Abstract
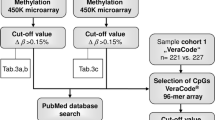
A methylation-based EWAS on carefully phenotyped individuals with Parkinson’s disease (PD) was conducted to reveal prioritised genes and pathways with statistically significant and sizable changes in PD and in the anxiety that often accompanies it. This was followed by subsequent replication of top-ranked CpG sites. Using the Infinium® HumanMethylation 450K beadchip (Illumina Inc., USA), twenty unique genes with a sizable difference in methylation (P adjusted < 0.05, Δβ ≥ 0.2), after correction for multiple testing, were identified between PD and controls, while seventeen were identified between PD with anxiety and PD without anxiety. Twelve top ranked, significantly associated loci in PD were evaluated in an independent replicate population using Sequenom EpiTYPER for 219 individuals with similar phenotypes to the cross-sectional case–control discovery design. FANCC cg14115740 and TNKS2 cg11963436 show significant differential methylation between PD cases and controls using both techniques and their Δβ values, which have the same direction of effect, are reasonable to warrant further investigation.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida Mdo, R. (2012). Glucocerebrosidase involvement in Parkinson disease and other synucleinopathies. Frontiers in Neurology, 3, 65.
Ardley, H. C., Scott, G. B., Rose, S. A., Tan, N. G., & Robinson, P. A. (2004). UCH-L1 aggresome formation in response to proteasome impairment indicates a role in inclusion formation in Parkinson’s disease. Journal of Neurochemistry, 90(2), 379–391.
Bajaj, A., Driver, J. A., & Schernhammer, E. S. (2010). Parkinson’s disease and cancer risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Causes & Control: CCC, 21(5), 697–707.
Bando, Y., Onuki, R., Katayama, T., Manabe, T., Kudo, T., Taira, K., et al. (2005). Double-strand RNA dependent protein kinase (PKR) is involved in the extrastriatal degeneration in Parkinson’s disease and Huntington’s disease. Neurochemistry International, 46(1), 11–18.
Bell, C. G., Teschendorff, A. E., Rakyan, V. K., Maxwell, A. P., Beck, S., & Savage, D. A. (2010). Genome-wide DNA methylation analysis for diabetic nephropathy in type 1 diabetes mellitus. BMC Medical Genomics, 3, 33.
Benjamini, Y., & H, Y. (1995). Controlling the false discovery rate: a practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B, 57(1), 289–300.
Ben-Shlomo, Y. (1996). How far are we in understanding the cause of Parkinson’s disease? Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 61(1), 4–16.
Breitling, L. P., Yang, R., Korn, B., Burwinkel, B., & Brenner, H. (2011). Tobacco-smoking-related differential DNA methylation: 27 K discovery and replication. American Journal of Human Genetics, 88(4), 450–457.
Chan, N. C., & Chan, D. C. (2011). Parkin uses the UPS to ship off dysfunctional mitochondria. Autophagy, 7(7), 771–772.
Chowdhury, S., Erickson, S. W., Macleod, S. L., Cleves, M. A., Hu, P., Karim, M. A., et al. (2011). Maternal genome-wide DNA methylation patterns and congenital heart defects. PLoS one, 6(1), e16506.
Clarke, C. E. (Ed.). (2007). Parkinson’s Disease (2nd ed.). London: Royal Society of Medicine Press Ltd.
Cook, C., Stetler, C., & Petrucelli, L. (2012). Disruption of protein quality control in Parkinson’s disease. Cold Spring Harbor Perspectives in Medicine, 2(5), a009423.
Cummings, J. L., Mega, M., Gray, K., Rosenberg-Thompson, S., Carusi, D. A., & Gornbein, J. (1994). The Neuropsychiatric Inventory: Comprehensive assessment of psychopathology in dementia. Neurology, 44(12), 2308–2314.
Dahl, C., & Guldberg, P. (2003). DNA methylation analysis techniques. Biogerontology, 4(4), 233–250.
Daniel, S. E., & Lees, A. J. (1993). Parkinson’s Disease Society Brain Bank, London: Overview and research. Journal of Neural Transmission. Supplementum, 39, 165–172.
Dehay, B., Martinez-Vicente, M., Ramirez, A., Perier, C., Klein, C., Vila, M., et al. (2012). Lysosomal dysfunction in Parkinson disease: ATP13A2 gets into the groove. Autophagy, 8(9), 1389–1391.
Desideri, E., & Martins, L.M. (2012). Mitochondrial stress signalling: HTRA2 and Parkinson’s disease. International Journal of Cell Biology, 2012, 607929.
Flintoft, L. (2011). Disease epigenomics: A smoking gun. Nature Reviews Genetics, 12(5), 300.
Folstein, M. F., Folstein, S. E., & McHugh, P. R. (1975). “Mini-mental state”. A practical method for grading the cognitive state of patients for the clinician. Journal of Psychiatric Research, 12(3), 189–198.
Grupe, A., Li, Y., Rowland, C., Nowotny, P., Hinrichs, A. L., Smemo, S., et al. (2006). A scan of chromosome 10 identifies a novel locus showing strong association with late-onset Alzheimer disease. American Journal of Human Genetics, 78(1), 78–88.
Hancock, D. B., Martin, E. R., Mayhew, G. M., Stajich, J. M., Jewett, R., Stacy, M. A., et al. (2008). Pesticide exposure and risk of Parkinson’s disease: A family-based case-control study. BMC Neurology, 8, 6.
Handel, A. E., Ebers, G. C., & Ramagopalan, S. V. (2010). Epigenetics: Molecular mechanisms and implications for disease. Trends in Molecular Medicine, 16(1), 7–16.
Harris, R. A., Nagy-Szakal, D., Pedersen, N., Opekun, A., Bronsky, J., Munkholm, P., et al. (2012). Genome-wide peripheral blood leukocyte DNA methylation microarrays identified a single association with inflammatory bowel diseases. Inflammatory Bowel Diseases, 18(12), 2334–2341.
Illumina, 09/03/12, 2012-last update, Infinium HumanMethylation450 BeadChip. [Homepage of Illumina] [Online]. Available: http://www.illumina.com/documents/products/datasheets/datasheet_humanmethylation450.pdf [03/20, 2012].
International Parkinson’s Disease Genomics Consortium (IPDGC) And Wellcome Trust Case Control Consortium 2 (WTCCC2). (2011). A two-stage meta-analysis identifies several new loci for Parkinson’s disease. PLoS Genetics, 7(6), e1002142.
Jellinger, K. (1988). The pedunculopontine nucleus in Parkinson’s disease, progressive supranuclear palsy and Alzheimer’s disease. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery and Psychiatry, 51(4), 540–543.
Jellinger, K. A. (2009). Formation and development of Lewy pathology: A critical update. Journal of Neurology, 256(Suppl 3), 270–279.
Johnson, M. R., Lydiard, R. B., Zealberg, J. J., Fossey, M. D., & Ballenger, J. C. (1994). Plasma and CSF HVA levels in panic patients with comorbid social phobia. Biological Psychiatry, 36(6), 425–427.
Jowaed, A., Schmitt, I., Kaut, O., & Wullner, U. (2010). Methylation regulates alpha-synuclein expression and is decreased in Parkinson’s disease patients’ brains. The Journal of Neuroscience: The Official Journal of the Society for Neuroscience, 30(18), 6355–6359.
Junn, E., Taniguchi, H., Jeong, B. S., Zhao, X., Ichijo, H., & Mouradian, M. M. (2005). Interaction of DJ-1 with Daxx inhibits apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1 activity and cell death. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 102(27), 9691–9696.
Kaminker, P. G., Kim, S. H., Taylor, R. D., Zebarjadian, Y., Funk, W. D., Morin, G. B., et al. (2001). TANK2, a new TRF1-associated poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase, causes rapid induction of cell death upon overexpression. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 276(38), 35891–35899.
Kummer, A., Cardoso, F., & Teixeira, A. L. (2008). Frequency of social phobia and psychometric properties of the Liebowitz social anxiety scale in Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disorders: Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 23(12), 1739–1743.
Kummer, A., & Teixeira, A. L. (2009). Neuropsychiatry of Parkinson’s disease. Arquivos de Neuro-Psiquiatria, 67(3B), 930–939.
Lang, A. E. T., & Fahn, S. (1989). Assessment of Parkinson’s disease. In T. L. Munsat (Ed.), Quantification of neurological deficit (pp. 285–309). Boston: Butterworths.
Langston, J. W., Ballard, P., Tetrud, J. W., & Irwin, I. (1983). Chronic Parkinsonism in humans due to a product of meperidine-analog synthesis. Science (New York), 219(4587), 979–980.
Lill, C. M., Roehr, J. T., McQueen, M. B., Kavvoura, F. K., Bagade, S., Schjeide, B. M., et al. (2012). Comprehensive research synopsis and systematic meta-analyses in Parkinson’s disease genetics: The PDGene database. PLoS Genetics, 8(3), e1002548.
Liu, B., Gao, H. M., & Hong, J. S. (2003). Parkinson’s disease and exposure to infectious agents and pesticides and the occurrence of brain injuries: Role of neuroinflammation. Environmental Health Perspectives, 111(8), 1065–1073.
Liu, H., Liu, W., Wu, Y., Zhou, Y., Xue, R., Luo, C., et al. (2005). Loss of epigenetic control of synuclein-gamma gene as a molecular indicator of metastasis in a wide range of human cancers. Cancer Research, 65(17), 7635–7643.
Mailman, M. D., Feolo, M., Jin, Y., Kimura, M., Tryka, K., Bagoutdinov, R., et al. (2007). The NCBI dbGaP database of genotypes and phenotypes. Nature Genetics, 39(10), 1181–1186.
Marques, S. C., Oliveira, C. R., Pereira, C. M., & Outeiro, T. F. (2011). Epigenetics in neurodegeneration: A new layer of complexity. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry, 35(2), 348–355.
Marsit, C. J., Koestler, D. C., Christensen, B. C., Karagas, M. R., Houseman, E. A., & Kelsey, K. T. (2011). DNA methylation array analysis identifies profiles of blood-derived DNA methylation associated with bladder cancer. Journal of clinical Oncology: Official Journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology, 29(9), 1133–1139.
Muzerengi, S., Contrafatto, D., & Chaudhuri, K. R. (2007). Non-motor symptoms: Identification and management. Parkinsonism and Related Disorders, 13(Suppl 3), 450–456.
Nutt, D. J., Bell, C. J., & Malizia, A. L. (1998). Brain mechanisms of social anxiety disorder. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 59(Suppl 17), 4–11.
Polymeropoulos, M. H., Lavedan, C., Leroy, E., Ide, S. E., Dehejia, A., Dutra, A., et al. (1997). Mutation in the alpha-synuclein gene identified in families with Parkinson’s disease. Science (New York), 276(5321), 2045–2047.
Pontone, G. M., Williams, J. R., Anderson, K. E., Chase, G., Goldstein, S. A., Grill, S., et al. (2009). Prevalence of anxiety disorders and anxiety subtypes in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disorders: Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 24(9), 1333–1338.
Qureshi, I. A., & Mehler, M. F. (2011). Advances in epigenetics and epigenomics for neurodegenerative diseases. Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports, 11(5), 464–473.
Rakyan, V. K., Down, T. A., Balding, D. J., & Beck, S. (2011). Epigenome-wide association studies for common human diseases. Nature Reviews Genetics, 12(8), 529–541.
Ren, H., Fu, K., Wang, D., Mu, C., & Wang, G. (2011). Oxidized DJ-1 interacts with the mitochondrial protein BCL-XL. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 286(40), 35308–35317.
Robinson, H. M., Hood, S. D., Bell, C. J., & Nutt, D. J. (2006). Dopamine and social anxiety disorder. Revista brasileira de psiquiatria (Sao Paulo, Brazil: 1999), 28(4), 263–264.
Schneier, F. R., Liebowitz, M. R., Abi-Dargham, A., Zea-Ponce, Y., Lin, S. H., & Laruelle, M. (2000). Low dopamine D(2) receptor binding potential in social phobia. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 157(3), 457–459.
Schrag, A. (2006). Quality of life and depression in Parkinson’s disease. Journal of the Neurological Sciences, 248(1–2), 151–157.
Siemers, E. R., Shekhar, A., Quaid, K., & Dickson, H. (1993). Anxiety and motor performance in Parkinson’s disease. Movement Disorders: Official Journal of the Movement Disorder Society, 8(4), 501–506.
Smyth, L. J., McKay, G. J., Maxwell, A. P., & McKnight, A. J. (2014). DNA hypermethylation and DNA hypomethylation is present at different loci in chronic kidney disease. Epigenetics: Official Journal of the DNA Methylation Society, 9(3), 366–376.
Stern, M., Dulaney, E., Gruber, S. B., Golbe, L., Bergen, M., Hurtig, H., et al. (1991). The epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease: A case-control study of young-onset and old-onset patients. Archives of Neurology, 48(9), 903–907.
Sun, F., Kanthasamy, A., Anantharam, V., & Kanthasamy, A. G. (2007). Environmental neurotoxic chemicals-induced ubiquitin proteasome system dysfunction in the pathogenesis and progression of Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 114(3), 327–344.
Wilhelmus, M. M., Nijland, P. G., Drukarch, B., de Vries, H. E., & van Horssen, J. (2012). Involvement and interplay of Parkin, PINK1, and DJ1 in neurodegenerative and neuroinflammatory disorders. Free Radical Biology & Medicine, 53(4), 983–992.
Wing, M. R., Devaney, J. M., Joffe, M. M., Xie, D., Feldman, H. I., Dominic, E. A., et al. (2014). DNA methylation profile associated with rapid decline in kidney function: Findings from the CRIC study. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation: Official Publication of the European Dialysis and Transplant Association—European Renal Association, 29(4), 864–872.
Zhu, Y., Stevens, R. G., Hoffman, A. E., Tjonneland, A., Vogel, U. B., Zheng, T., et al. (2011). Epigenetic impact of long-term shiftwork: Pilot evidence from circadian genes and whole-genome methylation analysis. Chronobiology International, 28(10), 852–861.
Acknowledgments
A grant was received from the Department of Education and Learning to fund this study. Gen-Probe ran the 450K arrays. The DNA used in the replication phase was historically archived by Dr Owen Ross and Dr Mark Gibson.
Conflict of interest
All authors agreed the final version of this manuscript and the authors declare no conflict of interest.
Ethical standard
Ethical approval was granted for this project, and all participants provided informed consent.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moore, K., McKnight, A.J., Craig, D. et al. Epigenome-Wide Association Study for Parkinson’s Disease. Neuromol Med 16, 845–855 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8332-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8332-8