Abstract
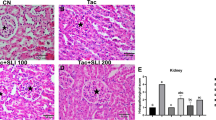
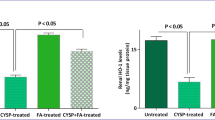
Several monomers isolated from Tripterygium wilfordii Hook f. (Celastraceae) have attracted worldwide interest. In this study, we established a simple and reliable kidney transplantation model in beagle dog to evaluate the immunosuppressive activity of demethylzeylasteral (T-96), an immunosuppressive monomer isolated from the root xylem of T. wilfordii. Recipient and donor male beagle dogs were obtained from two different breeders to ensure MHC mismatching. All dogs were randomly divided into six groups following kidney transplantation, and different doses of T-96 or cyclosporine A (CsA) were administered to each group during 14 days of observation. The results showed that T-96 alone at a dosage of 10 or 20 mg/kg/day prolonged graft survival up to 10.83 ± 1.47 or 11.17 ± 1.47 days. A combination of T-96 and CsA significantly prolonged the survival time to 13.33 ± 1.75 days. The results demonstrated that T-96 can inhibit acute rejection in kidney transplantation, and the inhibitory effect of T-96 was enhanced when combined with CsA, which suggests the possible use in organ transplantation to prevent immune rejection.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Legendre, C., & Kreis, H. (2010). A tribute to Jean Hamburger’s contribution to organ transplantation. American Journal of Transplantation, 10, 2392–2395.
Murray, J. E. (2011). Ronald Lee Herrick Memorial: June 15, 1931–December 27, 2010. American Journal of Transplantation, 11, 419.
Garcia, G. G., Harden, P. N., & Chapman, J. R. (2012). World Kidney Day 2012: the global role of kidney transplantation. American Journal of Kidney Diseases, 59, 319–324.
Wissing, K. M., Abramowicz, D., Broeders, N., & Vereerstraeten, P. (2000). Hypercholesterolemia is associated with increased kidney graft loss caused by chronic rejection in male patients with previous acute rejection. Transplantation, 70, 464–472.
Meier-Kriesche, H. U., Ojo, A. O., Hanson, J. A., Cibrik, D. M., Punch, J. D., Leichtman, A. B., et al. (2000). Increased impact of acute rejection on chronic allograft failure in recent era. Transplantation, 70, 1098–1100.
Tanabe, K. (2003). Calcineurin inhibitors in renal transplantation: what is the best option? Drugs, 63, 1535–1548.
Borel, J. F. (2002). History of the discovery of cyclosporin and of its early pharmacological development. Wiener Klinische Wochenschrift, 114, 433–437.
Stahelin, H. F. (1996). The history of cyclosporin A (Sandimmune) revisited: another point of view. Experientia, 52, 5–13.
Kunzendorf, U., Ziegler, E., & Kabelitz, D. (2004). FTY720–the first compound of a new promising class of immunosuppressive drugs. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 19, 1677–1681.
First, M. R., & Fitzsimmons, W. E. (2004). New drugs to improve transplant outcomes. Transplantation, 77, S88–S92.
Cohen, D. J., Loertscher, R., Rubin, M. F., Tilney, N. L., Carpenter, C. B., & Strom, T. B. (1984). Cyclosporine: A new immunosuppressive agent for organ transplantation. Annals of Internal Medicine, 101, 667–682.
Vincenti, F. (2002). What’s in the pipeline? New immunosuppressive drugs in transplantation. American Journal of Transplantation, 2, 898–903.
Jin, M. B., Nakayama, M., Ogata, T., Fujita, M., Mino, K., Taniguchi, M., et al. (2002). A novel leflunomide derivative, FK778, for immunosuppression after kidney transplantation in dogs. Surgery, 132, 72–79.
Mihatsch, M. J., Kyo, M., Morozumi, K., Yamaguchi, Y., Nickeleit, V., & Ryffel, B. (1998). The side-effects of ciclosporine-A and tacrolimus. Clinical Nephrology, 49, 356–363.
Liu, L., & Li, Y. (2014). The unexpected side effects and safety of therapeutic monoclonal antibodies. Drugs of Today, 50, 33–50.
Hansel, T. T., Kropshofer, H., Singer, T., Mitchell, J. A., & George, A. J. (2010). The safety and side effects of monoclonal antibodies. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery, 9, 325–338.
Bao, J., & Dai, S. M. (2011). A Chinese herb Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: mechanism, efficacy, and safety. Rheumatology International, 31, 1123–1129.
Xu, W., Lin, Z., Yang, C., Zhang, Y., Wang, G., Xu, X., et al. (2009). Immunosuppressive effects of demethylzeylasteral in a rat kidney transplantation model. International Immunopharmacology, 9, 996–1001.
Tao, X., & Lipsky, P. E. (2000). The Chinese anti-inflammatory and immunosuppressive herbal remedy Tripterygium wilfordii Hook F. Rheumatic Diseases Clinics of North America, 26, 29–50. viii.
Chou, C. T., & Chang, S. C. (1998). The inhibitory effect of common traditional anti-rheumatic herb formulas on prostaglandin E and interleukin 2 in vitro: a comparative study with Tripterygium wilfordii. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 62, 167–171.
Brinker, A. M., Ma, J., Lipsky, P. E., & Raskin, I. (2007). Medicinal chemistry and pharmacology of genus Tripterygium (Celastraceae). Phytochemistry, 68, 732–766.
Ren, B., Sun, J., Hu, C., Cong, L., Zhang, L., King, N., et al. (2001). Immunosuppressive effects of Tripterygium wilfordii hook F in a rat liver transplant model. Transplantation Proceedings, 33, 520–521.
Bai, J. P., Shi, Y. L., Fang, X., & Shi, Q. X. (2003). Effects of demethylzeylasteral and celastrol on spermatogenic cell Ca2 + channels and progesterone-induced sperm acrosome reaction. European Journal of Pharmacology, 464, 9–15.
Tamaki, T., Kawamura, A., Komatsu, Y., Kawamura, H., Maruyama, H., & Morota, T. (1996). Phenolic nortriterpene demethylzeylasteral: A new immunosuppressive component of Tripterygium wilfordii Hook f. Transplantation Proceedings, 28, 1379–1380.
Yu, D. F., Hu, B. H., Chen, G. P., Yang, C. X., Yang, J., Xu, J. Y., et al. (1990). Structure revision of triptophenolide. Yao xue xue bao = Acta pharmaceutica Sinica, 25, 929–931.
Qian, S. Z. (1987). Tripterygium wilfordii, a Chinese herb effective in male fertility regulation. Contraception, 36, 335–345.
Tamaki, T., Morota, T., Kawamula, H., Maruyama, H., Kaneko, A., Nunome, S., et al. (1997). Immunosuppressive and anti-inflammatory effects of phenolic nortriterpenoid, demethylzeylasteral, from Tripterygium wilfordii. Journal of Natural Medicines, 51, 98–104.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Huimin An and Yu Zhu have contributed equally to this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
An, H., Zhu, Y., Xu, W. et al. Evaluation of Immunosuppressive Activity of Demethylzeylasteral in a Beagle Dog Kidney Transplantation Model. Cell Biochem Biophys 73, 673–679 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0684-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0684-7