Abstract
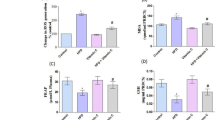
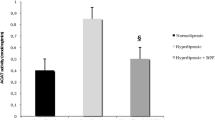
Hypercholesterolemia and lipid peroxidation play complementary roles in atherosclerosis. Artichoke (Cynara scolymus L., Asteraceae) leaf extract (ALE), rich in antioxidants, has cholesterol-reducing effect. We investigated the effect of ALE on serum and hepatic lipid levels and pro-oxidant–antioxidant balance in the liver and heart of hypercholesterolemic rats. Rats were fed on 4% (w/w) cholesterol and 1% cholic acid (w/w) supplemented diet for 1 month. ALE (1.5 g/kg/day) was given by gavage during the last 2 weeks. High cholesterol (HC) diet caused significant increases in serum and liver cholesterol and triglyceride levels. It increased malondialdehyde (MDA) and diene conjugate (DC) levels in both tissues. Hepatic vitamin E levels and hepatic and cardiac glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activities decreased, but superoxide dismutase and glutathione transferase activities, glutathione, and vitamin C levels remained unchanged due to HC diet. Serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels and ratio of cholesterol to high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol decreased in ALE plus HC-treated rats, but liver cholesterol and triglyceride levels remained unchanged. Significant decreases in hepatic and cardiac MDA and DC levels and increases in hepatic vitamin E and GSH-Px activities were observed in ALE-treated hypercholesterolemic rats. Our results indicate that ALE decreases serum lipids and hypercholesterolemia-induced pro-oxidant state in both tissues.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
O’Brien KD, Chait A (1994) The biology of the artery wall in atherogenesis. Med Clin North Am 78:41–67
Nakajima K, Nakano T, Tanaka A (2006) The oxidative modification hypothesis of atherosclerosis: the comparison of atherogenic effects on oxidized LDL and remnant lipoproteins in plasma. Clin Chim Acta 367:36–47
Moghadasian MH (2002) Experimental atherosclerosis. A historical overview. Life Sci 70:855–865
Mahfouz MM, Kummerow FA (2000) Cholesterol-rich diets have different effects on lipid peroxidation, cholesterol oxides, and antioxidant enzymes in rats and rabbits. J Nutr Biochem 11:293–302
Balkan J, Hatipoğlu A, Aykaç-Toker G, Uysal M (2003) Influence of hazelnut oil administration on peroxidation status of erythrocytes and apolipoprotein B-100 containing lipoproteins in rabbits fed on a high cholesterol diet. J Agric Food Chem 51:3905–3909
Balkan J, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S, Aykaç-Toker G, Uysal M (2004) The effects of high cholesterol diets on lipids and oxidative stress in plasma, liver and aorta of rabbits and rats. Nutr Res 24:229–234
Şener G, Balkan J, Çevikbaş U, Keyer-Uysal M, Uysal M (2004) Melatonin reduces cholesterol accumulation and prooxidant state induced by high cholesterol diet in the plasma, the liver and probably in the aorta of C57BL/6J mice. J Pineal Res 36:212–216
Kumar SA, Sudhahar V, Varalakshmi P (2006) Protective role of eicosapentaenoate-lipoate (EPA-LA) derivative in combating in hypercholesterolemic atherogenesis. Atherosclerosis 189:115–122
Sudhahar V, Kumar SA, Varalakshmi P (2006) Role of lupeol and lupeol linoleate on lipemic-oxidative stress in experimental hypercholesterolemia. Life Sci 78:1329–1335
Sudhahar V, Kumar SA, Varalakshmi P, Sundarapandiyan R (2007) Mitigating role of lupeol and lupeol linoleate on hepatic lipemic-oxidative injury and lipoprotein peroxidation in experimental hypercholesterolemia. Mol Cell Biochem 295:189–198
Ramesh E, Elanchezhian R, Sakthivel M, Jayakumar T, Senthil-Kumar RS, Geraldine P, Thomas PA (2008) Epigallocathechin gallate improves serum lipid profile and erythrocyte and cardiac tissue antioxidant parameters in Wistar rats fed an atherogenic diet. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 22:275–284
Jemai H, Bouaziz M, Fki I, El Feki A, Sayadi S (2008) Hypolipidimic and antioxidant activities of oleuropein and its hydrolysis derivative-rich extracts from Chemlali olive leaves. Chem Biol Interact 176:88–98
Prasad K (2008) Regression of hypercholesterolemic atherosclerosis in rabbits by secoisolariciresinol diglucoside isolated from flaxseed. Atherosclerosis 197:4–42
Özdemirler G, Küçük S, Orhan Y, Aykaç-Toker G, Uysal M (2001) Increased lipid and protein oxidation in erythrocyte membranes of hypercholesterolemic subjects. Clin Biochem 34:335–339
Balkan J, Doğru-Abbasoğlu S, Aykaç-Toker G, Uysal M (2004) Serum prooxidant-antioxidant balance and LDL oxidation in healthy subjects with different cholesterol levels. Clin Exp Med 3:237–242
Llorach R, Espin JC, Tomas-Barberan FA, Ferreres F (2002) Artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) byproducts as a potential source of health-promoting antioxidant phenolics. J Agric Food Chem 50:3458–3464
Wang M, Simon JE, Aviles IF, He K, Zheng QY, Tadmor Y (2003) Analysis of antioxidative phenolic compounds in artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.). J Agric Food Chem 51:601–608
Aktay G, Deliorman D, Ergun E, Ergun F, Yeşilada E, Çevik C (2000) Hepatoprotective effects of Turkish folk remedies on experimental liver injury. J Ethnopharmacol 73:121–129
Speroni E, Cervellati R, Govoni P, Guizzardi S, Renzulli C, Guerra MC (2003) Efficiency of different Cynara scolymus preparations liver complaints. J Ethnopharmacol 86:203–211
Mehmetçik G, Özdemirler G, Koçak-Toker N, Cevikbaş U, Uysal M (2008) Effect of pretreatment with artichoke extract on carbon tetrachloride-induced liver injury and oxidative stres. Exp Toxicol Pathol 60:475–480
Pittler MH, Thompson CJ, Ernst E (2002) Artichoke leaf extract for treating hypercholesterolemia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3:CD003335
Joy JF, Haber SL (2007) Clinical uses of artichoke leaf extract. Am J Health-Syst Pharm 64:1906–1909
Gebhardt R (1997) Antioxidative and protective properties of extracts from leaves of the artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) against hydroperoxide-induced oxidative stress in cultured rat hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 144:279–286
Brown JE, Rice-Evans JA (1998) Luteolin-rich artichoke extract protects low density lipoprotein from oxidation in vitro. Free Radic Res 29:247–255
Perez-Garcia F, Adzet T, Canigueral S (2000) Activity of artichoke leaf extract on reactive oxygen species in human leukocytes. Free Radic Res 33:661–665
Zapolska-Downar D, Zapolski-Downar A, Naruszewicz M, Siennicka A, Krasnodebska B, Kolodziej B (2002) Protective properties of artichoke (Cynara scolymus) against oxidative stress induced in cultered endothelial cells and monocytes. Life Sci 71:2897–2908
Juzyszyn Z, Czerny B, Pawlik A, Drozdzik M (2008) The effect of artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) extract on ROS generation in HUVEC cells. Phytother Res 22:1159–1161
Folch J, Lees M, Stanley GHS (1957) A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissues. J Biol Chem 226:497–509
Ohkawa H, Ohishi N, Yagi K (1979) Assay for lipid peroxidation in animal tissues by thiobarbituric acid reaction. Anal Biochem 95:351–358
Buege JA, Aust JD (2008) Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol 52:302–310
Mylroie AA, Collins H, Umbles C, Kyle J (1986) Erythrocyte superoxide dismutase activity and other parameters of copper status in rats ingesting lead acetate. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol 82:512–520
Paglia DE, Valentine WN (1967) Studies on the quantitative and qualitative characterization of erythrocyte glutathione peroxidase. J Lab Clin Med 70:158–169
Habig WH, Jacoby WB (1981) Assays for differentation of glutathione S-transferases. Methods Enzymol 77:398–405
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano M, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Beutler E, Duron O, Kelly BM (1979) Improved method for the determination of blood glutathione. J Lab Clin Med 61:882–888
Desai D (2000) Vitamin E analysis methods for animal tissues. Methods Enzymol 105:138–147
Omaye ST, Turnbull JD, Sauberlich HE (1979) Selected methods for the determination of ascorbic acid in animal cells, tissues and fluids. Methods Enzymol 62:3–8
Gebhardt R (1998) Inhibition of cholesterol biosynthesis in primary cultered rat hepatocytes by artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) extracts. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 286:1122–1128
Jimenez-Escrig A, Dragsted LO, Daneshvar B, Pulido R, Saura-Calixto F (2003) In vitro antioxidant activities of edible artichoke (Cynara scolymus L.) and effect on biomarkers of antioxidants in rats. J Agric Food Chem 51:5540–5545
Lupattelli G, Marchesi S, Lombardini R, Roscini AR, Trinca F, Gemelli F, Vaudo G, Mannarino E (2004) Artichoke juice improves endothelial function in hyperlipemia. Life Sci 76:775–782
Englisch W, Beckers C, Unkauf M, Ruepp M, Zinserling V (2000) Efficacy of artichoke dry extract in patients with hyperlipoproteinemia. Arzneim-Forsch/Drug Res 50:260–265
Bundy R, Walker AF, Middleton RW, Wallis C, Simpson HCR (2008) Artichoke leaf extract (Cynara scolymus) reduces plasma cholesterol in otherwise healthy hypercholesterolemic adults: a randomized, double blind placebo controlled trial. Phytomedicine 15:668–675
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Research Fund of Istanbul University (BYP 2316). The authors thank Ari Engineering for their kind gift of ALE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Küçükgergin, C., Aydın, A.F., Özdemirler-Erata, G. et al. Effect of Artichoke Leaf Extract on Hepatic and Cardiac Oxidative Stress in Rats Fed on High Cholesterol Diet. Biol Trace Elem Res 135, 264–274 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8484-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12011-009-8484-9