neurotoxic deoxysphingolipids in mice and humans with hereditary sensory autonomic neuropathy type 1. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 121, 4735–4745. doi:10.1172/JCI57549.
Guelly, C., Zhu, P. P., Leonardis, L., Papic, L., Zidar, J., Schabhuttl, M., et al. (2011). Targeted high-throughput sequencing identifies mutations in atlastin-1 as a cause of hereditary sensory neuropathy type I. American Journal of Human Genetics, 88, 99–105. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.12.003.
Hanada, K. (2003). Serine palmitoyltransferase, a key enzyme of sphingolipid metabolism. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1632, 16–30.
Houlden, H., Blake, J., & Reilly, M. M. (2004). Hereditary sensory neuropathies. Current Opinion in Neurology, 17, 569–577.
Houlden, H., King, R., Blake, J., Groves, M., Love, S., Woodward, C., et al. (2006). Clinical, pathological and genetic characterization of hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 1 (HSAN I). Brain, 129, 411–425.
Kircher, M., Witten, D. M., Jain, P., O’Roak, B. J., Cooper, G. M., & Shendure, J. (2014). A general framework for estimating the relative pathogenicity of human genetic variants. Nature Genetics, 46, 310–315. doi:10.1038/ng.2892.
Klein, C. J., Botuyan, M. V., Wu, Y., Ward, C. J., Nicholson, G. A., Hammans, S., et al. (2011). Mutations in DNMT1 cause hereditary sensory neuropathy with dementia and hearing loss. Nature Genetics, 43, 595–600. doi:10.1038/ng.830.
Kornak, U., Mademan, I., Schinke, M., Voigt, M., Krawitz, P., Hecht, J., et al. (2014). Sensory neuropathy with bone destruction due to a mutation in the membrane-shaping atlastin GTPase 3. Brain, 137, 683–692. doi:10.1093/brain/awt357.
Koskinen, M., Hietaharju, A., Kylaniemi, M., Peltola, J., Rantala, I., Udd, B., & Haapasalo, H. (2005). A quantitative method for the assessment of intraepidermal nerve fibers in small-fiber neuropathy. Journal of Neurology, 252, 789–794. doi:10.1007/s00415-005-0743-x.
Laura, M., Eichler, F., Hornemann, T., Murphy, S. M., Polke, J., Bull, K., et al. (2012a). Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 1: correlation of severity and plasma atypical deoxy-sphyngoid bases. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 83, e1. doi:10.1136/jnnp-2011-301993.16.
Laura, M., Murphy, S. M., Hornemann, T., Bode, H., Polke, J., Blake, J., et al. (2012b). Hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1: Correlation of severity and plasma atypical deoxy-sphyngoid base. Neuromuscular Disorders, 22, S18. doi:10.1016/S0960-8966(12)70050-0.
Lim, E. T., Wurtz, P., Havulinna, A. S., Palta, P., Tukiainen, T., Rehnstrom, K., et al. (2014). Distribution and medical impact of loss-of-function variants in the finnish founder population. PLoS Genetics, 10, e1004494. doi:10.1371/journal.pgen.1004494.
Lindahl, A. J., Lhatoo, S. D., Campbell, M. J., Nicholson, G., & Love, S. (2006). Late-onset hereditary sensory neuropathy type I due to SPTLC1 mutation: Autopsy findings. Clinical Neurology and Neurosurgery, 108, 780–783.
Murphy, S. M., Ernst, D., Wei, Y., Laura, M., Liu, Y. T., Polke, J., et al. (2013). Hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type 1 (HSANI) caused by a novel mutation in SPTLC2. Neurology, 80, 2106–2111. doi:10.1212/WNL.0b013e318295d789.
Othman, A., Bianchi, R., Alecu, I., Wei, Y., Porretta-Serapiglia, C., Lombardi, R., et al. (2015a). Lowering plasma 1-deoxysphingolipids improves neuropathy in diabetic rats. Diabetes, 64, 1035–1045. doi:10.2337/db14-1325.
Othman, A., Rutti, M. F., Ernst, D., Saely, C. H., Rein, P., Drexel, H., et al. (2012). Plasma deoxysphingolipids: A novel class of biomarkers for the metabolic syndrome? Diabetologia, 55, 421–431. doi:10.1007/s00125-011-2384-1.
Othman, A., Saely, C. H., Muendlein, A., Vonbank, A., Drexel, H., von Eckardstein, A., & Hornemann, T. (2015b). Plasma 1-deoxysphingolipids are predictive biomarkers for type 2 diabetes mellitus. BMJ Open Diabetes Research and Care, 3, e000073. doi:10.1136/bmjdrc-2014-000073.
Penno, A., Reilly, M. M., Houlden, H., Laura, M., Rentsch, K., Niederkofler, V., et al. (2010). Hereditary sensory neuropathy type 1 is caused by the accumulation of two neurotoxic sphingolipids. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285, 11178–11187. doi:10.1074/jbc.M109.092973.
Rotthier, A., Auer-Grumbach, M., Janssens, K., Baets, J., Penno, A., Almeida-Souza, L., et al. (2010). Mutations in the SPTLC2 subunit of serine palmitoyltransferase cause hereditary sensory and autonomic neuropathy type I. American Journal of Human Genetics, 87, 513–522. doi:10.1016/j.ajhg.2010.09.010.
Verhoeven, K., De Jonghe, P., Coen, K., Verpoorten, N., Auer-Grumbach, M., Kwon, J. M., et al. (2003). Mutations in the small GTP-ase late endosomal protein RAB7 cause Charcot-Marie-Tooth type 2B neuropathy. American Journal of Human Genetics, 72, 722–727. doi:10.1086/367847.
Wang, K., Li, M., & Hakonarson, H. (2010). ANNOVAR: Functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Research, 38, e164. doi:10.1093/nar/gkq603.
Ylikallio, E., Johari, M., Konovalova, S., Moilanen, J. S., Kiuru-Enari, S., Auranen, M., et al. (2014). Targeted next-generation sequencing reveals further genetic heterogeneity in axonal Charcot-Marie-Tooth neuropathy and a mutation in HSPB1. European Journal of Human Genetics, 22, 522–527. doi:10.1038/ejhg.2013.190.
Zuellig, R. A., Hornemann, T., Othman, A., Hehl, A. B., Bode, H., Guntert, T., et al. (2014). Deoxysphingolipids, novel biomarkers for type 2 diabetes, are cytotoxic for insulin-producing cells. Diabetes, 63, 1326–1339. doi:10.2337/db13-1042.
Acknowledgments
In memoriam to B.R. a dear colleague and friend who unexpectedly passed away too premature. We thank Riitta Lehtinen for technical assistance. The authors wish to thank the following funding sources for support: Hospital District of Helsinki and Uusimaa (for M.A. and E.Y.), Sigrid Jusélius Foundation (for H.T.), University of Helsinki (for H.T.), the Academy of Finland (for H.T. and E.Y.), The 7th Framework Program of the European Commission (“RESOLVE”, Project Number 305707) for S.S. Furthermore, T.H. and S.S are grateful to the Hurka Foundation, the Novartis Foundation, and the Rare Disease Initiative Zurich (“radiz”, Clinical Research Priority Program for Rare Diseases, University of Zurich).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suriyanarayanan, S., Auranen, M., Toppila, J. et al. The Variant p.(Arg183Trp) in SPTLC2 Causes Late-Onset Hereditary Sensory Neuropathy. Neuromol Med 18, 81–90 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-015-8379-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-015-8379-1