Abstract
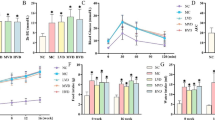
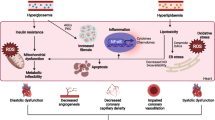
Diabetes mellitus is associated with significant morbidity and mortality that contributes to pathogenesis of cardiovascular diseases. Diosgenin, a naturally occurring aglycone, is present abundantly in fenugreek. The steroidal saponin is being used as a traditional medicine for diabetes. The present study has investigated the effects of diosgenin on lipid profile in the heart and brain, mRNA expression, and hepatic HMG-CoA reductase (HMGR) activity of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. In our study, diosgenin was administered (40 mg/kg b.w.) orally for 45 days to control animals and experimentally induced diabetic rats. The effects of diosgenin on glucose, plasma insulin, cholesterol, triglycerides, free fatty acids, and phospholipids (PLs) in the heart and brain were studied. The levels of glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides, free fatty acids, PLs, and HMGR activity were increased significantly (P < 0.05) whereas plasma insulin level was decreased in diabetic rats. Administration of diosgenin to diabetic rats significantly reduced blood glucose, cholesterol, triglycerides, free fatty acids, PLs levels, and also HMGR activity. In addition, the plasma insulin level was increased in diosgenin-treated diabetic rats. The above findings were correlated with histological observations of the heart and brain. The results showed that administration of diosgenin remarkably increased plasma insulin level with absolute reduction of blood glucose, lipid profile, and HMGR level when compared to diabetic control rats. The results have suggested that diosgenin prevents hypercholesterolemia and hepatosteatosis by modulation of enzymatic expression that is associated with cholesterol metabolism.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular diseases
- VLDL:
-
Very low density lipoproteins
References
Farhad, R., Danesh, D., Yashpal, S., & Kanwar, M. (2004). Modulatory effects of HMG-CoA reductase inhibitors in diabetic microangiopathy. The FASEB Journal, 18, 806–810.
Kim, S. H., Hyun, S. H., & Choung, S. Y. (2006). Anti-diabetic effect of cinnamon extract on blood glucose in db/db mice. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 104, 119–123.
Farag, Y. M. K., & Gaballa, M. R. (2011). Diabesity: An overview of a rising epidemic. Nephrology, Dialysis, Transplantation, 26(1), 28–35.
Reasner, C. A. (2008). Reducing cardiovascular complications of diabetes by targeting multiple risk factors. Journal of Cardiovascular Pharmacology, 52, 136–144.
Nagappa, A. N., Thakurdesai, P. A., Rao, N. V., & Singh, J. (2003). Antidiabetic activity of Termanalia catappa Linn fruits. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 88, 45–50.
Deedwania, P. C., Hunninghake, D. B., & Bays, H. (2004). Effects of lipid-altering treatment in diabetes mellitus and metabolic syndrome. American Journal of Cardiology, 93, 18C–20C.
Tiwari, A. K., & Madhusudana, R. J. (2002). Diabetes mellitus and multiple therapeutic approaches of phytochemicals: Present status and future prospects. Current Science, 83, 30–38.
Erukainure, O. L., Abovwe, J. A., Adefegha, A. S., & Egwuche, R. U. (2011). Antilipemic and hypocholesteremic activities of Globimetula braunii in rats. Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology, 63, 657–661.
Pushparaj, P., Tan, C. H., & Tan, B. K. H. (2000). Effects of Averrhoa bilimbi leaf extract on blood glucose and lipids in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Journal of Ethnopharmacology, 72, 69–76.
Superko, H. R. (1989). Drug therapy and the prevention of atherosclerosis in humans. American Journal of Cardiology, 64, 31G–38G.
Jagadeesan, A. J., Langeswaran, K., & Gowtham Kumar, S. (2013). Chemopreventive potential of diosgenin on modulating glycoproteins, tca cycle enzymes, carbohydrate metabolising enzymes and biotransformation enzymes against n-methyl-n-nitrosourea induced mammary carcinogenesis. International Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, 5, 575–582.
Pari, L., Monisha, P., & Mohamed Jalaludeen, A. (2012). Beneficial role of diosgenin on oxidative stress in aorta of streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. European Journal of Pharmacology, 691, 143–150.
Mastan, S., & Eswar Kumar, K. (2009). Effect of ritonavir on the pharmacodynamics of gliclazide in animal models. Diabetologia Croatia, 38, 105–113.
Pulido, N., Suarez, A., & Casanova, B. (1997). Glyclazide treatment of streptozotocin diabetic rats restores GLUT4 protein content and basal glucose uptake in skeletal muscle. Metabolism, 46, 10–13.
Folch, C., Lees, M., & Solane, S. G. H. (1957). A simple method for isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 226, 497–509.
Zlatkis, A., Zak, B., & Boyle, G. J. (1953). A simple method for determination of serum cholesterol. Clinic Journal of Medicine, 41, 486–492.
Fossati, P., & Lorenzo, P. (1982). Serum triglycerides determined calorimetrically with an enzyme that produces hydrogen peroxide. Clinical Chemistry, 28, 2077–2080.
Falholt, K., Falholt, W., & Lund, B. (1973). An easy colorimetric method for routine determination of free fatty acids in plasma. Clinica Chimica Acta, 46, 105–111.
Zilversmit, D. B., & Davis, A. K. (1950). Microdetermination of phospholipids by TCA precipitation. Journal of Laboratory and Clinical Medicine, 35, 155–159.
Shapiro, D. J., Nordstrom, J. L., Mitschelen, J. J., Rodwell, V. W., & Schimke, R. T. (1974). Microassay for 3-hydroxy- 3-methylglutaryl-CoA reductase in rat liver and in L-cell fibroblasts. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 370, 369–377.
Proks, P., Reimann, F., Green, N., Gribble, F., & Aschroft, F. (2002). Sulfonyl urea stimulation in insulin secretion. Diabetes, 51, S368–S376.
Satheesh, A., & Pari, L. (2008). Effect of pterostilbene on lipids and lipid profiles in streptozotocin–nicotinamide induced type 2 diabetes mellitus. Journal of Applied Biomedicine, 6, 31–37.
Chauhan, U. P. S., Jagi, C. B., & Singh, V. N. (1987). Incorporation of 32Pi into plasma phosphatidylcholine of diabetic rats. Indian Journal of Nuclear Medicine, 2, 92–98.
Kang, T. H., Moon, E., Hong, B. N., Choi, S. Z., Son, M., Park, J. H., & Kim, S. Y. (2011). Diosgenin from Dioscoreanipponica ameliorates diabetic neuropathy by inducing nerve growth factor. Biological and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 34, 1493–1498.
Cohn, R. M., & Roth, K. S. (1996). Lipid and lipoprotein metabolism. Biochemistry and disease. Baltimore: Williams and Wilkins Publishers.
Draznin, B., & Eckel, R. H. (1993). Diabetes and Atherosclerosis. Molecular Basis and Clinical Aspects (Vol. 12, p. 203). New York: Elsevier.
Frayn, K. N. (1993). Insulin resistance and lipid metabolism. Current Opinion in Lipidology, 4, 197–204.
Ashokkumar, N., Pari, L., Manimekalai, A., & Selvaraju, K. (2005). Effect of N-benzoyl-d-phenylalanine on streptozotocin induced changes in the lipids and lipoprotein profile in rats. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 57, 359–366.
Pari, L., & Ashokkumar, N. (2005). Effect of N-benzoyl-d-phenyalanine on lipid profile in liver of neonatal streptozotocin diabetic rats. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology, 19, 563–568.
Saravanan, G., & Ponmurugan, P. (2011). Ameliorative potential of S-allylcysteine on oxidative stress in STZ induced diabetic rats. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 189, 100–106.
Saravanan, G., & Ponmurugan, P. (2012). Ameliorative potential of S-allylcysteine: Effect on lipid profile and changes in tissue fatty acid composition in experimental diabetes. Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology, 64, 639–644.
Braun, J. E., & Severson, D. L. (1992). Regulation of the synthesis, processing and translocation of lipoprotein lipase. Biochemical Journal, 287, 337–347.
Palsamy, P., & Subramanian, S. (2008). Resveratrol, a natural phytoalexin, normalizes hyperglycemia in streptozotocin nicotinamide induced experimental diabetic rats. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 62, 598–605.
Kuwahara, Y., Yanagishita, T., Konno, N., & Katagiri, T. (1997). Changes in microsomal membrane phospholipids and fatty acids and in activities of membrane-bound enzymes in diabetic rat heart. Basic Research in Cardiology, 92, 214–222.
Yagi, K. (1987). Lipid peroxides and human diseases. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids, 45, 337–351.
Anandh Babu, P. V., Sabitha, K. E., & Shyamaladevi, C. S. (2006). Green tea impedes dyslipidemia, lipid peroxidation, protein glycation and ameliorates Ca2+-ATPase and Na+/K+-ATPase activity in the heart of streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 162, 157–164.
Akiyama, S., Katsumata, S. I., & Suzuki, K. (2009). Hypoglycemic and hypolipidemic effect of hesperidine. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 73, 2779–2782.
Rydgren, T., & Sandler, S. (2009). The protective effect of simvastatin against low dose streptozotocin induced type 1 diabetes in mice is independent of inhibition of HMG-CoA reductase. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications, 379, 1076–1079.
Ness, G. C., Holland, R. C., & Lopez, D. (2006). Selective compensatory induction of hepatic HMG-CoA reductase in response to inhibition of cholesterol absorption. Experimental Biology and Medicine, 231, 559–565.
Kaleem, M., Asif, M., Ahmed, Q., & Bano, B. (2006). Antidiabetic and antioxidant activity of Annona squamosa extract in streptozotozin induced diabetic rats. Singapore Medical Journal, 47, 670–675.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hao, S., Xu, R., Li, D. et al. Attenuation of Streptozotocin-Induced Lipid Profile Anomalies in the Heart, Brain, and mRNA Expression of HMG-CoA Reductase by Diosgenin in Rats. Cell Biochem Biophys 72, 741–749 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0525-8
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0525-8