Abstract
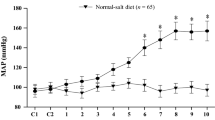
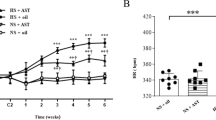
Findings from our laboratory indicate that expressions of some proinflammatory cytokines such as tumor necrosis factor, interleukin-6 and oxidative stress responses are increased in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus (PVN) and contribute to the progression of salt-sensitive hypertension. In this study, we determined whether interleukin-1 beta (IL-1β) activation within the PVN contributes to sympathoexcitation during development of salt-dependent hypertension. Eight-week-old male Dahl salt-sensitive (S) rats received a high-salt diet (HS, 8 % NaCl) or a normal-salt diet (NS, 0.3 % NaCl) for 6 weeks, and all rats were treated with bilateral PVN injection of gevokizumab (IL-1β inhibitor, 1 μL of 10 μg) or vehicle once a week. The mean arterial pressure (MAP), heart rate (HR) and plasma norepinephrine (NE) were significantly increased in high-salt-fed rats. In addition, rats with high-salt diet had higher levels of NOX-2, NOX-4 [subunits of NAD (P) H oxidase], IL-1β, NLRP3 (NOD-like receptor family pyrin domain containing 3), Fra-LI (an indicator of chronic neuronal activation) and lower levels of IL-10 in the PVN than normal-diet rats. Bilateral PVN injection of gevokizumab decreased MAP, HR and NE, attenuated the levels of oxidative stress and restored the balance of cytokines. These findings suggest that IL-1β activation in the PVN plays a role in salt-sensitive hypertension.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Li, N., Luo, W., Juhong, Z., Yang, J., Wang, H., Zhou, L., & Chang, J. (2010). Associations between genetic variations in the FURIN gene and hypertension. BMC Medical Genetics, 11, 124.
Zhang, M., Qin, D. N., Suo, Y. P., Su, Q., Li, H. B., Miao, Y. W., et al. (2015). Endogenous hydrogen peroxide in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus regulates neurohormonal excitation in high salt-induced hypertension. Toxicology Letters, 235, 206–215.
Huang, B. S., Zheng, H., Tan, J., Patel, K. P., & Leenen, F. H. (2011). Regulation of hypothalamic renin-angiotensin system and oxidative stress by aldosterone. Experimental Physiology, 96, 1028–1038.
Kang, Y. M., Ma, Y., Zheng, J. P., Elks, C., Sriramula, S., Yang, Z. M., & Francis, J. (2009). Brain nuclear factor-kappa B activation contributes to neurohumoral excitation in angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Cardiovascular Research, 82, 503–512.
Yu, Y., Qin, J., Chen, D., Wang, H., & Wang, J. (2015). Chronic cardiovascular disease-associated gene network analysis in human umbilical vein endothelial cells exposed to 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 15, 157–171.
Janahmadi, Z., Nekooeian, A. A., Moaref, A. R., & Emamghoreishi, M. (2015). Oleuropein offers cardioprotection in rats with acute myocardial infarction. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 15, 61–68.
Nguyen, K. T., Deak, T., Will, M. J., Hansen, M. K., Hunsaker, B. N., Fleshner, M., et al. (2000). Timecourse and corticosterone sensitivity of the brain, pituitary, and serum interleukin-1beta protein response to acute stress. Brain Research, 859, 193–201.
Wei, S. G., Yu, Y., Zhang, Z. H., & Felder, R. B. (2015). Proinflammatory cytokines upregulate sympathoexcitatory mechanisms in the subfornical organ of the rat. Hypertension, 65, 1126–1133.
Song, X. A., Jia, L. L., Cui, W., Zhang, M., Chen, W., Yuan, Z. Y., et al. (2014). Inhibition of TNF-alpha in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus attenuates hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy by inhibiting neurohormonal excitation in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 281, 101–108.
Cao, Y., Mu, J. J., Fang, Y., Yuan, Z. Y., & Liu, F. Q. (2013). Impact of high salt independent of blood pressure on PRMT/ADMA/DDAH pathway in the aorta of Dahl salt-sensitive rats. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 14, 8062–8072.
Gan, Y., Xing, J., Jing, Z., Stetler, R. A., Zhang, F., Luo, Y., et al. (2012). Mutant erythropoietin without erythropoietic activity is neuroprotective against ischemic brain injury. Stroke; A Journal of Cerebral Circulation, 43, 3071–3077.
Kang, Y. M., Gao, F., Li, H. H., Cardinale, J. P., Elks, C., Zang, W. J., et al. (2011). NF-kappaB in the paraventricular nucleus modulates neurotransmitters and contributes to sympathoexcitation in heart failure. Basic Research in Cardiology, 106, 1087–1097.
Francis, J., MohanKumar, S. M., & MohanKumar, P. S. (2000). Correlations of norepinephrine release in the paraventricular nucleus with plasma corticosterone and leptin after systemic lipopolysaccharide: blockade by soluble IL-1 receptor. Brain Research, 867, 180–187.
Chen, A. D., Zhang, S. J., Yuan, N., Xu, Y., De, W., Gao, X. Y., & Zhu, G. Q. (2011). Angiotensin AT1 receptors in paraventricular nucleus contribute to sympathetic activation and enhanced cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in renovascular hypertensive rats. Experimental Physiology, 96, 94–103.
Li, H. B., Qin, D. N., Ma, L., Miao, Y. W., Zhang, D. M., Lu, Y., et al. (2014). Chronic infusion of lisinopril into hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus modulates cytokines and attenuates oxidative stress in rostral ventrolateral medulla in hypertension. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 279, 141–149.
Zhu, G. Q., Gao, L., Patel, K. P., Zucker, I. H., & Wang, W. (2004). ANG II in the paraventricular nucleus potentiates the cardiac sympathetic afferent reflex in rats with heart failure. Journal of Applied Physiology, 97, 1746–1754.
Su, Q., Qin, D. N., Wang, F. X., Ren, J., Li, H. B., Zhang, M., et al. (2014). Inhibition of reactive oxygen species in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus attenuates the renin-angiotensin system and proinflammatory cytokines in hypertension. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 276, 115–120.
Kang, Y. M., He, R. L., Yang, L. M., Qin, D. N., Guggilam, A., Elks, C., et al. (2009). Brain tumour necrosis factor-alpha modulates neurotransmitters in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus in heart failure. Cardiovascular Research, 83, 737–746.
MohanKumar, S. M., MohanKumar, P. S., & Quadri, S. K. (1998). Specificity of interleukin-1beta-induced changes in monoamine concentrations in hypothalamic nuclei: blockade by interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Brain Research Bulletin, 47, 29–34.
Kang, Y. M., Zhang, Z. H., Johnson, R. F., Yu, Y., Beltz, T., Johnson, A. K., et al. (2006). Novel effect of mineralocorticoid receptor antagonism to reduce proinflammatory cytokines and hypothalamic activation in rats with ischemia-induced heart failure. Circulation Research, 99, 758–766.
Sriramula, S., Cardinale, J. P., Lazartigues, E., & Francis, J. (2011). ACE2 overexpression in the paraventricular nucleus attenuates angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Cardiovascular Research, 92, 401–408.
Miller, F. J, Jr, Gutterman, D. D., Rios, C. D., Heistad, D. D., & Davidson, B. L. (1998). Superoxide production in vascular smooth muscle contributes to oxidative stress and impaired relaxation in atherosclerosis. Circulation Research, 82, 1298–1305.
Sriramula, S., Cardinale, J. P., & Francis, J. (2013). Inhibition of TNF in the brain reverses alterations in RAS components and attenuates angiotensin II-induced hypertension. PLoS ONE, 8, e63847.
Yu, X. J., Zhang, D. M., Jia, L. L., Qi, J., Song, X. A., Tan, H., et al. (2015). Inhibition of NF-kappaB activity in the hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus attenuates hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy by modulating cytokines and attenuating oxidative stress. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 284, 315–322.
Kang, Y. M., Zhang, Z. H., Xue, B., Weiss, R. M., & Felder, R. B. (2008). Inhibition of brain proinflammatory cytokine synthesis reduces hypothalamic excitation in rats with ischemia-induced heart failure. American journal of physiology. Heart and Circulatory Physiology, 295, H227–H236.
Qi, J., Zhang, D. M., Suo, Y. P., Song, X. A., Yu, X. J., Elks, C., et al. (2013). Renin-angiotensin system modulates neurotransmitters in the paraventricular nucleus and contributes to angiotensin II-induced hypertensive response. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 13, 48–54.
Yu, X. J., Suo, Y. P., Qi, J., Yang, Q., Li, H. H., Zhang, D. M., et al. (2013). Interaction between AT1 receptor and NF-kappaB in hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus contributes to oxidative stress and sympathoexcitation by modulating neurotransmitters in heart failure. Cardiovascular Toxicology, 13, 381–390.
Leenen, F. H., & Yuan, B. (2001). Prevention of hypertension by irbesartan in Dahl S rats relates to central angiotensin II type 1 receptor blockade. Hypertension, 37, 981–984.
Kang, Y. M., Zhang, D. M., Yu, X. J., Yang, Q., Qi, J., Su, Q., et al. (2014). Chronic infusion of enalaprilat into hypothalamic paraventricular nucleus attenuates angiotensin II-induced hypertension and cardiac hypertrophy by restoring neurotransmitters and cytokines. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 274, 436–444.
Shi, P., Diez-Freire, C., Jun, J. Y., Qi, Y., Katovich, M. J., Li, Q., et al. (2010). Brain microglial cytokines in neurogenic hypertension. Hypertension, 56, 297–303.
Leemans, J. C., Cassel, S. L., & Sutterwala, F. S. (2011). Sensing damage by the NLRP3 inflammasome. Immunological Reviews, 243, 152–162.
Kang, Y. M., Zhang, A. Q., Zhao, X. F., Cardinale, J. P., Elks, C., Cao, X. M., et al. (2011). Paraventricular nucleus corticotrophin releasing hormone contributes to sympathoexcitation via interaction with neurotransmitters in heart failure. Basic Research in Cardiology, 106, 473–483.
Mohamed, I. N., Hafez, S. S., Fairaq, A., Ergul, A., Imig, J. D., & El-Remessy, A. B. (2014). Thioredoxin-interacting protein is required for endothelial NLRP3 inflammasome activation and cell death in a rat model of high-fat diet. Diabetologia, 57, 413–423.
Luzardo, L., Noboa, O. and Boggia, J. (2015). Mechanisms of Salt-Sensitive Hypertension. Current hypertension reviews.
Trinchieri, G., & Sher, A. (2007). Cooperation of Toll-like receptor signals in innate immune defence. Nature Reviews Immunology, 7, 179–190.
Zheng, F., Xing, S., Gong, Z., & Xing, Q. (2013). NLRP3 inflammasomes show high expression in aorta of patients with atherosclerosis. Heart, Lung and Circulation, 22, 746–750.
Tschopp, J., Martinon, F., & Burns, K. (2003). NALPs: a novel protein family involved in inflammation. Nature Reviews Molecular Cell Biology, 4, 95–104.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2012CB517805) and National Natural Science Foundation of China (Nos. 91439120, 81370356 and 81170248). The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qi, J., Zhao, XF., Yu, XJ. et al. Targeting Interleukin-1 beta to Suppress Sympathoexcitation in Hypothalamic Paraventricular Nucleus in Dahl Salt-Sensitive Hypertensive Rats. Cardiovasc Toxicol 16, 298–306 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-015-9338-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12012-015-9338-7