Abstract
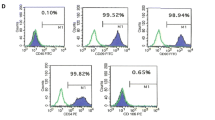
In this study, we examined the effect of preoperatively administered resveratrol (RV) and mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) on regeneration of partially hepatectomized rat liver. We also evaluated the effect of RV on homing of MSCs. MSCs were isolated from bone marrow and cultured in vitro. Wistar albino rats were randomly divided into four groups. In groups, rats received (1) no treatment, (2) single dose RV, (3) MSCs and (4) RV plus MSCs before partial hepatectomy (PH). Injected MSCs were traced by labeling them with green fluorescent protein, and liver regeneration was determined by comparison of liver weight gain, histological examination and immunohistochemical staining with proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA) for mitotic cells. The expression levels of tumor necrosis factor –alpha (TNF-α), interleukin-6 (IL-6) and hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) were also determined in the parafin sections of liver specimens with immunohistochemical staining. Administration of RV and MSCs separately or together enhanced liver regeneration despite decreasing the TNF-α and IL-6 expression. This positive contribution was probably due to direct raising effect on HGF for RV and HGF expression for MSCs that we demonstrated with immunohistochemical staining. Additionally, RV increased the homing of MSCs in liver probably related to life prolonging effect on MSCs. These results indicate that preoperative RV as well as MSCs application enhances liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats. Paying attention to RV about the effect on liver regeneration and homing of MSCs might be the goal of further investigations.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Michalopoulos, G. K., & DeFrances, M. C. (1997). Liver regeneration. Science, 276(5309), 60–66.
Schmidt, C., Bladt, F., Goedecke, S., Brinkmann, V., Zschiesche, W., Sharpe, M., et al. (1995). Scatter factor/hepatocyte growth factor is essential for liver development. Nature, 373(6516), 699–702.
Webber, E. M., Bruix, J., Pierce, R. H., & Fausto, N. (1998). Tumor necrosis factor primes hepatocytes for DNA replication in the rat. Hepatology, 28(5), 1226–1234.
Cressman, D. E., Greenbaum, L. E., DeAngelis, R. A., Ciliberto, G., Furth, E. E., Poli, V., et al. (1996). Liver failure and defective hepatocyte regeneration in interleukin-6-deficient mice. Science, 274(5291), 1379–1383.
Duncan, A. W., Dorrell, C., & Grompe, M. (2009). Stem cells and liver regeneration. Gastroenterology, 137(2), 466–481.
Abdel Aziz, M. T., Atta, H. M., Mahfouz, S., Fouad, H. H., Roshdy, N. K., Ahmed, H. H., et al. (2007). Therapeutic potential of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells on experimental liver fibrosis. Clinical Biochemistry, 40(12), 893–899.
Li, D. L., He, X. H., Zhang, S. A., Fang, J., Chen, F. S., & Fan, J. J. (2013). Bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells promote hepatic regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats. Pathobiology, 80(5), 228–234.
Sgambato, A., Ardito, R., Faraglia, B., Boninsegna, A., Wolf, F. I., & Cittadini, A. (2001). Resveratrol, a natural phenolic compound, inhibits cell proliferation and prevents oxidative DNA damage. Mutation Research, 496(1–2), 171–180.
Burkitt, M. J., & Duncan, J. (2000). Effects of trans-resveratrol on copper-dependent hydroxyl-radical formation and DNA damage: evidence for hydroxyl-radical scavenging and a novel, glutathione-sparing mechanism of action. Archives of Biochemistry and Biophysics, 381(2), 253–263.
Gorbunov, N., Petrovski, G., Gurusamy, N., Ray, D., do Kim, H., & Das, D. K. (2012). Regeneration of infarcted myocardium with resveratrol-modified cardiac stem cells. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, 16(1), 174–184.
Mohsin, S., Shams, S., Ali Nasir, G., Khan, M., Javaid Awan, S., Khan, S. N., et al. (2011). Enhanced hepatic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells after pretreatment with injured liver tissue.Differentiation. Research in Biological Diversity, 81(1), 42–48.
Kirimlioglu, H., Ecevit, A., Yilmaz, S., Kirimlioglu, V., & Karabulut, A. B. (2008). Effect of resveratrol and melatonin on oxidative stress enzymes, regeneration, and hepatocyte ultrastructure in rats subjected to 70 % partial hepatectomy. Transplantation Proceedings, 40(1), 285–289.
Karaoz, E., Kabatas, S., Duruksu, G., Okcu, A., Subasi, C., Ay, B., et al. (2012). Reduction of lesion in injured rat spinal cord and partial functional recovery of motility after bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation. Turkish Neurosurgery, 22(2), 207–217.
Higgins, G. M., & Anderson, R. M. (1931). Experimental pathology of the liver: Restoration of the liver of the white rat following partial surgical removal. Archieves of Pathology, 12, 186–202.
Pediaditakis, P., Lopez-Talavera, J. C., Petersen, B., Monga, S. P., & Michalopoulos, G. K. (2001). The processing and utilization of hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor following partial hepatectomy in the rat. Hepatology, 34(4 Pt 1), 688–693.
Naldini, L., Vigna, E., Narsimhan, R. P., Gaudino, G., Zarnegar, R., Michalopoulos, G. K., et al. (1991). Hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) stimulates the tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor encoded by the proto-oncogene c-MET. Oncogene, 6(4), 501–504.
Yamada, Y., Kirillova, I., Peschon, J. J., & Fausto, N. (1997). Initiation of liver growth by tumor necrosis factor: deficient liver regeneration in mice lacking type I tumor necrosis factor receptor. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 94(4), 1441–1446.
Scotté, M., Masson, S., Lyoumi, S., Hiron, M., Ténière, P., Lebreton, J. P., et al. (1997). Cytokine gene expression in liver following minor or major hepatectomy in rat. Cytokine, 9(11), 859–867.
Selzner, M., Camargo, C. A., & Clavien, P. A. (1999). Ischemia impairs liver regeneration after major tissue loss in rodents: protective effects of interleukin-6. Hepatology, 30(2), 469–475.
Kimura, T., Sakaida, I., Terai, S., Matsumura, Y., Uchida, K., & Okita, K. (1997). Inhibition of tumor necrosis factor-alpha production retards liver regeneration after partial hepatectomy in rats.Biochemical and. Biophysical Research Communications, 231(3), 557–560.
Chan, C. C., Cheng, L. Y., Lin, C. L., Huang, Y. H., Lin, H. C., & Lee, F. Y. (2011). The protective role of natural phytoalexin resveratrol on inflammation, fibrosis and regeneration in cholestatic liver injury.Molecular. Nutrition and Food Research, 55(12), 1841–1849.
Kirimlioglu, V., Karakayali, H., Turkoglu, S., & Haberal, M. (2008). Effect of resveratrol on oxidative stress enzymes in rats subjected to 70 % partial hepatectomy. Transplantation Proceedings, 40(1), 293–296.
Stervbo, U., Vang, O., & Bonnesen, C. (2006). Time- and concentration dependent effects of resveratrol in HL-60 and HepG2 cells. Cell Proliferation, 39(6), 479–493.
Feng, Y. H., Zhou, W. L., Wu, Q. L., Li, X. Y., Zhao, W. M., & Zou, J. P. (2002). Low dose of resveratrol enhanced immune response of mice. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica, 23(10), 893–897.
Kung, J. W., & Forbes, S. J. (2009). Stem cells and liver repair. Current Opinion in Biotechnology, 20(5), 568–574.
Li, J., Li, M., Niu, B., & Gong, J. (2011). Therapeutic potential of stem cell in liver regeneration. Frontiers of Medicine., 5(1), 26–32.
Zocco, M. A., Piscaglia, A. C., Giuliante, F., Arena, V., Novi, M., Rinninella, E., et al. (2011). CD133+ stem cell mobilization after partial hepatectomy depends on resection extent and underlying disease. Digestive and Liver Disease, 43(2), 147–154.
Almeida-Porada, G., Zanjani, E. D., & Porada, C. D. (2010). Bone marrow stem cells and liver regeneration. Experimental Hematology, 38(7), 574–580.
Ogawa, S., & Miyagawa, S. (2009). Potentials of regenerative medicine for liver disease. Surgery Today, 39(12), 1019–1025.
Bellayr, I. H., Gharaibeh, B., Huard, J., & Li, Y. (2010). Skeletal muscle-derived stem cells differentiate into hepatocyte-like cells and aid in liver regeneration. International Journal of Clinical and Experimental Pathology, 3(7), 681–690.
Weil, B. R., Markel, T. A., HermannJ, L., Abarbanell, A. M., & Meldrum, D. R. (2009). Mesenchymal stem cells enhance the viability and proliferation of human fetal intestinal epithelial cells following hypoxic injury via paracrine mechanisms. Surgery, 146(2), 190–197.
Lee, K. D., Kuo, T. K., Whang-Peng, J., Chung, Y. F., Lin, C. T., Chou, S. H., et al. (2004). In vitro hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Hepatology, 40(6), 1275–1284.
Schwartz, R. E., Reyes, M., Koodie, L., Jiang, Y., Blackstad, M., Lund, T., et al. (2002). Multipotent adult progenitor cells from bone marrow differentiate into functional hepatocyte-like cells. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 109(10), 1291–1302.
Popp, F. C., Slowik, P., Eggenhofer, E., Renner, P., Lang, S. A., Stoeltzing, O., et al. (2007). No contribution of multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells to liver regeneration in a rat model of prolonged hepatic injury. Stem Cells, 25(3), 639–645.
Wang, X., Willenbring, H., Akkari, Y., Torimaru, Y., Foster, M., Al-Dhalimy, M., et al. (2003). Cell fusion is the principal source of bone-marrow-derived hepatocytes. Nature, 422(6934), 897–901.
van Poll, D., Parekkadan, B., Cho, C. H., Berthiaume, F., Nahmias, Y., Tilles, A. W., et al. (2008). Mesenchymal stem cell-derived molecules directly modulate hepatocellular death and regeneration in vitro and in vivo. Hepatology, 47(5), 1634–1643.
Herrera, M. B., Fonsato, V., Bruno, S., Grange, C., Gilbo, N., Romagnoli, R., et al. (2013). Human liver stem cells improve liver injury in a model of fulminant liver failure. Hepatology, 57(1), 311–319.
Rustad, K. C., & Gurtner, G. C. (2012). Mesenchymal stem cells home to sites of injury and inflammation. Advances in Wound Care (New Rochelle), 1(4), 147–152.
Kidd, S., Spaeth, E., Dembinski, J. L., Dietrich, M., Watson, K., Klopp, A., et al. (2009). Direct evidence of mesenchymal stem cell tropism for tumor and wounding microenvironments using in vivo bioluminescent imaging. Stem Cells, 27(10), 2614–2623.
Kraitchman, D. L., Tatsumi, M., Gilson, W. D., Ishimori, T., Kedziorek, D., Walczak, P., et al. (2005). Dynamic imaging of allogeneic mesenchymal stem cells trafficking to myocardial infarction. Circulation, 112(10), 1451–1461.
Acknowledgments
Authors thank to Kocaeli University Research Fund for financial support (2013/67 HDP)
Conflict of Interest
All authors confirm that there is no conflict of interest in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Okay, E., Simsek, T., Subasi, C. et al. Cross Effects of Resveratrol and Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Liver Regeneration and Homing in Partially Hepatectomized Rats. Stem Cell Rev and Rep 11, 322–331 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-014-9572-6
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12015-014-9572-6