Abstract
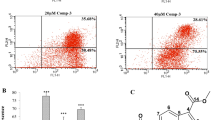
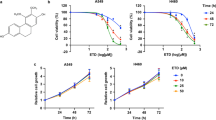
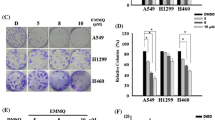
Migration and invasion are two core processes during cancer metastasis, and several signaling pathways have been shown to be involved. A key regulator of metastasis is the mitogen-activated protein kinase signaling pathway. Here, we report that the small molecule, 6,7-dimethyl-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one, inhibited isocitrate dehydrogenase activity and had anti-metastatic effects in A549 human non-small-cell lung cancer cells. 6,7-dimethyl-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one induced sequential inactivation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinases and p38 signaling pathways, both representative mitogen-activated protein kinase family members. We also found that 6,7-dimethyl-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one suppressed the transcription factor c-Myc, a regulator of cancer metastasis. This led to selective attenuation of matrix metalloproteinase-2 and subsequent suppression of migration and invasion in A549 non-small-cell lung cancer cells. 6,7-dimethyl-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one also suppressed metastasis in H1299 non-small-cell lung cancer cells, suggesting that the effects of 6,7-dimethyl-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one are not limited to A549 non-small-cell lung cancer cells. We therefore propose that the antimetastatic effects of 6,7-dimethyl-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one are due to sequential inactivation of the extracellular signal-regulated kinases and p38 signaling pathways.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- DTDQ:
-
(6,7-dimethyl-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxyphenyl)-3,4-dihydroquinolin-2(1H)-one)
- IDH:
-
(Isocitrate dehydrogenase)
- MAPK:
-
(Mitogen-activated protein kinase)
- MMP:
-
(Matrix metalloproteinase)
- NSCLC:
-
(Non-small-cell lung cancer)
References
Jemal, A., Cokkinides, V. E., Shafey, O., & Thun, M. J. (2003). Lung cancer trends in young adults: An early indicator of progress in tobacco control (United States). Cancer causes & control: CCC, 14, 579–585.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Database; SID=106673860. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/substance/106673860. Accessed 24 Feb 2016.
National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem BioAssay Database; AID=686970. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/bioassay/686970. Accessed 24 Feb 2016.
Basset, P., Okada, A., Chnard, M. P., Kannanb, R., Stoll, I., Anglard, P., Bellocq, J. P., & Rio, M. C. (1997). Matrix metalloproteinases as stromal effectors of human carcinoma progression: Therapeutic implicaitons. Matrix biology: Journal of the International Society for Matrix Biology, 15, 535–541.
Johnsen, M., Lund, L. R., Rømer, J., Almholt, K., & Danø, K. (1998). Cancer invasion and tissue remodeling: Common themes in proteolytic matrix degradation. Current opinion in cell biology, 10, 667–671.
Sahai, E. (2007). Illuminating the metastatic process. Nature reviews cancer, 7, 737–749.
Deryugina, E. I., & Quigley, J. P. (2006). Matrix metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer metastasis reviews, 25, 9–34.
Westermarck, J., & Kähäri, V. M. (1999). Regulation of matrix metalloproteinase expression in tumor invasion. The FASEB journal: Official publication of the Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology, 13, 781–792.
Wolfer, A., & Ramaswamy, S. (2011). MYC and metastasis. Cancer research, 71, 2034–2037.
Dang, C. V. (2012). MYC on the path to cancer. Cell, 149, 22–35.
Schmittgen, T. D., & Livak, K. J. (2008). Analyzing real-time PCR data by the comparative C(T) method. Nature protocols, 3, 1101–1108.
Kim, J. H., Cho, E. B., Lee, J., Jung, O., Ryu, B. J., Kim, S. H., Cho, J. Y., Ryou, C., & Lee, S. Y. (2015). Emetine inhibits migration and invasion of human non-small-cell lung cancer cells via regulation of ERK and p38 signaling pathways. Chemico-biological interactions, 242, 25–33.
Ryu, B. J., Lee, H., Kim, S. H., Heo, J. N., Choi, S. W., Yeon, J. T., Lee, J., Lee, J., Cho, J. Y., Kim, S. H., & Lee, S. Y. (2014). PF-3758309, p21-activated kinase 4 inhibitor, suppresses migration and invasion of A549 human lung cancer cells via regulation of CREB, NF-κB, and β-catenin signaling. Molecular and cellular biochemistry, 389, 69–77.
Ku, M. J., Kim, J. H., Lee, J., Cho, J. Y., Chun, T., & Lee, S. Y. (2015). Maclurin suppresses migration and invasion of human non-small-cell lung cancer cells via anti-oxidative activity and inhibition of the Src/FAK-ERK-β-catenin pathway. Molecular and cellular biochemistry, 402, 243–252.
Tan, F., Jiang, Y., Sun, N., Chen, Z., Ly, Y., Shao, K., Li, N., Qiu, B., Gao, Y., Li, B., Tan, X., Zhou, F., Wang, Z., Ding, D., Wang, J., Sun, J., Hang, J., Shi, S., Feng, X., He, F., & He, J. (2012). Identification of isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 as a potential diagnostic and prognostic biomarker for non-small cell lung cancer by proteomic analysis. Molecular & cellular proteomics: MCP, 2, 008821.
Sun, N., Chen, Z., Tan, F., Zhang, B., Yao, R., Zhou, C., Li, J., Gao, Y., Liu, Z., Tan, X., Zhou, F., He, M. Y., Shao, K., Li, N., Qiu, B., Sun, J., Yu, Y., Wang, S., Zhao, Y., Shi, X., & He, J. (2013). Isocitrate dehydrogenase 1 is a novel plasma biomarker for the diagnosis of non-small cell lung cancer. Clinical cancer research: An official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research, 18, 5136–5145.
Dufour, A., Sampson, N. S., Zucker, S., & Cao, J. (2008). Role of the hemopexin domain of matrix metalloproteinases in cell migration. Journal of cellular physiology, 217, 643–651.
Huang, C., Jacobson, K., & Schaller, M. D. (2004). MAP kinases and cell migration. Journal of cell science, 117, 4619–4628.
Munshi, H. G., Wu, Y. I., Mukhopadhyay, S., Ottaviano, A. J., Sassano, A., Koblinski, J. E., Platanias, L. C., & Stack, M. S. (2004). Differential regulation of membrane type 1-matrix metalloproteinase activity by ERK1/2- and p38 MAPK-modulated tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 2 expression controls transforming growth factor-beta 11-induced pericellular collagenases. The Journal of biological chemistry, 279, 39042–39050.
Ku, M. J., Park, J. W., Ryu, B. J., Son, Y. J., Kim, S. H., & Lee, S. Y. (2013). CK2 inhibitor CX4945 induces sequential inactivation of proteins in the signaling pathways related with cell migration and suppresses metastasis of A549 human lung cancer cells. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters, 23, 5609–5613.
Acknowledgements
We thank Eun Byul Cho and Okkeun Jung for their comments and suggestions. This research was supported by Basic Science Research Program through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education (NRF-2015R1D1A1A09058494).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Additional information
Soonchan Park and Jongsung Lee contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, S., Lee, J. & Lee, S. IDH-Inhibiting Small Molecule DTDQ Inhibits Migration and Invasion of A549 Human Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer Cells via Sequential Inactivation Of ERK and P38 Signaling Pathways. Cell Biochem Biophys 76, 255–263 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-017-0789-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-017-0789-2