Abstract
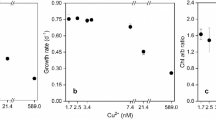
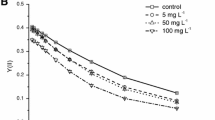
Responses of photosystem I and II activities of Microcystis aeruginosa to various concentrations of Cu2+ were simultaneously examined using a Dual-PAM-100 fluorometer. Cell growth and contents of chlorophyll a were significantly inhibited by Cu2+. Photosystem II activity [Y(II)] and electron transport [rETRmax(II)] were significantly altered by Cu2+. The quantum yield of photosystem II [Y(II)] decreased by 29 % at 100 μg L−1 Cu2+ compared to control. On the contrary, photosystem I was stable under Cu2+ stress and showed an obvious increase of quantum yield [Y(I)] and electron transport [rETRmax(I)] due to activation of cyclic electron flow (CEF). Yield of cyclic electron flow [Y(CEF)] was enhanced by 17 % at 100 μg L−1 Cu2+ compared to control. The contribution of linear electron flow to photosystem I [Y(II)/Y(I)] decreased with increasing Cu2+ concentration. Yield of cyclic electron flow [Y(CEF)] was negatively correlated with the maximal photosystem II photochemical efficiency (F v/F m). In summary, photosystem II was the major target sites of toxicity of Cu2+, while photosystem I activity was enhanced under Cu2+ stress.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Küpper H, Šetlík I, Spiller M, Küpper FC, Prášil O (2002) Heavy metal-induced inhibition of photosynthesis: targets of in vivo heavy metal chlorophyll formation. J Phycol 38:429–441
Roussel H, Ten-Hage L, Joachim S, Cohu RL, Gauthier L, Bonzom J-M (2007) A long-term copper exposure on freshwater ecosystem using lotic mesocosms: primary producer community responses. Aquat Toxicol 81:168–182
Elder JF, Horne AJ (1978) Copper cycles and CuSO4 algicidal capacity in two California lakes. Environ Manag 2:17–30
Nikookar K, Moradshahi A, Hosseini L (2005) Physiological responses of Dunaliella salina and Dunaliella tertiolecta to copper toxicity. Biomol Eng 22:141–146
Qian HF, Li JJ, Sun LW, Chen W, Sheng GD, Liu WP, Fu ZW (2009) Combined effect of copper and cadmium on Chlorella vulgaris growth and photosynthesis-related gene transcription. Aquat Toxicol 94:56–61
Qian HF, Yu SQ, Sun ZQ, Xie XC, Liu WP, Fu ZW (2010) Effects of copper sulfate, hydrogen peroxide and N-phenyl-2-naphthylamine on oxidative stress and the expression of genes involved photosynthesis and microcystin disposition in Microcystis aeruginosa. Aquat Toxicol 99:405–412
Backor M, Záczi P (2002) Copper tolerance in the lichen photobiont Trebouxia erici (Chlorophyta). Environ Exp Bot 48:11–20
Oukarroum A, Perreault F, Popovic R (2012) Interactive effects of temperature and copper on photosystem II photochemistry in Chlorella vulgaris. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 110:9–14
Küpper H, Küpper F, Spiller M (1996) Environmental relevance of heavy metal-substituted chlorophylls using the example of water plants. J Exp Bot 47:259–266
Cid A, Herrero C, Torres E, Abalde J (1995) Copper toxicity on the marine microalga Phaeodactylum tricornutum: effects on photosynthesis and related parameters. Aquat Toxicol 31:165–174
Mijovilovich A, Leitenmaier B, Meyer-Klaucke W, Kroneck PMH, Götz B, Küpper H (2009) Complexation and toxicity of copper in higher plants. II. Different mechanisms for copper versus cadmium detoxification in the copper-sensitive cadmium/zinc hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens (Ganges Ecotype). Plant Physiol 151:715–731
Mishra S, Dubey RS (2005) Heavy metal toxicity induced alterations in photosynthetic metabolism in plants. In: Pressarakli M (ed) Handbook of photosynthesis. Taylor and Francis Group, CRC Press, Boca Raton, pp 845–863
Boucher N, Carpentier R (1999) Hg2+, Cu2+, and Pb2+-induced changes in photosystem II photochemical yield and energy storage in isolated thylakoid membranes: a study using simultaneous fluorescence and photoacoustic measurements. Photosynth Res 59:167–174
Wu X, Hong FS, Liu C, Su MY, Zheng L, Gao FQ, Yang F (2008) Effects of Pb2+ on energy distribution and photochemical activity of spinach chloroplast. Spectrochim Acta A 69:738–742
Singh R, Dubey G, Singh VP, Srivastava PK, Kumar S, Prasad SM (2012) High light intensity augments mercury toxicity in cyanobacterium Nostoc muscorum. Biol. Trace Elem Res 149:262–272
Deng CN, Zhang DY, Pan XL, Chang FQ, Wang SZ (2013) Toxic effect of mercury on PSI and PSII activites, membrane potential and transthylakoid proton gradient in Microsorium pteropus. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 127:1–7
Ouzounidou G (1996) The use of photoacoustic spectroscopy in assessing leaf photosynthesis under copper stress: correlation of energy storage to photosystem II fluorescence parameters and redox change of P700. Plant Sci 113:229–237
Yan K, Chen P, Shao H, Shao C, Zhao S et al (2013) Dissection of photosynthetic electron transport process in sweet sorghum under heat stress. PLoS ONE 8(5):e62100. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0062100
Chen W, Yao X, Cai K, Chen J (2011) Silicon alleviates drought stress of rice plants by improving plant water status, photosynthesis and mineral nutrient absorption. Biol Trace Elem Res 142:67–76
Perreault F, Ali NA, Saison C, Popovic R, Juneau P (2009) Dichromate effect on energy dissipation of photosystem II and photosystem I in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Photochem Photobiol B Biol 96:24–29
Coopman RE, Fuentes-Neira FP, Briceño VF, Cabrera HM, Corcuera LJ, Bravo LA (2010) Light energy partitioning in photosystems I and II during development of Nothofagus nitida growing under different light environments in the Chilean evergreen temperate rain forest. Trees 24:247–259
Leunert F, Grossart HP, Gerhardt V, Eckert W (2013) Toxicant induced changes on delayed fluorescence decay kinetics of Cyanoobacteria and green algae: a rapid and sensitive biotest. PLoS ONE 8(4):e63127. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0063127
Stanier RY, Kunisawa R, Mandel M, Cohen-Bazire G (1971) Purification and properties of unicellular blue-green algae (oder Chroococcales). Bacteriol Rev 35:171–205
Pfündel E, Klughammer C, Schreiber U (2008) Monitoring the effects of reduced PS II antenna size on quantum yields of photosystems I and II using the Dual-PAM-100 measuring system. PAM Appl Notes 1:21–24
Hout Y, Babin M (2010) Overview of fluorescence protocols: theory, basic concepts and practice. In: Suggett DJ, Prášil O, Borowitzka MA, Prasil O (eds) Chlorophyll a fluorescence in aquatic sciences: methods and applications. Springer, London, p 59
Klughammer C, Schreiber U (2008) Complementary PS II quantum yields calculated from simple fluorescence parameters measured by PAM fluorometry and the Saturation Pulse method. PAM Appl Notes 1:27–35
Wang SZ, Chen FL, Mu SY, Zhang DY, Pan XL, Lee DJ (2013) Simultaneous analysis of photosystem response of Microcystis aeruginoga under chromium stress. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 88:163–168
Kramer DM, Johnson G, Kiirats O, Edwards GE (2004) New fluorescence parameters for the determination of QA redox state and excitation energy fluxes. Photosynth Res 79:209–218
Miyake C, Horiguchi S, Makino A, Shinzaki Y, Yamamoto H, Tomizawa K (2005) Effects of light intensity on cyclic electron flow around PSI and its relationship to non-photochemical quenching of Chl fluorescence in tobacco leaves. Plant Cell Physiol 46:1819–1830
Huang W, Zhang SB, Cao KF (2010) Stimulation of cyclic electron flow during recovery after chilling-induced photoinhibition of PSII. Plant Cell Physiol 51:1922–1928
Schreiber U, Klughammer C (2012) Assessment of wavelength-dependent parameters of photosynthetic electron transport with a new type of multi-color PAM chlorophyll fluorometer. Photosynth Res 113:127–144
Platt T, Gallegos CL, Harrison WG (1980) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis in natural assemblages of marine phytoplankton. J Mar Res 38:687–701
Saroussi S, Beer S (2007) Alpha and quantum yield of aquatic plants derived from PAM fluorometry: uses and misuses. Aquat Bot 86:89–92
White S, Anandraj A, Bux F (2011) PAM fluorometry as a tool to assess microalgal nutrient stress and monitor cellular neutral lipids. Bioresour Technol 102:1675–1682
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983) Determination of total carotenoids and chlorophyll a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 603:591–592
Ling QF, Hong FS (2009) Effects of Pb2+ on the structure and function of photosystem II of Spirodela polyrrhiza. Biol Trace Elem Res 129:251–260
Suzuki K, Ohmori Y, Ratel E (2011) High root temperature blocks both linear and cyclic electron transport in the dark during chilling of the leaves of rice seedlings. Plant Cell Physiol 52:1697–1707
Papageorgio GC, Govindjee (2004) Chlorophyll a fluorescence: a signature of photosynthesis. Advances in photosynthesis and Respiration, vol 19. Springer, Dordrecht
Karukstis KK (1991) Chlorophyll fluorescence as a physiological probe of the photosynthetic apparatus. In: Scheer H (ed) Chlorophyll. CRC Press, London, pp 770–797
Ibelings BW, Kroon BMA, Mur LR (1994) Acclimation of photosystem-II in a cyanobacterium and a eukaryotic green-alga to high and fluctuating photosynthetic photon flux densities, simulating light regimes induced by mixing in lakes. New Phyto 128:407–424
Campbell D, Hurry V, Clarke AK, Gustafsson P, Őquist G (1998) Chlorophyll fluorescence analysis of cyanobacterial photosynthesis and acclimation. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 62:667–683
Toncheva-Panova T, Merakchiyska M, Djinggova R, Ivanova J, Sholeva M (2006) Effect of Cu2+ on the red microalga Rhodella reticulata. Gen Appl Plant Physiology (Special Issue) 53-60
Zhou S, Shao Y, Gao N, Deng Y, Qiao J, Ou H, Deng J (2013) Effects of different algaecides on the photosynthetic capacity, cell integrity and microcystin-LR release of Microcystis aeruginosa. Sci Total Environ 463–464:111–119
Wang SZ, Zhang DY, Pan XL (2013) Effects of cadmium on the activities of photosystems of Chlorella pyrenoidosa and the protective role of cyclic electron flow. Chemosphere 93:230–237
Dhir B, Sharmila P, Saradhi PP, Sharma S, Kumar R, Mehta D (2011) Heavy metal induced physiological alterations in Salvinia natans. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 74:1678–1684
Wodala B, Eitel G, Gyula TN, Őrdög A, Horváth F (2012) Monitoring moderate Cu and Cd toxicity by chlorophyll fluorescence and P700 absorbance in pea leaves. Photosynthetica 50:380–386
Ralph PJ, Gademann R (2005) Rapid light curves: a powerful tool to assess photosynthetic activity. Aquat Bot 82:222–237
Munekage Y, Mihoko H, Miyake C, Tomizawa KI, Endo T, Tasaka M, Shikanai T (2004) Cyclic electron flow around photosystem I is essential for photosynthesis. Nature 429:579–582
Gao S, Wang G (2012) The enhancement of cyclic electron flow around photosystem I improves the recovery of severely desiccated Porphyra yezoensis (Bangiales, Rhodophyta). J Exp Bot 63:4349–4358
Takahashi S, Milward SE, Fan DY, Chow WS, Badger MR (2009) How does cyclic electron flow alleviate photoinhibition in Arabidopsis? Plant Physiol 149:1560–1567
Ouzounidou G, Lannoye R, Karataglis S (1993) Photoacoustic measurements of photosynthetic activities in intact leaves under copper stress. Plant Sci 89:221–226
Allakhverdiev SI, Nishiyama Y, Takahashi S, Miyairi S, Suzuki I, Murata N (2005) Systematic analysis of the relation of electron transport and ATP synthesis to the photodamage and repair of photosystem II in Synechocystis. Plant Physiol 137:263–273
Kudoh H, Sonoike K (2002) Irreversible damage to photosystem I by chilling in the light: cause of the degradation of chlorophyll after returning to normal growth temperature. Planta 215:541–548
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the the National Natural Science Foundation of China (U1120302 and 21177127) and the Specialized Research Fund for the Doctoral Program of Higher Education (20125303120003).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, C., Pan, X., Wang, S. et al. Cu2+ Inhibits Photosystem II Activities but Enhances Photosystem I Quantum Yield of Microcystis aeruginosa . Biol Trace Elem Res 160, 268–275 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0039-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-014-0039-z