Abstract
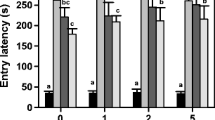
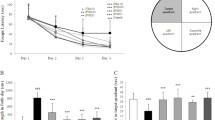
Exposure to organophosphorous (OP) nerve agents such as soman inhibits the critical enzyme acetylcholinesterase (AChE) leading to excessive acetylcholine accumulation in synapses, resulting in cholinergic crisis, status epilepticus and brain damage in survivors. The hippocampus is profoundly damaged after soman exposure leading to long-term memory deficits. We have previously shown that treatment with three sequential doses of alpha-linolenic acid, an essential omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid, increases brain plasticity in naïve animals. However, the effects of this dosing schedule administered after a brain insult and the underlying molecular mechanisms in the hippocampus are unknown. We now show that injection of three sequential doses of alpha-linolenic acid after soman exposure increases the endogenous expression of mature BDNF, activates Akt and the mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1), increases neurogenesis in the subgranular zone of the dentate gyrus, increases retention latency in the passive avoidance task and increases animal survival. In sharp contrast, while soman exposure also increases mature BDNF, this increase did not activate downstream signaling pathways or neurogenesis. Administration of the inhibitor of mTORC1, rapamycin, blocked the alpha-linolenic acid-induced neurogenesis and the enhanced retention latency but did not affect animal survival. Our results suggest that alpha-linolenic acid induces a long-lasting neurorestorative effect that involves activation of mTORC1 possibly via a BDNF-TrkB-mediated mechanism.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abe, O., Yamasue, H., Kasai, K., Yamada, H., Aoki, S., et al. (2006). Voxel-based diffusion tensor analysis reveals aberrant anterior cingulum integrity in posttraumatic stress disorder due to terrorism. Psychiatry Research, 146, 231–242.
Adachi, M., Barrot, M., Autry, A. E., Theobald, D., & Monteggia, L. M. (2008). Selective loss of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in the dentate gyrus attenuates antidepressant efficacy. Biological Psychiatry, 63, 642–649.
Ahn, Y. J., Park, S. J., Woo, H., Lee, H. E., Kim, H. J., et al. (2014). Effects of allantoin on cognitive function and hippocampal neurogenesis. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 64, 210–216.
Aimone, J. B., Wiles, J., & Gage, F. H. (2006). Potential role for adult neurogenesis in the encoding of time in new memories. Nature Neuroscience, 9, 723–727.
Alderson, R. F., Alterman, A. L., Barde, Y. A., & Lindsay, R. M. (1990). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor increases survival and differentiated functions of rat septal cholinergic neurons in culture. Neuron, 5, 297–306.
Aroniadou-Anderjaska, V., Figueiredo, T. H., Apland, J. P., Qashu, F., & Braga, M. F. (2009). Primary brain targets of nerve agents: The role of the amygdala in comparison to the hippocampus. Neurotoxicology, 30, 772–776.
Bajgar, J. (2005). Complex view on poisoning with nerve agents and organophosphates. Acta Medica (Hradec Kralove), 48, 3–21.
Ballarin, M., Ernfors, P., Lindefors, N., & Persson, H. (1991). Hippocampal damage and kainic acid injection induce a rapid increase in mRNA for BDNF and NGF in the rat brain. Experimental Neurology, 114, 35–43.
Bateman, J. M., & McNeill, H. (2004). Temporal control of differentiation by the insulin receptor/tor pathway in Drosophila. Cell, 119, 87–96.
Bergami, M., Berninger, B., & Canossa, M. (2009). Conditional deletion of TrkB alters adult hippocampal neurogenesis and anxiety-related behavior. Communicative and Integrative Biology, 2, 14–16.
Binder, D. K., Croll, S. D., Gall, C. M., & Scharfman, H. E. (2001). BDNF and epilepsy: Too much of a good thing? Trends in Neurosciences, 24, 47–53.
Blondeau, N., Nguemeni, C., Debruyne, D. N., Piens, M., Wu, X., et al. (2009). Subchronic alpha-linolenic acid treatment enhances brain plasticity and exerts an anti-depressant effect: A versatile potential therapy for stroke. Neuropsychopharmacology, 34, 2548–2559.
Blondeau, N., Widmann, C., Lazdunski, M., & Heurteaux, C. (2002). Polyunsaturated fatty acids induce ischemic and epileptic tolerance. Neuroscience, 109, 231–241.
Bovolenta, R., Zucchini, S., Paradiso, B., Rodi, D., Merigo, F., et al. (2010). Hippocampal FGF-2 and BDNF overexpression attenuates epileptogenesis-associated neuroinflammation and reduces spontaneous recurrent seizures. Journal of Neuroinflammation, 7, 81.
Buccafusco, J. J., Heithold, D. L., & Chon, S. H. (1990). Long-term behavioral and learning abnormalities produced by the irreversible cholinesterase inhibitor soman: Effect of a standard pretreatment regimen and clonidine. Toxicology Letters, 52, 319–329.
Buckmaster, P. S., & Lew, F. H. (2011). Rapamycin suppresses mossy fiber sprouting but not seizure frequency in a mouse model of temporal lobe epilepsy. Journal of Neuroscience, 31, 2337–2347.
Cameron, H. A., & McKay, R. D. (2001). Adult neurogenesis produces a large pool of new granule cells in the dentate gyrus. The Journal of Comparative Neurology, 435, 406–417.
Carpentier, P., Lambrinidis, M., & Blanchet, G. (1991). Early dendritic changes in hippocampal pyramidal neurones (field CA1) of rats subjected to acute soman intoxication: A light microscopic study. Brain Research, 541, 293–299.
Chen, J., Pan, H., Wu, W., Iskandar, K., He, J., et al. (2014). (-)-Phenserine attenuates soman-induced neuropathology. PLoS One, 9(6), e99818. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0099818.
Cheng, A., Wang, S., Cai, J., Rao, M. S., & Mattson, M. P. (2003). Nitric oxide acts in a positive feedback loop with BDNF to regulate neural progenitor cell proliferation and differentiation in the mammalian brain. Developmental Biology, 258, 319–333.
Choi, E. K., Park, D., Yon, J. M., Hur, G. H., Ha, Y. C., et al. (2004). Protection by sustained release of physostigmine and procyclidine of soman poisoning in rats. European Journal of Pharmacology, 505, 83–91.
Clement, J. G., & Broxup, B. (1993). Efficacy of diazepam and avizafone against soman-induced neuropathology in brain of rats. Neurotoxicology, 14, 485–504.
Collombet, J. M., Four, E., Bernabe, D., Masqueliez, C., Burckhart, M. F., et al. (2005). Soman poisoning increases neural progenitor proliferation and induces long-term glial activation in mouse brain. Toxicology, 208, 319–334.
Cornu, M., Oppliger, W., Albert, V., Robitaille, A. M., Trapani, F., et al. (2014). Hepatic mTORC1 controls locomotor activity, body temperature, and lipid metabolism through FGF21. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 111, 11592–11599.
Costa-Mattioli, M., & Monteggia, L. M. (2013). mTOR complexes in neurodevelopmental and neuropsychiatric disorders. Nature Neuroscience, 16, 1537–1543.
Dash, P. K., Orsi, S. A., & Moore, A. N. (2006). Spatial memory formation and memory-enhancing effect of glucose involves activation of the tuberous sclerosis complex-Mammalian target of rapamycin pathway. The Journal of Neuroscience, 26, 8048–8056.
Deblon, N., Bourgoin, L., Veyrat-Durebex, C., Peyrou, M., Vinciguerra, M., et al. (2012). Chronic mTOR inhibition by rapamycin induces muscle insulin resistance despite weight loss in rats. British Journal of Pharmacology, 165, 2325–2340.
Deng, W., Saxe, M. D., Gallina, I. S., & Gage, F. H. (2009). Adult-born hippocampal dentate granule cells undergoing maturation modulate learning and memory in the brain. The Journal of Neuroscience, 29, 13532–13542.
Deng, W., Aimone, J. B., & Gage, F. H. (2010). New neurons and new memories: How does adult hippocampal neurogenesis affect learning and memory? Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 11, 339–350.
Dupret, D., Revest, J. M., Koehl, M., Ichas, F., De Giorgi, F., et al. (2008). Spatial relational memory requires hippocampal adult neurogenesis. PLoS One, 3, e1959.
Duvel, K., Yecies, J. L., Menon, S., Raman, P., Lipovsky, A. I., et al. (2010). Activation of a metabolic gene regulatory network downstream of mTOR complex 1. Molecular Cell, 39, 171–183.
Elmer, E., Kokaia, Z., Kokaia, M., Carnahan, J., Nawa, H., & Lindvall, O. (1998). Dynamic changes of brain-derived neurotrophic factor protein levels in the rat forebrain after single and recurring kindling-induced seizures. Neuroscience, 83, 351–362.
Faivre, E., Gault, V. A., Thorens, B., & Holscher, C. (2011). Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor knockout mice are impaired in learning, synaptic plasticity, and neurogenesis. Journal of Neurophysiology, 105, 1574–1580.
Felix, M. S., Popa, N., Djelloul, M., Boucraut, J., Gauthier, P., et al. (2012). Alteration of forebrain neurogenesis after cervical spinal cord injury in the adult rat. Frontiers in Neuroscience, 6, 45.
Filliat, P., Baubichon, D., Burckhart, M. F., Pernot-Marino, I., Foquin, A., et al. (1999). Memory impairment after soman intoxication in rat: Correlation with central neuropathology. Improvement with anticholinergic and antiglutamatergic therapeutics. Neurotoxicology, 20, 535–549.
Filliat, P., Coubard, S., Pierard, C., Liscia, P., Beracochea, D., et al. (2007). Long-term behavioral consequences of soman poisoning in mice. Neurotoxicology, 28, 508–519.
Garcia-Calatayud, S., Redondo, C., Martin, E., Ruiz, J. I., Garcia-Fuentes, M., & Sanjurjo, P. (2005). Brain docosahexaenoic acid status and learning in young rats submitted to dietary long-chain polyunsaturated fatty acid deficiency and supplementation limited to lactation. Pediatric Research, 57, 719–723.
Ge, S., Yang, C. H., Hsu, K. S., Ming, G. L., & Song, H. (2007). A critical period for enhanced synaptic plasticity in newly generated neurons of the adult brain. Neuron, 54, 559–566.
Gheusi, G., Cremer, H., McLean, H., Chazal, G., Vincent, J. D., & Lledo, P. M. (2000). Importance of newly generated neurons in the adult olfactory bulb for odor discrimination. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 97, 1823–1828.
Hagg, T. (2005). Molecular regulation of adult CNS neurogenesis: An integrated view. Trends in Neurosciences, 28, 589–595.
Han, J., Wang, B., Xiao, Z., Gao, Y., Zhao, Y., et al. (2008). Mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) is involved in the neuronal differentiation of neural progenitors induced by insulin. Molecular and Cellular Neurosciences, 39, 118–124.
Hartman, A. L., Santos, P., Dolce, A., & Hardwick, J. M. (2012). The mTOR inhibitor rapamycin has limited acute anticonvulsant effects in mice. PLoS One, 7, e45156.
Heinrich, C., Lahteinen, S., Suzuki, F., Anne-Marie, L., Huber, S., et al. (2011). Increase in BDNF-mediated TrkB signaling promotes epileptogenesis in a mouse model of mesial temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiology of Disease, 42, 35–47.
Hentges, K. E., Sirry, B., Gingeras, A. C., Sarbassov, D., Sonenberg, N., et al. (2001). FRAP/mTOR is required for proliferation and patterning during embryonic development in the mouse. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 98, 13796–13801.
Heurteaux, C., Laigle, C., Blondeau, N., Jarretou, G., & Lazdunski, M. (2006). Alpha-linolenic acid and riluzole treatment confer cerebral protection and improve survival after focal brain ischemia. Neuroscience, 137, 241–251.
Hoeffer, C. A., & Klann, E. (2010). mTOR signaling: At the crossroads of plasticity, memory and disease. Trends in Neurosciences, 33, 67–75.
Hofer, M. M., & Barde, Y. A. (1988). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor prevents neuronal death in vivo. Nature, 331, 261–262.
Hohn, A., Leibrock, J., Bailey, K., & Barde, Y. A. (1990). Identification and characterization of a novel member of the nerve growth factor/brain-derived neurotrophic factor family. Nature, 344, 339–341.
Hom, J., Haley, R. W., & Kurt, T. L. (1997). Neuropsychological correlates of Gulf War syndrome. Archives of Clinical Neuropsychology, 12, 531–544.
Hong, J. G., Kim, D. H., Park, S. J., Kim, J. M., Cai, M., et al. (2011). The memory-enhancing effects of Kami-ondam-tang in mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 137, 251–256.
Hou, J. G., Xue, J. J., Lee, M. R., Sun, M. Q., Zhao, X. H., et al. (2013). Compound K is able to ameliorate the impaired cognitive function and hippocampal neurogenesis following chemotherapy treatment. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 436, 104–109.
Howell, J. J., Ricoult, S. J., Ben-Sahra, I., & Manning, B. D. (2013). A growing role for mTOR in promoting anabolic metabolism. Biochemical Society Transactions, 41, 906–912.
Humpel, C., Wetmore, C., & Olson, L. (1993). Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor messenger RNA and protein at the cellular level in pentylenetetrazol-induced epileptic seizures. Neuroscience, 53, 909–918.
Jaholkowski, P., Kiryk, A., Jedynak, P., Ben Abdallah, N. M., Knapska, E., et al. (2009). New hippocampal neurons are not obligatory for memory formation; cyclin D2 knockout mice with no adult brain neurogenesis show learning. Learning Memory, 16, 439–451.
Jessberger, S., Zhao, C., Toni, N., Clemenson, G. D, Jr, Li, Y., & Gage, F. H. (2007). Seizure-associated, aberrant neurogenesis in adult rats characterized with retrovirus-mediated cell labeling. The Journal of Neuroscience, 27, 9400–9407.
Jobim, P. F., Pedroso, T. R., Werenicz, A., Christoff, R. R., Maurmann, N., et al. (2012). Impairment of object recognition memory by rapamycin inhibition of mTOR in the amygdala or hippocampus around the time of learning or reactivation. Behavioural Brain Research, 228, 151–158.
Joosen, M. J., Jousma, E., van den Boom, T. M., Kuijpers, W. C., Smit, A. B., et al. (2009). Long-term cognitive deficits accompanied by reduced neurogenesis after soman poisoning. Neurotoxicology, 30, 72–80.
Katoh-Semba, R., Asano, T., Ueda, H., Morishita, R., Takeuchi, I. K., et al. (2002). Riluzole enhances expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor with consequent proliferation of granule precursor cells in the rat hippocampus. FASEB Journal, 16, 1328–1330.
Kelleher, R. J, 3rd, Govindarajan, A., Jung, H. Y., Kang, H., & Tonegawa, S. (2004). Translational control by MAPK signaling in long-term synaptic plasticity and memory. Cell, 116, 467–479.
Kempermann, G., Kuhn, H. G., & Gage, F. H. (1997). More hippocampal neurons in adult mice living in an enriched environment. Nature, 386, 493–495.
Kim, K. B., Nam, Y. A., Kim, H. S., Hayes, A. W., & Lee, B. M. (2014). Alpha-Linolenic acid: Nutraceutical, pharmacological and toxicological evaluation. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 70, 163–178.
Kron, M. M., Zhang, H., & Parent, J. M. (2010). The developmental stage of dentate granule cells dictates their contribution to seizure-induced plasticity. The Journal of Neuroscience, 30, 2051–2059.
Kuhn, H. G., Dickinson-Anson, H., & Gage, F. H. (1996). Neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the adult rat: Age-related decrease of neuronal progenitor proliferation. The Journal of Neuroscience, 16, 2027–2033.
Lallement, G., Carpentier, P., Pernot-Marino, I., Baubichon, D., Collet, A., & Blanchet, G. (1991). Involvement of the different rat hippocampal glutamatergic receptors in development of seizures induced by soman: An autoradiographic study. Neurotoxicology, 12, 655–664.
Lallement, G., Dorandeu, F., Filliat, P., Carpentier, P., Baille, V., & Blanchet, G. (1998). Medical management of organophosphate-induced seizures. Journal of physiology, 92, 369–373.
Lauritzen, I., Blondeau, N., Heurteaux, C., Widmann, C., Romey, G., & Lazdunski, M. (2000). Polyunsaturated fatty acids are potent neuroprotectors. The EMBO Journal, 19, 1784–1793.
Lazarov, O., Mattson, M. P., Peterson, D. A., Pimplikar, S. W., & van Praag, H. (2010). When neurogenesis encounters aging and disease. Trends in Neurosciences, 33, 569–579.
Lee, J., Duan, W., & Mattson, M. P. (2002). Evidence that brain-derived neurotrophic factor is required for basal neurogenesis and mediates, in part, the enhancement of neurogenesis by dietary restriction in the hippocampus of adult mice. Journal of Neurochemistry, 82, 1367–1375.
Lee, C. H., Kim, J. M., Kim, D. H., Park, S. J., Liu, X., et al. (2013a). Effects of Sun ginseng on memory enhancement and hippocampal neurogenesis. Phytotherapy Research, 27, 1293–1299.
Lee, Y., Kim, J., Jang, S., & Oh, S. (2013b). Administration of phytoceramide enhances memory and upregulates the expression of pCREB and BDNF in hippocampus of Mice. Biomolecules and Therapeutics, 21, 229–233.
Li, Y., Luikart, B. W., Birnbaum, S., Chen, J., Kwon, C. H., et al. (2008). TrkB regulates hippocampal neurogenesis and governs sensitivity to antidepressive treatment. Neuron, 59, 399–412.
Li, N., Lee, B., Liu, R. J., Banasr, M., Dwyer, J. M., et al. (2010). mTOR-dependent synapse formation underlies the rapid antidepressant effects of NMDA antagonists. Science, 329, 959–964.
Lindholm, D., Dechant, G., Heisenberg, C. P., & Thoenen, H. (1993). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor is a survival factor for cultured rat cerebellar granule neurons and protects them against glutamate-induced neurotoxicity. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 5, 1455–1464.
Lipsky, R. H., & Marini, A. M. (2007). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor in neuronal survival and behavior-related plasticity. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences, 1122, 130–143.
Lledo, P. M., Alonso, M., & Grubb, M. S. (2006). Adult neurogenesis and functional plasticity in neuronal circuits. Nature Reviews Neuroscience, 7, 179–193.
Magri, L., Cambiaghi, M., Cominelli, M., Alfaro-Cervello, C., Cursi, M., et al. (2011). Sustained activation of mTOR pathway in embryonic neural stem cells leads to development of tuberous sclerosis complex-associated lesions. Cell Stem Cell, 9, 447–462.
Marini, A. M., Rabin, S. J., Lipsky, R. H., & Mocchetti, I. (1998). Activity-dependent release of brain-derived neurotrophic factor underlies the neuroprotective effect of N-methyl-D-aspartate. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 273, 29394–29399.
Marsden, W. N. (2012). Synaptic plasticity in depression: Molecular, cellular and functional correlates. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 43C, 168–184.
McDonough, J. H, Jr, & Shih, T. M. (1997). Neuropharmacological mechanisms of nerve agent-induced seizure and neuropathology. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 21, 559–579.
McDonough, J. H, Jr, Smith, R. F., & Smith, C. D. (1986). Behavioral correlates of soman-induced neuropathology: Deficits in DRL acquisition. Neurobehavioral Toxicology and Teratology, 8, 179–187.
McDonough, J. H, Jr, Dochterman, L. W., Smith, C. D., & Shih, T. M. (1995). Protection against nerve agent-induced neuropathology, but not cardiac pathology, is associated with the anticonvulsant action of drug treatment. Neurotoxicology, 16, 123–132.
Merz, K., Herold, S., & Lie, D. C. (2011). CREB in adult neurogenesis–master and partner in the development of adult-born neurons? The European Journal of Neuroscience, 33, 1078–1086.
Miyaki, K., Nishiwaki, Y., Maekawa, K., Ogawa, Y., Asukai, N., et al. (2005). Effects of sarin on the nervous system of subway workers seven years after the Tokyo subway sarin attack. Journal of Occupational Health, 47, 299–304.
Moffett, M. C., Schultz, M. K., Schwartz, J. E., Stone, M. F., & Lumley, L. A. (2011). Impaired auditory and contextual fear conditioning in soman-exposed rats. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 98, 120–129.
Nawa, H., Carnahan, J., & Gall, C. (1995). BDNF protein measured by a novel enzyme immunoassay in normal brain and after seizure: Partial disagreement with mRNA levels. The European Journal of Neuroscience, 7, 1527–1535.
Oh, S. B., Park, H. R., Jang, Y. J., Choi, S. Y., Son, T. G., & Lee, J. (2013). Baicalein attenuates impaired hippocampal neurogenesis and the neurocognitive deficits induced by gamma-ray radiation. British Journal of Pharmacology, 168, 421–431.
Ohbu, S., Yamashina, A., Takasu, N., Yamaguchi, T., Murai, T., et al. (1997). Sarin poisoning on Tokyo subway. Southern Medical Journal, 90, 587–593.
Otaegi, G., Yusta-Boyo, M. J., Vergano-Vera, E., Mendez-Gomez, H. R., Carrera, A. C., et al. (2006). Modulation of the PI 3-kinase-Akt signalling pathway by IGF-I and PTEN regulates the differentiation of neural stem/precursor cells. Journal of Cell Science, 119, 2739–2748.
Paliouras, G. N., Hamilton, L. K., Aumont, A., Joppe, S. E., Barnabe-Heider, F., & Fernandes, K. J. (2012). Mammalian target of rapamycin signaling is a key regulator of the transit-amplifying progenitor pool in the adult and aging forebrain. The Journal of Neuroscience, 32, 15012–15026.
Pan, H., Hu, X. Z., Jacobowitz, D. M., Chen, C., McDonough, J., et al. (2012a). Alpha-linolenic acid is a potent neuroprotective agent against soman-induced neuropathology. Neurotoxicology, 33, 1219–1229.
Pan, Y. W., Chan, G. C., Kuo, C. T., Storm, D. R., & Xia, Z. (2012b). Inhibition of adult neurogenesis by inducible and targeted deletion of ERK5 mitogen-activated protein kinase specifically in adult neurogenic regions impairs contextual fear extinction and remote fear memory. The Journal of Neuroscience, 32, 6444–6455.
Paradiso, B., Zucchini, S., Su, T., Bovolenta, R., Berto, E., et al. (2011). Localized overexpression of FGF-2 and BDNF in hippocampus reduces mossy fiber sprouting and spontaneous seizures up to 4 weeks after pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus. Epilepsia, 52, 572–578.
Parent, J. M. (2008). Persistent hippocampal neurogenesis and epilepsy. Epilepsia, 49(Suppl 5), 1–2.
Parent, J. M., Yu, T. W., Leibowitz, R. T., Geschwind, D. H., Sloviter, R. S., & Lowenstein, D. H. (1997). Dentate granule cell neurogenesis is increased by seizures and contributes to aberrant network reorganization in the adult rat hippocampus. The Journal of Neuroscience, 17, 3727–3738.
Philippens, I. H., Melchers, B. P., de Groot, D. M., & Wolthuis, O. L. (1992). Behavioral performance, brain histology, and EEG sequela after immediate combined atropine/diazepam treatment of soman-intoxicated rats. Pharmacology, Biochemistry and Behavior, 42, 711–719.
Platel, J. C., Stamboulian, S., Nguyen, I., & Bordey, A. (2010). Neurotransmitter signaling in postnatal neurogenesis: The first leg. Brain Research Reviews, 63, 60–71.
Raman, L., Kong, X., & Kernie, S. G. (2013). Pharmacological inhibition of the mTOR pathway impairs hippocampal development in mice. Neuroscience Letters, 541, 9–14.
Rao, M. S., Hattiangady, B., & Shetty, A. K. (2006). The window and mechanisms of major age-related decline in the production of new neurons within the dentate gyrus of the hippocampus. Aging Cell, 5, 545–558.
Raveh, L., Chapman, S., Cohen, G., Alkalay, D., Gilat, E., et al. (1999). The involvement of the NMDA receptor complex in the protective effect of anticholinergic drugs against soman poisoning. Neurotoxicology, 20, 551–559.
Reibel, S., Depaulis, A., & Larmet, Y. (2001). BDNF and epilepsy—the bad could turn out to be good. Trends in Neurosciences, 24, 318–319.
Rogers, M. A., Yamasue, H., Abe, O., Yamada, H., Ohtani, T., et al. (2009). Smaller amygdala volume and reduced anterior cingulate gray matter density associated with history of post-traumatic stress disorder. Psychiatry Research, 174, 210–216.
Rossi, C., Angelucci, A., Costantin, L., Braschi, C., Mazzantini, M., et al. (2006). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) is required for the enhancement of hippocampal neurogenesis following environmental enrichment. The European journal of Neuroscience, 24, 1850–1856.
Rudge, J. S., Pasnikowski, E. M., Holst, P., & Lindsay, R. M. (1995). Changes in neurotrophic factor expression and receptor activation following exposure of hippocampal neuron/astrocyte cocultures to kainic acid. The Journal of Neuroscience, 15, 6856–6867.
Rudge, J. S., Mather, P. E., Pasnikowski, E. M., Cai, N., Corcoran, T., et al. (1998). Endogenous BDNF protein is increased in adult rat hippocampus after a kainic acid induced excitotoxic insult but exogenous BDNF is not neuroprotective. Experimental Neurology, 149, 398–410.
Saarelainen, T., Hendolin, P., Lucas, G., Koponen, E., Sairanen, M., et al. (2003). Activation of the TrkB neurotrophin receptor is induced by antidepressant drugs and is required for antidepressant-induced behavioral effects. The Journal of Neuroscience, 23, 349–357.
Sairanen, M., Lucas, G., Ernfors, P., Castren, M., & Castren, E. (2005). Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and antidepressant drugs have different but coordinated effects on neuronal turnover, proliferation, and survival in the adult dentate gyrus. The Journal of Neuroscience, 25, 1089–1094.
Saxe, M. D., Battaglia, F., Wang, J. W., Malleret, G., David, D. J., et al. (2006). Ablation of hippocampal neurogenesis impairs contextual fear conditioning and synaptic plasticity in the dentate gyrus. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 103, 17501–17506.
Shih, T. M., Koviak, T. A., & Capacio, B. R. (1991). Anticonvulsants for poisoning by the organophosphorus compound soman: Pharmacological mechanisms. Neuroscience and Biobehavioral Reviews, 15, 349–362.
Shih, T. M., Skovira, J. W., O’Donnell, J. C., & McDonough, J. H. (2010). In vivo reactivation by oximes of inhibited blood, brain and peripheral tissue cholinesterase activity following exposure to nerve agents in guinea pigs. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 187, 207–214.
Shors, T. J., Townsend, D. A., Zhao, M., Kozorovitskiy, Y., & Gould, E. (2002). Neurogenesis may relate to some but not all types of hippocampal-dependent learning. Hippocampus, 12, 578–584.
Sinor, A. D., & Lillien, L. (2004). Akt-1 expression level regulates CNS precursors. The Journal of Neuroscience, 24, 8531–8541.
Slipczuk, L., Bekinschtein, P., Katche, C., Cammarota, M., Izquierdo, I., & Medina, J. H. (2009). BDNF activates mTOR to regulate GluR1 expression required for memory formation. PLoS One, 4, e6007.
Smith, E. D., Prieto, G. A., Tong, L., Sears-Kraxberger, I., Rice, J. D., et al. (2014). Rapamycin and interleukin-1beta impair brain-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent neuron survival by modulating autophagy. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 289, 20615–20629.
Snyder, J. S., Hong, N. S., McDonald, R. J., & Wojtowicz, J. M. (2005). A role for adult neurogenesis in spatial long-term memory. Neuroscience, 130, 843–852.
Solberg, Y., & Belkin, M. (1997). The role of excitotoxicity in organophosphorous nerve agents central poisoning. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences, 18, 183–185.
Soppet, D., Escandon, E., Maragos, J., Middlemas, D. S., Reid, S. W., et al. (1991). The neurotrophic factors brain-derived neurotrophic factor and neurotrophin-3 are ligands for the trkB tyrosine kinase receptor. Cell, 65, 895–903.
Stubley-Weatherly, L., Harding, J. W., & Wright, J. W. (1996). Effects of discrete kainic acid-induced hippocampal lesions on spatial and contextual learning and memory in rats. Brain Research, 716, 29–38.
Suarez-Pereira, I., Canals, S., & Carrion, A. M. (2014). Adult newborn neurons are involved in learning acquisition and long-term memory formation: The distinct demands on temporal neurogenesis of different cognitive tasks. Hippocampus, 25, 51–61.
Swiech, L., Perycz, M., Malik, A., & Jaworski, J. (2008). Role of mTOR in physiology and pathology of the nervous system. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1784, 116–132.
Toni, N., Laplagne, D. A., Zhao, C., Lombardi, G., Ribak, C. E., et al. (2008). Neurons born in the adult dentate gyrus form functional synapses with target cells. Nature Neuroscience, 11, 901–907.
Toomey, R., Alpern, R., Vasterling, J. J., Baker, D. G., Reda, D. J., et al. (2009). Neuropsychological functioning of U.S. Gulf War veterans 10 years after the war. Journal of the International Neuropsychological Society, 15, 717–729.
van Praag, H., Schinder, A. F., Christie, B. R., Toni, N., Palmer, T. D., & Gage, F. H. (2002). Functional neurogenesis in the adult hippocampus. Nature, 415, 1030–1034.
Wullschleger, S., Loewith, R., & Hall, M. N. (2006). TOR signaling in growth and metabolism. Cell, 124, 471–484.
Yamada, T., Uchida, H., & Ichikawa, A. (1983). Detection of learning impairment in offspring in reproduction tests. Jikken dobutsu. Experimental Animals, 32, 107–113.
Yamasue, H., Kasai, K., Iwanami, A., Ohtani, T., Yamada, H., et al. (2003). Voxel-based analysis of MRI reveals anterior cingulate gray-matter volume reduction in posttraumatic stress disorder due to terrorism. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100, 9039–9043.
Yang, W. M., Shim, K. J., Choi, M. J., Park, S. Y., Choi, B. J., et al. (2008). Novel effects of Nelumbo nucifera rhizome extract on memory and neurogenesis in the dentate gyrus of the rat hippocampus. Neuroscience Letters, 443, 104–107.
Zeng, L. H., Xu, L., Gutmann, D. H., & Wong, M. (2008). Rapamycin prevents epilepsy in a mouse model of tuberous sclerosis complex. Annals of neurology, 63, 444–453.
Zhao, C., Deng, W., & Gage, F. H. (2008). Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell, 132, 645–660.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Defense Threat Reduction Agency-Joint Science and Technology Office, Medical S&T Division (Grant Nos. CBM.NEURO.01.10.US.012 and CBM.NEURO.01.10.US.019) to AMM.
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The views of the authors do not reflect any position or policies of the Department of Defense
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Piermartiri, T.C., Pan, H., Chen, J. et al. Alpha-Linolenic Acid-Induced Increase in Neurogenesis is a Key Factor in the Improvement in the Passive Avoidance Task After Soman Exposure. Neuromol Med 17, 251–269 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-015-8353-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-015-8353-y