Abstract
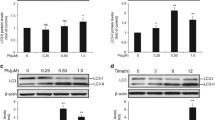
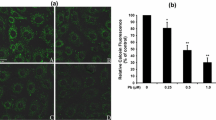
Previous study has demonstrated that mitochondrial-dependent apoptotic pathway is involved in the nephroprotective effect of puerarin (PU) against lead-induced cytotoxicity in primary cultures of rat proximal tubular (rPT) cells. To further clarify how PU exerts its antiapoptotic effects, this study was designed to investigate the role of mitochondrial permeability transition (MPT) and subsequent apoptotic events in the process of PU against Pb-induced cytotoxicity in rPT cells. The results showed that Pb-mediated mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) opening together with mitochondrial cytochrome c release, activations of caspase-9 and caspase-3, and subsequent poly-ADP-ribose polymerase (PARP) cleavage can be effectively blocked by the addition of PU. Simultaneously, upregulation and downregulation of Bcl-2 and Bax with increased Bcl-2/Bax ratio due to PU administration further alleviated Pb-induced mitochondrial apoptosis. Moreover, PU can reverse Pb-induced ATP depletion by restoring mitochondrial fragmentation to affect ATP production and by regulating expression levels of ANT-1 and ANT-2 to improve ATP transport. In summary, PU produced a significant protection against Pb-induced mitochondrial apoptosis in rPT cells by inhibiting MPTP opening to ameliorate the mitochondrial dysfunction.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MPT:
-
Mitochondrial permeability transition
- rPT:
-
Rat proximal tubular
- MPTP:
-
Mitochondrial permeability transition pore
- ANT:
-
Adenine nucleotide translocase
- cyt-c :
-
Cytochrome c
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- BCA:
-
Bicinchonininc acid
- MMP:
-
Mitochondrial membrane potential
- PI:
-
Propidium iodide
- CoCl2 :
-
Cobalt chloride
- Calcein-AM:
-
Calcein acetoxymethyl ester
References
Bilandžić N, Sedak M, Vratarić D, Perić T, Šimić B (2009) Lead and cadmium in red deer and wild boar from different hunting grounds in Croatia. Sci Total Environ 407:4243–4247
Oyagbemi AA, Omobowale TO, Akinrinde AS, Saba AB, Ogunpolu BS, Daramola O (2015) Lack of reversal of oxidative damage in renal tissues of lead acetate-treated rats. Environ Toxicol 30:1235–1243
Patrick L (2006) Lead toxicity, a review of the literature. Part 1: exposure, evaluation, and treatment. Altern Med Rev 11:2–22
Wang H, Wang ZK, Jiao P, Zhou XP, Yang DB, Wang ZY, Wang L (2015) Redistribution of subcellular calcium and its effect on apoptosis in primary cultures of rat proximal tubular cells exposed to lead. Toxicology 333:137–146
Jia Q, Ha X, Yang Z, Hui L, Yang X (2012) Oxidative stress: a possible mechanism for lead-induced-apoptosis and nephrotoxicity. Toxicol Mech Methods 22:705–710
Liu CM, Ma JQ, Sun YZ (2012) Puerarin protects rat kidney from lead-induced apoptosis by modulating the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 258:330–342
Wang L, Wang H, Li J, Chen D, Liu ZP (2011) Simultaneous effects of lead and cadmium on primary cultures of rat proximal tubular cells: interaction of apoptosis and oxidative stress. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 61:500–511
Wang L, Lin S, Li Z, Yang D, Wang Z (2013) Protective effects of puerarin on experimental chronic lead nephrotoxicity in immature female rats. Hum Exp Toxicol 32:172–185
Liu G, Li ZF, Wang JQ, Wang H, Wang ZY, Wang L (2014) Puerarin protects against lead- induced cytotoxicity in cultured primary rat proximal tubular cells. Hum Exp Toxicol 33:1071–1080
Lisea M, Shirihai OS (2013) Mitochondrial dynamics in the regulation of nutrient utilization and energy expenditure. Cell Metab 17:491–506
Sinha K, Das J, Pal PB, Sil PC (2013) Oxidative stress: the mitochondria-dependent and mitochondria-independent pathways of apoptosis. Arch Toxicol 87:1157–1180
Liu G, Wang ZK, Wang ZY, Yang DB, Liu ZP, Wang L (2015) Mitochondrial permeability transition and its regulatory components are implicated in apoptosis of primary cultures of rat proximal tubular cells exposed to lead. Arch Toxicol. doi:10.1007/s00204-015-1547-0
Kinnally KW, Peixoto PM, Ryu SY, Dejean LM (2011) Is mPTP the gatekeeper for necrosis, apoptosis, or both? Biochim Biophys Acta 1813:616–622
Wang L, Wang H, Hu M, et al. (2009) Oxidative stress and apoptotic changes in primary cultures of rat proximal tubular cells exposed to lead. Arch Toxicol 83:417–427
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(T)(−Delta Delta C) method. Methods 25:402–408
Jacotot E, Deniaud A, Borgne-Sanchez A, Touat Z, Briand JP, Le-Bras M, Brenner C (2006) Therapeutic peptides: targeting the mitochondrion to modulate apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1757:1312–1323
Armstrong JS (2006) The role of the mitochondrial permeability transition in cell death. Mitochondrion 6:225–234
Gupta S, Kass GE, Szegezdi E, Joseph B (2009) The mitochondrial death pathway: a promising therapeutic target in diseases. J Cell Mol Med 13:1004–1033
Parrish AB, Freel CD, Kornbluth S (2013) Cellular mechanisms controlling caspase activation and function. Cold Spring Harbor perspectives in biology 5(6). doi:10.1101/cshperspect.a008672
Li P, Nijhawan D, Budihardjo I, Srinivasula SM, Ahmad M, Alnemri ES, Wang X (1997) Cytochrome c and dATP-dependent formation of Apaf-1/caspase-9 complex initiates an apoptotic protease cascade. Cell 91:479–489
Dias-da-Silva D, Carmo H, Lynch A, Silva E (2013) An insight into the hepatocellular death induced by amphetamines, individually and in combination: the involvement of necrosis and apoptosis. Arch Toxicol 87:2165–2185
Guo X, Disatnik MH, Monbureau M, Shamloo M, Mochly-Rosen D, Qi X (2013) Inhibition of mitochondrial fragmentation diminishes Huntington’s disease-associated neurodegeneration. J Clin Invest 123:5371–5388
Arnoult D (2007) Mitochondrial fragmentation in apoptosis. Trends Cell Biol 17:6–12
Paradies G, Paradies V, Ruggiero FM, Petrosillo G (2015) Protective role of melatonin in mitochondrial dysfunction and related disorders. Arch Toxicol 89:923–939
Kroemer G, Reed JC (2000) Mitochondrial control of cell death. Nat Med 6:513–519
Chevrollier A, Loiseau D, Reynier P, Stepien G (2011) Adenine nucleotide translocase 2 is a key mitochondrial protein in cancer metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 1807:562–567
Giorgi C, Baldassari F, Bononi A, Bonora M, Marchi ED, Marchi S, Missiroli S, Patergnani S, Rimessi A, Suski JM, Wieckowski MR, Pinton P (2012) Mitochondrial Ca2+ and apoptosis. Cell Calcium:36–43
Brenner C, Cadiou H, Vieira HL, Zamzami N, Marzo I, Xie Z, Leber B, Andrews D, Duclohier H, Reed JC, Kroemer G (2000) Bcl-2 and Bax regulate the channel activity of the mitochondrial adenine nucleotide translocator. Oncogene 19:329–336
Siddiqui WA, Ahad A, Ahsan H (2015) The mystery of BCL2 family: Bcl-2 proteins and apoptosis: an update. Arch Toxicol 89:289–317
Sheridan C, Delivani P, Cullen SP, Martin SJ (2008) Bax- or Bak-induced mitochondrial fission can be uncoupled from cytochrome C release. Mol Cell 31:570–585
Ryu SW, Choi K, Yoon J, Kim S, Choi C (2012) Endoplasmic reticulum-specific BH3-only protein BNIP1 induces mitochondrial fragmentation in a Bcl-2- and Drp1-dependent manner. J Cell Physiol 227:3027–3035
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the national nature science foundation of China (No. 31472251), a foundation for the author of national excellent doctoral dissertation of People’s Republic of China (No. 201266) and the fund of Fok Ying Tung education foundation under grant no. 141022.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Zhong-Kun Wang, Xue-Lei Zhou, and Xiang-Bin Song contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, ZK., Zhou, XL., Song, XB. et al. Alleviation of Lead-Induced Apoptosis by Puerarin via Inhibiting Mitochondrial Permeability Transition Pore Opening in Primary Cultures of Rat Proximal Tubular Cells. Biol Trace Elem Res 174, 166–176 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0701-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-016-0701-8