Abstract
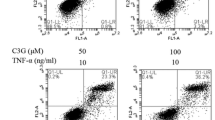
The aim of this study was to evaluate the effect of paeonol on the proliferation, migration, and inflammation induced by tumor necrosis factor (TNF-α) of rat vascular smooth muscle cells (VSMCs). Primary rat VSMCs were identified by immunofluorescence assay. The inhibition of VSMCs proliferation induced by TNF-α was observed after paeonol treatment in a dose-dependent manner. Treatment with 100 μM paeonol significantly reduced the expression of proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA). On the other hand, transwell assay showed that treatment with paeonol suppressed the invasion of TNF-α-induced VSMCs and the production of inflammation factors stimulated by TNF-α. For apoptosis induced by paeonol, Western blot analysis showed that cleaved caspase-3 and -9 were detected, and pro-apoptotic protein Bax was up-regulated, whereas anti-apoptotic protein Bcl-2 was down-regulated by paeonol in TNF-α-stimulated VSMCs. ELISA analysis data showed that both levels of IL-1β and IL-6 produced by the stimulation of TNF-α were decreased by paeonol in a dose-dependent manner in VSMCs. These results suggest that paeonol can effectively inhibit the proliferation through apoptotic induction through caspase pathway in VSMCs induced by TNF-α. Also, paeonol significantly reduced the invasion and the inflammation stimulated by TNF-α in VSMCs.





Similar content being viewed by others

References
Lusis, A. J. (2000). Atherosclerosis. Nature, 407, 233–241.
Doran, A. C., Meller, N., & McNamara, C. A. (2008). Role of smooth muscle cells in the initiation and early progression of atherosclerosis. Arteriosclerosis Thrombosis and Vascular Biology, 28, 812–819.
Williams KJ, Tabas I. (1999). Atherosclerosis–an inflammatory disease. The New England Journal of Medicine, 340, 1928; author reply 1929.
Newby, A. C., & Zaltsman, A. B. (1999). Fibrous cap formation or destruction—the critical importance of vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation, migration and matrix formation. Cardiovascular Research, 41, 345–360.
Liu, M. H., Lin, A. H., Lee, H. F., Ko, H. K., Lee, T. S., & Kou, Y. R. (2014). Paeonol attenuates cigarette smoke-induced lung inflammation by inhibiting ROS-sensitive inflammatory signaling. Mediators of Inflammation, 2014, 651890.
Cai, J., Chen, S., Zhang, W., Hu, S., Lu, J., Xing, J., & Dong, Y. (2014). Paeonol reverses paclitaxel resistance in human breast cancer cells by regulating the expression of transgelin 2. Phytomedicine, 21, 984–991.
Liu, J., Wang, S., Feng, L., Ma, D., Fu, Q., Song, Y., & Ma, S. (2013). Hypoglycemic and antioxidant activities of paeonol and its beneficial effect on diabetic encephalopathy in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Journal of Medicinal Food, 16, 577–586.
Hsieh, C. L., Cheng, C. Y., Tsai, T. H., Lin, I. H., Liu, C. H., Chiang, S. Y., & Tang, N. Y. (2006). Paeonol reduced cerebral infarction involving the superoxide anion and microglia activation in ischemia-reperfusion injured rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 106, 208–215.
Chou, T. C. (2003). Anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects of paeonol in carrageenan-evoked thermal hyperalgesia. British Journal of Pharmacology, 139, 1146–1152.
Dai, M., Zhi, X., Peng, D., & Liu, Q. (1999). Inhibitory effect of paeonol on experimental atherosclerosis in quails. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 24(488–490), 512.
Pan, L. L., & Dai, M. (2009). Paeonol from Paeonia suffruticosa prevents TNF-alpha-induced monocytic cell adhesion to rat aortic endothelial cells by suppression of VCAM-1 expression. Phytomedicine, 16, 1027–1032.
Wang, X., Zhu, G., Yang, S., Cheng, H., Wang, F., Li, X., & Li, Q. (2011). Paeonol prevents excitotoxicity in rat pheochromocytoma PC12 cells via downregulation of ERK activation and inhibition of apoptosis. Planta Medica, 77, 1695–1701.
Zhou, J., Zhou, L., Hou, D., Tang, J., Sun, J., & Bondy, S. C. (2011). Paeonol increases levels of cortical cytochrome oxidase and vascular actin and improves behavior in a rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Research, 1388, 141–147.
Lei, Y., Li, H. X., Jin, W. S., Peng, W. R., Zhang, C. J., Bu, L. J., & Sun, G. P. (2013). The radiosensitizing effect of Paeonol on lung adenocarcinoma by augmentation of radiation-induced apoptosis and inhibition of the PI3K/Akt pathway. International Journal of Radiation Biology, 89, 1079–1086.
Yin, J., Wu, N., Zeng, F., Cheng, C., Kang, K., & Yang, H. (2013). Paeonol induces apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cells. Acta Histochemica, 115, 835–839.
Li, M., Tan, S. Y., & Wang, X. F. (2014). Paeonol exerts an anticancer effect on human colorectal cancer cells through inhibition of PGE(2) synthesis and COX-2 expression. Oncology Reports, 32, 2845–2853.
Willis, S. N., & Adams, J. M. (2005). Life in the balance: how BH3-only proteins induce apoptosis. Current Opinion in Cell Biology, 17, 617–625.
Price, J. T., & Thompson, E. W. (2002). Mechanisms of tumour invasion and metastasis: Emerging targets for therapy. Expert opinion on therapeutic targets, 6, 217–233.
Chen, N., Liu, D., Soromou, L. W., Sun, J., Zhong, W., Guo, W., & Feng, H. (2014). Paeonol suppresses lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory cytokines in macrophage cells and protects mice from lethal endotoxin shock. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology, 28, 268–276.
Wang, J. C., & Bennett, M. (2012). Aging and atherosclerosis: Mechanisms, functional consequences, and potential therapeutics for cellular senescence. Circulation Research, 111, 245–259.
Lutgens, E., de Muinck, E. D., Kitslaar, P. J., Tordoir, J. H., Wellens, H. J., & Daemen, M. J. (1999). Biphasic pattern of cell turnover characterizes the progression from fatty streaks to ruptured human atherosclerotic plaques. Cardiovascular Research, 41, 473–479.
Dai, M., Liu, Q. Y., Gu, C. G., & Zhang, H. Y. (2000). Inhibitory effect of paeonol on lipid peroxidational reaction and oxidational decorate of low density lipoprotein. China Journal of Chinese Materia Medica, 25, 625–627.
Chen, J., Dai, M., & Wang, Y. (2014). Paeonol inhibits proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells stimulated by high glucose via Ras-Raf-ERK1/2 signaling pathway in coculture model. Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine, 2014, 484269.
Wang, Y. Q., Dai, M., Zhong, J. C., & Yin, D. K. (2012). Paeonol inhibits oxidized low density lipoprotein-induced monocyte adhesion to vascular endothelial cells by inhibiting the mitogen activated protein kinase pathway. Biological & Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 35, 767–772.
Galkina, E., & Ley, K. (2009). Immune and inflammatory mechanisms of atherosclerosis (*). Annual Review of Immunology, 27, 165–197.
Li, N., Fan, L. L., Sun, G. P., Wan, X. A., Wang, Z. G., Wu, Q., & Wang, H. (2010). Paeonol inhibits tumor growth in gastric cancer in vitro and in vivo. World Journal of Gastroenterology, 16, 4483–4490.
Adams, J. M. (2003). Ways of dying: Multiple pathways to apoptosis. Genes & Development, 17, 2481–2495.
Bennett, M. R., Evan, G. I., & Schwartz, S. M. (1995). Apoptosis of human vascular smooth muscle cells derived from normal vessels and coronary atherosclerotic plaques. The Journal of Clinical Investigation, 95, 2266–2274.
Ou, Y., Li, Q., Wang, J., Li, K., & Zhou, S. (2014). Antitumor and apoptosis induction effects of paeonol on mice bearing EMT6 breast carcinoma. Biomolecules & Therapeutics, 22, 341–346.
Yin, S., Wang, R., Zhou, F., Zhang, H., & Jing, Y. (2011). Bcl-xL is a dominant antiapoptotic protein that inhibits homoharringtonine-induced apoptosis in leukemia cells. Molecular Pharmacology, 79, 1072–1083.
Adams, J. M., & Cory, S. (2007). The Bcl-2 apoptotic switch in cancer development and therapy. Oncogene, 26, 1324–1337.
Ley, R., Ewings, K. E., Hadfield, K., & Cook, S. J. (2005). Regulatory phosphorylation of Bim: Sorting out the ERK from the JNK. Cell Death and Differentiation, 12, 1008–1014.
Itoh, Y. (2006). MT1-MMP: A key regulator of cell migration in tissue. IUBMB Life, 58, 589–596.
Feghali, C. A., & Wright, T. M. (1997). Cytokines in acute and chronic inflammation. Frontiers in Bioscience, 2, d12–d26.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Meng, L., Xu, W., Guo, L. et al. Paeonol Inhibits the Proliferation, Invasion, and Inflammatory Reaction Induced by TNF-α in Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells. Cell Biochem Biophys 73, 495–503 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0686-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0686-5