Abstract
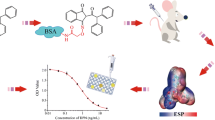
The detection of cadmium ions using enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISA) has been reported by several research groups. Because cadmium ions are too small to stimulate the immune system, high molecular weight immunogens of cadmium are constructed using bifunctional chelators. At present, the most commonly used bifunctional chelator for the preparation of antigens for heavy metal ions is 1-(4-isothiocyanobenzyl) ethylenediamine N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid (ITCBE). However, the price of ITCBE is high. So we are interested in a cheaper bifunctional chelator, 1-(4-aminobenzyl) ethylenediamine N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid (aminobenzyl-EDTA). Here, cadmium ions were conjugated to carrier proteins using aminobenzyl-EDTA to make artificial antigens. Then, several mice were immunized with the antigen. And monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) against cadmium were produced. Spleen cells of immunized mice were fused with myeloma cells. The resulting hybridomas were screened using protein conjugates which were covalently bound to metal-free EDTA or cadmium. Three hybridoma cell lines (A3, E4 and B5) that produced MAbs with high selectivity and sensitivity were expanded for further study. Cross-reactivities with other metals were below 1 %. These antibodies were used to construct competitive ELISAs. The IC50 for A3 was 8.4 μg/l. The detection range and the lowest detection limit using the antibody A3 was 0.394–64.39 and 0.051 μg/l, respectively. Spike–recovery studies in tap water showed that the antibody A3 could be used for cadmium detection in drinking water.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Aminobenzyl-EDTA:
-
1-(4-Aminobenzyl) ethylenediamine N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid
- EDTA:
-
N,N,N′,N′-Ethylenediamine-tetraaceticacid
- MAb:
-
Monoclonal antibodies
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- KLH:
-
Keyhole limpet hemocyanin
- HAT:
-
Hypoxanthine, aminopterin and thymidine
- HT:
-
Hypoxanthine, thymidine
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- OPD:
-
o-Phenylenediamine
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- PEG:
-
Polyethylene glycol
- Ka:
-
Affinity constants
- CR:
-
Cross-reactivity
- CI-ELISA:
-
Indirect competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- ITCBE:
-
1-(4-Isothiocyanobenzyl) ethylenediamine N,N,N′,N′-tetraacetic acid
References
Vahter M, Berglund M, Nermell B et al (1996) Bioavailability of cadmium from shellfish and mixed diet in women. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 2:332–341
Darwish IA, Blake DA (2001) One-step competitive immunoassay for cadmium ions: development and validation for environmental water samples. Anal Chem 73:1889–1895
Darwish IA, Blake DA (2002) Development and validation of a sensitive one-step immunoassay for determination of cadmium in human serum. Anal Chem 74:52–58
Yu H, Jones RM, Blake DA (2005) An immunosensor for autonomous in-line detection of heavy metals: validation for hexavalent uranium. Int J Environ Anal Chem 85:817–830
Zhu XX, Xu LN, Lou Y et al (2007) Preparation of specific monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) against heavy metals: MAbs that recognize chelated cadmium ions. J Agric Food Chem 55:7648–7653
Zhu XX, Hu BS, Lou Y et al (2007) Characterization of monoclonal antibodies for lead-chelate complexes: applications in antibody-based assays. J Agric Food Chem 55:4993–4998
Blake RC II, Pavlov AR, Khosraviani M et al (2004) Novel monoclonal antibodies with specificity for chelated uranium (VI): isolation and binding properties. Bioconjugate Chem 15:1125–1136
Reardan DT, Meares CF, Goodwin DA et al (1985) Antibodies against metal chelates. Nature 316:265–268
Kong T, Liu GW, Li XB et al (2010) Synthesis and identification of artificial antigens for cadmium and copper. Food Chem 4:1204–1209
Blake DA, Chakrabarti P, Khosraviani M et al (1996) Metal binding properties of a monoclonal antibody directed toward metal–chelator complexes. J Biol Chem 271:27677–27685
Kong T, Liu GW, Li XB et al (2012) Preparation of specific monoclonal antibodies against chelated copper ions. Biol Trace Elem Res 3:388–395
Jones RM, Yu H, Delehanty JB et al (2002) Monoclonal antibodies that recognize minimal differences in the three-dimensional structures of metal–chelate complexes. Bioconjugate Chem 13:408–415
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National “863” Project (2007AA10Z440 and 2007AA10Z426) of China, the National Natural Science Foundation of China (nos. 30600441, 30230260, and 30871897), and The PhD Start-up Foundation of Henan University of Science and Technology (09001514).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Authors Tao Kong, Xue-Qin Hao, and Xiao-Bing Li of Jilin University and Henan University of Science and Technology contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kong, T., Hao, XQ., Li, XB. et al. Preparation of Novel Monoclonal Antibodies Against Chelated Cadmium Ions. Biol Trace Elem Res 152, 117–124 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-013-9599-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-013-9599-6