Abstract
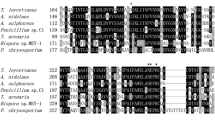
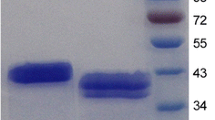
A gene encoding a highly thermostable β-mannanase from a thermophilic Bacillus subtilis (TBS2) was successfully expressed in Pichia pastoris. The maximum activity of the recombinant thermostable β-mannanase (ReTMan26) was 5435 U/mL, which was obtained by high-density, fed-batch cultivation after 168-h induction with methanol in a 50-L bioreactor. The protein yield reached 3.29 mg/mL, and the protein had a molecular weight of ~42 kDa. After fermentation, ReTMan26 was purified using a 10-kDa cut-off membrane and Sephadex G-75 column. The pH and temperature optima of purified ReTMan26 were pH 6.0 and 60 °C, respectively, and the enzyme was stable at pH 2.0–8.0 and was active at 20–100 °C. HPLC analysis of the products of locust bean gum hydrolysis showed that the mannan-oligosaccharide content was 62.5%. ReTMan26 retained 58.6% of its maximum activity after treatment at 100 °C for 10 min, which was higher than any other β-mannanase reported up to now, suggesting its potential for industrial applications.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chauhan, P. S., Puri, N., Sharma, P., & Gupta, N. (2012). Mannanases: microbial sources, production, properties and potential biotechnological applications. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 93, 1817–1830.
Akita, M., Takeda, N., & Hirasawa, K. (2004). Crystallization and preliminary X-ray study of alkaline mannanase from an alkaliphilic Bacillus isolate. Acta Crystallographica. Section D, Biological Crystallography, 60, 1490–1492.
Dhawan, S., & Kaur, J. (2007). Microbial mannanases: an overview of production and applications. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology, 27, 197–216.
Yu, S., Li, Z., Wang, Y., Chen, W., & Lin, F. (2015). High-level expression and characterization of a thermophilic β-mannanase from Aspergillus niger in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology Letters, 37, 1853–1859.
Hirst, E. L., Jones, J. K. N. (1948). The galactomannan of carob-seed gum (gum gatto). J. Chem. Soc, 1278–1282
Katsuraya, K., Okuyamab, K., Hatanakab, K., Oshimab, R., Satoc, T., & Matsuzakic, K. (2003). Constitution of konjac glucomannan: chemical analysis and 13C NMR spectroscopy. Carbohydrate Polymers, 53, 183–189.
Petkowicz, C. L. O., Reicher, F., Chanzy, H., Taravel, F. R., & Vuong, R. (2001). Linear mannan in the endosperm of Schizolobium amazonicum. Carbohyd Polym, 44, 107–112.
McCleary, B. V. (1988). β-Mannanase. Method Enzymol, 160, 596–610.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Yoon, K. H., Chung, S., & Lim, B. L. (2008). Characterization of the Bacillus subtilis WL-3 mannanase from a recombinant Escherichia coli. Journal of Microbiology, 46, 344–349.
Puchart, V., Vršanská, M., Svoboda, P., Pohl, J., Ögel, Z. B., & Biely, P. (2004). Purification and characterization of two forms of endo-beta-1,4-mannanase from a thermotolerant fungus, Aspergillus fumigatus IMI 385708 (formerly Thermomyces lanuginosus IMI 158749). Biochimica et Biophysica Acta, 1674, 239–250.
Zhang, Y. L., Ju, J. S., Peng, H., Gao, F., Zhou, C., Zeng, Y., Xue, Y. F., Li, Y., Henrissat, B., Gao, G. F., & Ma, Y. H. (2008). Biochemical and structural characterization of the intracellular mannanase AaManA of Alicyclobacillus acidocaldarius reveals a novel glycoside hydrolase family belonging to clan GH-A. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 283, 31551–31558.
Zhao, W., Zheng, J., & Zhou, H. (2011). A thermotolerant and cold-active mannan endo-1,4-β-mannosidase from Aspergillus niger CBS513.88: constitutive overexpression and high density fermentation in Pichia pastoris. Bioresource Technology, 102, 7538–7547.
Luo H., Wang Y., Wang H., Yang J., Yang Y., et al.(2009). A novel highly acidic beta-mannanase from the acidophilic fungus Bispora sp. MEY-1: gene cloning and overexpression in Pichia pastoris. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 82,453–461.
Kjeldsen, T., Pettersson, A. F., & Hach, M. (1999). Secretory expression and characterization of insulin in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology and Applied Biochemistry, 29, 79–86.
Van Dijl, J. M., Braun, P. G., Robinson, C., Quax, W. J., Antelmann, H., et al. (2002). Functional genomic analysis of the Bacillus subtilis Tat pathway for protein secretion. Journal of Biotechnology, 98, 243–254.
Mendoza, N. S., Arai, M., Kawaguchi, T., Yoshida, T., & Joson, L. M. (1994). Purification and properties of mannanase from Bacillus subtilis. World Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology, 5, 551–555.
Lv, J., Chen, Y., Pei, H., Yang, W., Li, Z., Dong, B., & Cao, Y. (2013). Cloning, expression, and characterization of β-mannanase from Bacillus subtilis MAFIC-S11 in Pichia pastoris. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology, 169, 2326–2340.
Li, J.-F., Zhao, S.-G., Tang, C.-D., Wang, J.-Q., & Wu, M.-C. (2012). Cloning and functional expression of an acidophilic β-mannanase gene (Anman5A) from Aspergillus niger LW-1 in Pichia pastoris. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 60, 765–773.
Wu, M., Tang, C., Li, J., Zhang, H., & Guo, J. (2011). Bimutation breeding of Aspergillus niger strain for enhancing β-mannanase production by solid-state fermentation. Carbohydrate Research, 346, 2149–2155.
Fliedrova, B., Gerstorferova, D., Kren, V., & Weignerova, L. (2012). Production of Aspergillus niger β-mannosidase in Pichia pastoris. Protein Expression and Purification, 85, 159–164.
Yu, S., Li, Z., Wang, Y., Chen, W., Lin, F., Tang, W., Chen, C., Liu, Y., Xue, Z., & Ma, L. (2015). High-level expression and characterization of a thermophilic β-mannanase from Aspergillus niger in Pichia pastoris. Biotechnology Letters, 37, 1853–1859.
Yang, H., Shi, P., Lu, H., Wang, H., Luo, H., Huang, H., Yang, P., & Yao, B. (2015). A thermophilic β-mannanase from Neosartorya fischeri P1 with broad pH stability and significant hydrolysis ability of various mannan polymers. Food Chemistry, 173, 283–289.
Ramachandran, P., Zhao, Z., Singh, R., Dhiman, S. S., et al. (2014). Characterization of a β-1,4-mannanase from a newly isolated strain of Pholiota adiposa and its application for biomass pretreatment. Bioprocess and Biosystems Engineering, 37, 1817–1824.
Zhou, J., Zhang, R., Gao, Y., Li, J., Tang, X., et al. (2012). Novel low-temperature-active, salt-tolerant and proteases-resistant endo-1,4-β-mannanase from a new Sphingomonas strain. Journal of Bioscience and Bioengineering, 5, 568–574.
Ghosh, A., Luís, A. S., Brás, J. L. A., Fontes, C. M. G. A., & Goyal, A. (2013). Thermostable recombinant β-(1→4)-mannanase from C. thermocellum: biochemical characterization and manno-oligosaccharides production. J. Agric. Food Chemistry, 61, 12333–12344.
Moreira, L. R., & Filho, E. X. (2008). An overview of mannan structure and mannan-degrading enzyme systems. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 79, 165–178.
Malherbe, A. R., Rose, S. H., Viljoen-Bloom, M., & van Zyl, W. H. (2014). Expression and evaluation of enzymes required for the hydrolysis of galactomannan. Journal of Industrial Microbiology & Biotechnology, 41, 1201–1209.
Choct, M., & Annison, G. (1992). The inhibition of nutrient digestion by wheat pentosans. The British Journal of Nutrition, 67, 123–132.
Jackson, M. E., Fodge, D. W., & Hsiao, H. Y. (1999). Effects of β-mannanase in corn-soybean meal diets on laying hen performance. Poultry Science, 78, 1737–1741.
Agrawal, P., Verma, D., & Daniell, H. (2011). Expression of Trichoderma reesei β-mannanase in tobacco chloroplasts and its utilization in lignocellulosic woody biomass hydrolysis. PloS One, 6, 1–10.
Stetter, K. O. (1996). Hyperthermophiles in the history of life. Ciba Foundation Symposium, 202, 1–18.
Tang, X., Wang, Z., & Zhuge, J. (2001). High thermostable extremozymes for industrial application (in Chinese). Food and Fermentation Industries, 27, 65–70.
Maijala, P., Kango, N., Szijarto, N., & Viikari, L. (2012). Characterization of hemicellulases from thermophilic fungi. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek, 101, 905–917.
Miller, G. L. (1959). Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Analytical Chemistry, 31, 426–428.
Chen, X. L., Cao, Y. H., Ding, Y. H., Lu, W. Q., & Li, D. F. (2007). Cloning, functional expression and characterization of Aspergillus sulphureus β-mannanase in Pichia pastoris. Journal of Biotechnology, 128, 452–461.
Summpunn, P., Chaijan, S., Isarangkul, D., Wiyakrutta, S., & Meevootisom, V. (2011). Characterization, gene cloning, and heterologous expression of β-mannanase from a thermophilic Bacillus subtilis. Journal of Microbiology, 49, 86–93.
Macauley, S., Fazenda, M. L., McNeil, B., & Harvey, L. M. (2005). Heterologous protein production using the Pichia pastoris as expression system. Yeast, 22, 249–270.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the open project of Key Laboratory of Industrial Biotechnology, Ministry of Education, Jiangnan University (grant no. KLIB-KF201510), and the Fundamental Research Funds for the Central Universities (grant no. JUSRP111A24), the 111 Project (No. 111-2-06).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Luo, Z., Miao, J., Li, G. et al. A Recombinant Highly Thermostable β-Mannanase (ReTMan26) from Thermophilic Bacillus subtilis (TBS2) Expressed in Pichia pastoris and Its pH and Temperature Stability. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 182, 1259–1275 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2397-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-017-2397-4