Abstract
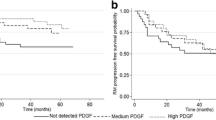
During multiple sclerosis (MS) inflammatory attacks, and in subsequent clinical recovery phases, immune cells contribute to neuronal and oligodendroglial cell survival and tissue repair by secreting growth factors. Animal studies showed that growth factors also play a substantial role in regulating synaptic plasticity, and namely in long-term potentiation (LTP). LTP could drive clinical recovery in relapsing patients by restoring the excitability of denervated neurons. We recently reported that maintenance of synaptic plasticity reserve is crucial to contrast clinical deterioration in MS and that the platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF) may play a key role in its regulation. We also reported that a Hebbian form of LTP-like cortical plasticity, explored by paired associative stimulation (PAS), correlates with clinical recovery from a relapse in MS. Here, we explored the role of PDGF in clinical recovery and in adaptive neuroplasticity in relapsing–remitting MS (RR-MS) patients. We found a correlation between the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) PDGF concentrations and the extent of clinical recovery after a relapse, as full recovery was more likely observed in patients with high PDGF concentrations and poor recovery in subjects with low PDGF levels. Consistently with the idea that PDGF-driven synaptic plasticity contributes to attenuate the clinical consequences of tissue damage in RR-MS, we also found a striking correlation between CSF levels of PDGF and the amplitude of LTP-like cortical plasticity explored by PAS. CSF levels of fibroblast growth factor, granulocyte colony-stimulating factor and granulocyte–macrophage colony-stimulating factor did not correlate with clinical recovery nor with measures of synaptic transmission and plasticity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bartlett, T. E., & Wang, Y. T. (2013). The intersections of NMDAR-dependent synaptic plasticity and cell survival. Neuropharmacology, 74, 59–68.
Beazely, M. A., Lim, A., Li, H., Trepanier, C., Chen, X., Sidhu, B., et al. (2009). Platelet-derived growth factor selectively inhibits NR2B-containing N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in CA1 hippocampal neurons. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 284(12), 8054–8063.
Boyd, T. D., Bennett, S. P., Mori, T., Governatori, N., Runfeldt, M., Norden, M., et al. (2010). GM-CSF upregulated in rheumatoid arthritis reverses cognitive impairment and amyloidosis in Alzheimer mice. Journal of Alzheimer’s Disease, 21(2), 507–518.
Centonze, D., Rossi, S., Tortiglione, A., Picconi, B., Prosperetti, C., De Chiara, V., et al. (2007). Synaptic plasticity during recovery from permanent occlusion of the middle cerebral artery. Neurobiology of Diseases, 27(1), 44–53.
Chadi, G., & Fuxe, K. (1998). Analysis of trophic responses in lesioned brain: Focus on basic fibroblast growth factor mechanisms. Brazilian Journal of Medical and Biological Research, 31(2), 231–241.
Cheeran, B., Talelli, P., Mori, F., Koch, G., Suppa, A., Edwards, M., et al. (2008). A common polymorphism in the brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene (BDNF) modulates human cortical plasticity and the response to rTMS. Journal of Physiology, 586(23), 5717–5725.
Confavreux, C., & Vukusic, S. (2006). Age at disability milestones in multiple sclerosis. Brain, 129(3), 595–605.
Cooke, S. F., & Bliss, T. V. (2006). Plasticity in the human central nervous system. Brain, 129(7), 1659–1673.
Di Lazzaro, V., Profice, P., Pilato, F., Capone, F., Ranieri, F., Pasqualetti, P., et al. (2010). Motor cortex plasticity predicts recovery in acute stroke. Cerebral Cortex, 20(7), 1523–1528.
Egawa-Tsuzuki, T., Ohno, M., Tanaka, N., Takeuchi, Y., Uramoto, H., Faigle, R., et al. (2004). The PDGF B-chain is involved in the ontogenic susceptibility of the developing rat brain to NMDA toxicity. Experimental Neurology, 186(1), 89–98.
Erlandsson, A., Enarsson, M., & Forsberg-Nilsson, K. (2001). Immature neurons from CNS stem cells proliferate in response to platelet-derived growth factor. Journal of Neuroscience, 21(10), 3483–3491.
Frost, E. E., Nielsen, J. A., Le, T. Q., & Armstrong, R. C. (2003). PDGF and FGF2 regulate oligodendrocyte progenitor responses to demyelination. Journal of Neurobiology, 54(3), 457–572.
Gong, N., Li, Y., Cai, G. Q., Niu, R. F., Fang, Q., Wu, K., et al. (2009). GABA transporter-1 activity modulates hippocampal theta oscillation and theta burst stimulation-induced long-term potentiation. Journal of Neuroscience, 29(50), 15836–15845.
Gozal, D., Simakajornboon, N., Czapla, M. A., Xue, Y. D., Gozal, E., Vlasic, V., et al. (2000). Brainstem activation of platelet-derived growth factor-beta receptor modulates the late phase of the hypoxic ventilatory response. Journal of Neurochemistry, 74(1), 310–319.
Hagemann, G., Redecker, C., Neumann-Haefelin, T., Freund, H. J., & Witte, O. W. (1998). Increased long-term potentiation in the surround of experimentally induced focal cortical infarction. Annals of Neurology, 44(2), 255–258.
Hanajima, R., Ugawa, Y., Terao, Y., Enomoto, H., Shiio, Y., Mochizuki, H., et al. (2002). Mechanisms of intracortical I-wave facilitation elicited with paired-pulse magnetic stimulation in humans. Journal of Physiology, 538(1), 253–261.
Harirchian, M. H., Tekieh, A. H., Modabbernia, A., Aghamollaii, V., Tafakhori, A., Ghaffarpour, M., et al. (2012). Serum and CSF PDGF-AA and FGF-2 in relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis: A case–control study. European Journal of Neurology, 19(2), 241–247.
Ishii, Y., Oya, T., Zheng, L., Gao, Z., Kawaguchi, M., Sabit, H., et al. (2006). Mouse brains deficient in neuronal PDGF receptor-beta develop normally but are vulnerable to injury. Journal of Neurochemistry, 98(2), 588–600.
Kerschensteiner, M., Stadelmann, C., Dechant, G., Wekerle, H., & Hohlfeld, R. (2003). Neurotrophic cross-talk between the nervous and immune systems: Implications for neurological diseases. Annals of Neurology, 53(3), 292–304.
Kierdorf, K., Wang, Y., & Neumann, H. (2010). Immune-mediated CNS damage. Results and Problems in Cell Differentiation, 51, 173–196.
Kujirai, T., Caramia, M. D., Rothwell, J. C., Day, B. L., Thompson, P. D., Ferbert, A., et al. (1993). Corticocortical inhibition in human motor cortex. Journal of Physiology, 471, 501–519.
Matsuyama, S., Taniguchi, T., Kadoyama, K., & Matsumoto, A. (2008). Long-term potentiation-like facilitation through GABAA receptor blockade in the mouse dentate gyrus in vivo. Neuroreport, 19(18), 1809–1813.
Mattson, M. P., Kumar, K. N., Wang, H., Cheng, B., & Michaelis, E. K. (1993). Basic FGF regulates the expression of a functional 71 kDa NMDA receptor protein that mediates calcium influx and neurotoxicity in hippocampal neurons. Journal of Neuroscience, 13, 4575–4588.
Messersmith, D. J., Murtie, J. C., Le, T. Q., Frost, E. E., & Armstrong, R. C. (2000). Fibroblast growth factor 2 (FGF2) and FGF receptor expression in an experimental demyelinating disease with extensive remyelination. Journal of Neuroscience Research, 62(2), 241–256.
Mezzapesa, D. M., Rocca, M. A., Rodegher, M., Comi, G., & Filippi, M. (2008). Functional cortical changes of the sensorimotor network are associated with clinical recovery in multiple sclerosis. Human Brain Mapping, 29(5), 562–573.
Morgen, K., Kadom, N., Sawaki, L., Tessitore, A., Ohayon, J., McFarland, H., et al. (2004). Training-dependent plasticity in patients with multiple sclerosis. Brain, 127(11), 2506–2517.
Mori, F., Kusayanagi, H., Nicoletti, C. G., Weiss, S., Marciani, M. G., & Centonze, D. (2013a). Cortical plasticity predicts recovery from relapse in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis. doi:10.1177/1352458513512541.
Mori, F., Rossi, S., Piccinin, S., Motta, C., Mango, D., Kusayanagi, H., et al. (2013b). Synaptic plasticity and PDGF signaling defects underlie clinical progression in multiple sclerosis. Journal of Neuroscience, 33(49), 19112–19119.
Müller-Dahlhaus, J. F., Orekhov, Y., Liu, Y., & Ziemann, U. (2008). Interindividual variability and age-dependency of motor cortical plasticity induced by paired associative stimulation. Experimental Brain Research, 187(3), 467–475.
Nguyen, P. T., Nakamura, T., Hori, E., Urakawa, S., Uwano, T., Zhao, J., et al. (2011). Cognitive and socio-emotional deficits in platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β gene knockout mice. PLoS One, 6(3), e18004.
Peng, F., Yao, H., Bai, X., Zhu, X., Reiner, B. C., Beazely, M., et al. (2010). Platelet-derived growth factor-mediated induction of the synaptic plasticity gene Arc/Arg3.1. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 285(28), 21615–21624.
Polman, C. H., Reingold, S. C., Banwell, B., Clanet, M., Cohen, J. A., Filippi, M., et al. (2011). Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis: 2010 Revisions to the McDonald criteria. Annals of Neurology, 69(2), 292–302.
Ponomarev, E. D., Shriver, L. P., Maresz, K., Pedras-Vasconcelos, J., Verthelyi, D., & Dittel, B. N. (2007). GM-CSF production by autoreactive T cells is required for the activation of microglial cells and the onset of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Journal of Immunology, 178(1), 39–48.
Rottlaender, A., Villwock, H., Addicks, K., & Kuerten, S. (2011). Neuroprotective role of fibroblast growth factor-2 in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. Immunology, 133(3), 370–378.
Sasahara, M., Fries, J. W., Raines, E. W., Gown, A. M., Westrum, L. E., Frosch, M. P., et al. (1991). PDGF B-chain in neurons of the central nervous system, posterior pituitary, and in a transgenic model. Cell, 64(1), 217–227.
Schneider, A., Krüger, C., Steigleder, T., Weber, D., Pitzer, C., Laage, R., et al. (2005). The hematopoietic factor G-CSF is a neuronal ligand that counteracts programmed cell death and drives neurogenesis. Journal of Clinical Investigation, 115(8), 2083–2098.
Schwartz, M., Moalem, G., Leibowitz-Amit, R., & Cohen, I. R. (1999). Innate and adaptive immune responses can be beneficial for CNS repair. Trends in Neurosciences, 22(7), 295–299.
Smith, K. J., & McDonald, W. I. (1999). The pathophysiology of multiple sclerosis: The mechanisms underlying the production of symptoms and the natural history of the disease. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series B, Biological Sciences, 354(1390), 1649–1673.
Stefan, K., Kunesch, E., Cohen, L. G., Benecke, R., & Classen, J. (2000). Induction of plasticity in the human motor cortex by paired associative stimulation. Brain, 123(3), 572–584.
Tseng, H. C., & Dichter, M. A. (2005). Platelet-derived growth factor-BB pretreatment attenuates excitotoxic death in cultured hippocampal neurons. Neurobiology of Diseases, 19(1–2), 77–83.
Valls-Solé, J., Pascual-Leone, A., Wassermann, E. M., & Hallett, M. (1992). Human motor evoked responses to paired transcranial magnetic stimuli. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology, 85(6), 355–364.
Vana, A. C., Flint, N. C., Harwood, N. E., Le, T. Q., Fruttiger, M., & Armstrong, R. C. (2007). Platelet-derived growth factor promotes repair of chronically demyelinated white matter. Journal of Neuropathology and Experimental Neurology, 66(11), 975–988.
Webster, H. D. (1997). Growth factors and myelin regeneration in multiple sclerosis. Multiple Sclerosis, 3(2), 113–120.
Zeller, D., Aufm Kampe, K., Biller, A., Stefan, K., Gentner, R., Schütz, A., et al. (2010). Rapid-onset central motor plasticity in multiple sclerosis. Neurology, 74(9), 728–735.
Ziemann, U., Tergau, F., Wassermann, E. M., Wischer, S., Hildebrandt, J., & Paulus, W. (1998). Demonstration of facilitatory I wave interaction in the human motor cortex by paired transcranial magnetic stimulation. Journal of Physiology, 511(1), 181–190.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by a Grant from Fondazione Italiana Sclerosi Multipla to DC (FISM Special Project 2012/S/2).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mori, F., Nicoletti, C.G., Rossi, S. et al. Growth Factors and Synaptic Plasticity in Relapsing–Remitting Multiple Sclerosis. Neuromol Med 16, 490–498 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8297-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12017-014-8297-7