Abstract
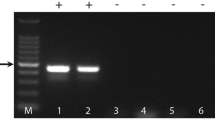
Scrub typhus is one of the most common infectious diseases of rural south and southeastern Asia and the western Pacific. It emerged in Shandong Province in northern China from autumn to winter of 1986. Since then, the “autumn–winter type scrub typhus” has been found in many areas of northern China. However, the principle genotypes of Orientia tsutsugamushi still remain unknown. This study was undertaken to identify the genotypes of O. tsutsugamushi obtained from scrub typhus patients, chigger mites and rodents from the focal point of the problem in Shandong Province. Forty-four isolates from patients, rodents, and chiggers, 47 blood clots from patients during the acute phase, 10 eschars from patients during the convalescence phase and 16 pools of larval chiggers were tested for the scrub typhus antigen 56-kD protein (Sta56) gene by nested PCR methodology and additional sequence analysis including DNA sequence alignment and phylogenetic analysis. Based on nested PCR, ninety-five initial PCR-positive samples produced amplicons using Kawasaki strain-specific primers, while the other two (the FXS4 and LHGM2 strains) produced amplicons using Karp strain-specific primers. The partial Sta56 gene sequence analysis indicated that the sequence homologies of 3 selected isolates (the B16, FXS2, and XDM2 strains) and 7 eschars out of the 95 samples, which were nested PCR-positive using Kawasaki strain-specific primers, were 94–98 % to that of Kawasaki strain. The sequence homology of the FXS4 and LHGM2 strains to that of the Karp strain was respectively 83 and 96 %. These findings implied that the key genotypes of O. tsutsugamushi in patients, rodents, and chiggers in Shandong Province were identical and similar to Kawasaki strains.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Silpapojakul, K. (1997). Scrub typhus in the Western Pacific region. Annual Academy Medicine Singapore, 26, 794–800.
Wu, G. H. (2000). The epidemiological characteristics and prevention and cure of scrub typhus in China. Chinese Journal of Public Health, 16, 777–779.
Chen, X. R. (2001). Scrub typhus and Orientia tsutsugamushi. Beijing: Military Medical Science Press.
Yang, Y. F., Wang, J. L., Yao, Y. C., Cheng, Z. R., Xu, Z. P., & Wang, M. (1987). Preliminary investigation of scrub typhus in Shandong Province. Chinese of Journal of Epidemiology, 8, 280.
Liu, Y. X., Yang, Z. Q., Wu, Q. Y., Sun, H. L., Peng, Z. L., Miao, Z. S., et al. (2000). Epidemiological study of autumn-winter type scrub typhus in a new endemic focus of Fei County, Shandong Province, China. Systematic and Applied Acarology, 5, 25–31.
Liu, Y. X., Zhao, Z. T., Yang, Z. Q., Zhang, J. L., Xu, J. J., Wu, Q. Y., et al. (2003). Epidemiological studies on host animals of scrub typhus of the autumn-winter type in Shandong Province, China. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, 34, 826–830.
Chen, X. R., Zhang, Y. G., Yu, Q., & Wang, H. X. (1997). The rapid detection and analysis of rickettsiae with monoclonal antibodies to Rickettsial heilongjingii and primer pairs for rickettsial PCR. Chinese Journal of Zoonoses, 13, 24–26.
Furuya, Y., Yoshida, Y., Katayama, T., Yamamoto, S., & Kawamura, J. R. (1993). Serotype-specific amplification of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi DNA by nested polymerase chain reaction. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 31, 1637–1640.
Guo, H. B., Pan, S. Z., Li, X. F., Tang, J. Q., Zhang, Y., & Wu, G. H. (1997). Studies on detecting and typing of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi by polymerase chain reaction. Chinese Journal of Zoonoses, 13, 8–11.
Xi, Z. Y., & Li, J. C. (1997). A systematic comparative study of gene techniques for detection of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi in chiggers and patients’ blood samples by nested polymerase chain reaction. Chinese Journal of Zoonoses, 13, 3–7.
Ohashi, N., Nashimoto, H., Ikeda, H., & Tamura, A. (1990). Cloning and sequencing of the gene (tsg56) encoding a type-specific antigen from Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Gene, 91, 119–122.
Ohashi, N., Nashimoto, H., Ikeda, H., & Tamura, A. (1992). Diversity of immunodominant 56-kDa type specific antigen (TSA) of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 267, 12728–12735.
Ohashi, N., Koyama, Y., Urakami, H., Fukuhara, M., Tamura, A., Kawamori, F., et al. (1996). Demonstration of antigenic and genotypic variation of Orientia tsutsugamushi which were isolated in Japan, and their classification into type and subtype. Microbiology and Immunology, 40, 627–638.
Stover, C. K., Marana, D. P., Carter, J. M., Roe, B. A., Mardis, E., & Oaks, E. V. (1990). The 56-kilodalton major protein antigen gene of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi: molecular cloning and sequencing analysis of the Sta56 gene and precise identification of a strain-specific epitope. Infectious Immunology, 58, 2076–2084.
Kumar, S., Tamura, K., & Nei, M. (2004). Mega 3: An integrated software for molecular evolutionary genetics analysis and sequence alignment. Brief Bioinformation, 5, 150–163.
Liu, Y. X., Gao, Y., Zhao, Z. T., Zhang, J. L., Yang, Z. Q., Bu, X. P., et al. (2004). Amplification and typing of Sta56 gene of Orientia tsutsugamushi from Shandong province. Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 25, 698–701.
Liu, Y. X., Zhao, Z. T., Gao, Y., Jia, C. Q., Zhang, J. L., Yang, Z. Q., et al. (2004). Characterization of Orientia tsutsugamushi strains isolated in Shandong province, China by immunofluorescence and restriction fragment length polymorphism (RFLP) analyses. Southeast Asian Journal of Tropical Medicine and Public Health, 35, 353–357.
Liu, Y. X., Cao, W. C., Gao, Y., Zhang, J. L., Yang, Z. Q., Zhao, Z. T., et al. (2006). Orientia tsutsugamushi in eschars from scrub typhus patients. Emerging Infectious Diseases, 12, 1109–1112.
Furuya, Y., Yamamoto, S., Out, M., Yoshida, Y., Ohashi, N., Murata, M., et al. (1991). Use of monoclonal antibodies against Rickettsia tsutsugamushi Kawasaki for serodiagnosis by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 29, 340–345.
Yamamoto, S., Kawabata, N., Tamura, A., Urakami, H., Ohashi, N., Murata, M., et al. (1986). Immunological properties of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi, Kawasaki strain, isolated from a patient in Kyushu. Microbiology and Immunology, 30, 611–620.
Iwasa, M., Kasuya, S., Noda, N., Hioki, A., Ito, A., & Ohtomo, H. (1990). Trombiculid mites (Acari: Trombiculidae) and Rickettsia tsutsugamushi isolated from wild rodents in a new endemic area of Japan. Journal of Medical Entomology, 27, 501–508.
Kawamori, F. M., Akiyama, M., Sugieda, M., Kanda, T., Akahane, S., Uchikawa, K., et al. (1992). Epidemiology of scrub typhus in relation to the serotypes of Rickettsia tsutsugamushi isolated from patient, field mice, and unfed chiggers on the eastern slope of Mount Fuji, Shizuoka prefecture, Japan. Journal of Clinical Microbiology, 30, 2842–2846.
Yang, Z. Q., Yu, X. M., Liu, Y. X., Wu, Q. Y., Meng, X. R., Sun, H. L., et al. (1997). Studies on clinical epidemiology of tsutsugamushi disease of autumn–winter type in the eastern suburbs of Jinan. Chinese Journal of Epidemiology, 18, 233–235.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 30872155 and No. 30972523); China Special Grant for the Prevention and Control of Infectious Diseases (2013ZX10004 805-003, 2013ZX10004 217-002); and the twelfth five year research foundation of Military Medical Sciences and Technology [the key program (AWS11L009) and the Special Grant for health protection (11BJZ01)].
Conflict of interest
The authors report no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
The GenBank accession numbers for Sta56 gene sequences reported in present study are: XDM2, DQ975371; FXS2, DQ975372; B16, DQ975373; LHGM2, DQ975374; FXS4, DQ975375; 03PE1, DQ188085; 03PE2, DQ188086; 03PE3, DQ188087; 03PE4, DQ188088; 04PE5, DQ188089; 04PE6, DQ188090; 04PE7, DQ188091.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, YX., Jia, N., Xing, YB. et al. Consistency of the Key Genotypes of Orientia tsutsugamushi in Scrub Typhus Patients, Rodents, and Chiggers from a New Endemic Focus of Northern China. Cell Biochem Biophys 67, 1461–1466 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-013-9646-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-013-9646-0