Abstract
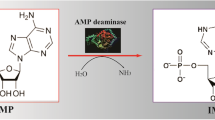
Adenylate deaminase (AMPD, EC 3.5.4.6) is an aminohydrolase that widely used in the food and medicine industries. In this study, the gene encoding Aspergillus oryzae AMPD was cloned and expressed in Escherichia coli. Induction with 0.75 mM isopropyl β-d-l-thiogalactopyranoside resulted in an enzyme activity of 1773.9 U/mL. Recombinant AMPD was purified to electrophoretic homogeneity using nickel affinity chromatography, and its molecular weight was calculated as 78.6 kDa. Purified AMPD exhibited maximal activity at 35 °C, pH 6.0 and 30 mM K+, with apparent K m and V max values of 2.7 × 10−4 M and 77.5 μmol/mg/min under these conditions. HPLC revealed that recombinant AMPD could effectively catalyse the synthesis of inosine-5′-monophosphate (IMP) with minimal by-products, indicating high specificity and suggesting that it could prove useful for IMP production.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asano, Y., Mihara, Y., & Yamada, H. (1999). A new enzymatic method of selective phosphorylation of nucleosides. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 6, 271–277.
Bradford, M. M. (1976). A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Analytical Biochemistry, 72, 248–254.
Cheng, L. F., Mu, W. M., Zhang, T. and Jiang, B. (2010) An L-arabinose isomerase from Acidothermus cellulolytics ATCC 43068: cloning, expression, purification, and characterization. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 86, 1089–1097.
Liu J, Duan Z, Shen M and Mao Z (2002) Production of AMP deaminase by solid-state fermentation. Ind Microbiol, 36–39.
Kim, M. H., Lee, J. K., Kim, H. K. and Oh, T. K. (1999) Isolation, purification, and partial characterization of an AMP deaminase from Saccharomyces cerevisiae D. J Microbiol Biotechn, 9, 429–435.
Liu, Z. Q., Zhang, L., Sun, L. H., Li, X. J., Wan, N. W., & Zheng, Y. G. (2012). Enzymatic production of 5ʹ-inosinic acid by a newly synthesised acid phosphatase/phosphotransferase. Food Chemistry, 134, 948–956.
Lushchak, V. I. (1996). Functional role and properties of AMP-deaminase. Biochemistry (Moscow), 61, 195–211.
Maniatis, T., Fritsch, E. F. and Sambrook, J. (1982) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. ed. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Cold Spring Harbor, NY.
Marquez-Rios, E., Pacheco-Aguilar, R., Castillo-Yanez, F. J., Figueroa-Soto, C. G., Ezquerra-Brauer, J. M., & Gollas-Galvan, T. (2008). Isolation and properties of AMP deaminase from jumbo squid (Dosidicus gigas) mantle muscle from. The Gulf of California, Mexico. Food Chemistry, 110, 69–75.
Martini, D., Montali, U., Ranieri-Raggi, M., Sabbatini, A. R. M., Thorpe, S. J., Moir, A. J. G., & Raggi, A. (2004). A calpain-like proteolytic activity produces the limited cleavage at the N-terminal regulatory domain of rabbit skeletal muscle AMP deaminase: evidence of a protective molecular mechanism. Bba-Proteins Proteom, 1702, 191–198.
Mei, G., Guo, Y., Rao, S., Zhang, X., P, L., Zhongyong, Y., & Ju, L. (2013). Screening of high-yield 5′-AMP deaminase strains from natural fermented sufu. China Brewing, 32, 30–34.
Meyer, S. L., Kvalnes-Krick, K. L., & Schramm, V. L. (1989). Characterization of AMD, the AMP deaminase gene in yeast. Production of amd strain, cloning, nucleotide sequence, and properties of the protein. Biochemistry, 28, 8734–8743.
Mihara, Y., Ishikawa, K., Suzuki, E. I., & Asano, Y. (2004). Improving the pyrophosphate-inosine phosphotransferase activity of Escherichia blattae acid phosphatase by sequential site-directed mutagenesis. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 68, 1046–1050.
Ranieri-Raggi, M., Martini, D., Sabbatini, A. R. M., Moir, A. J. G. and Raggi, A. (2003) Isolation by zinc-affinity chromatography of the histidine-proline-rich-glycoprotein molecule associated with rabbit skeletal muscle AMP deaminase—evidence that the formation of a protein-protein complex between the catalytic subunit and the novel component is critical for the stability of the enzyme. Bba-Proteins Proteom, 1645, 81–88.
Song, W., Niu, P. Q., Chen, X. L., & Liu, L. M. (2014). Enzymatic production of L-ornithine from L-arginine with recombinant thermophilic arginase. Journal of Molecular Catalysis B: Enzymatic, 110, 1–7.
Thompson, A., Hall, C., Karunakaran, T., & Gunasekaran, M. (1998). Properties of adenosine monophosphate deaminase of Candida albicans. Microbios, 96, 133–139.
Versavaud, A., Courcoux, P., Roulland, C., Dulau, L., & Hallet, J. N. (1995). Genetic diversity and geographical distribution of wild Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains from the wine-producing area of Charentes, France. Applied and Environmental Microbiology, 61, 3521–3529.
Wei F, Zhang L, Gu Z, Ding C and Shi G. (2014) Constitutive expression of AMP deaminase from Streptomyces murinus in Pichia pastoris GS115 using the GAP promoter. Microb China, 2022–2028.
Guo Z, Zhang L, Li Y, Li Y, Gu Z, Ding Z and Shi G. (2015) Expression of Adenosine Deaminase in Recombinant Bacillus subtilis. Food Science, 135–139.
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by Guangxi Natural Science Foundation (2015GXNSFBA139064), Fund of Guangxi Academy of Sciences (15YJ22SW05), the fund of Key Lab of Local Agricultural Product Depth Processing and Food Security Guarantee and the “Bagui Scholars Distinguished Professor” Special Project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary Table 1
(DOCX 18 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, S., Qian, Y., Liang, Y. et al. Overproduction, Purification and Characterization of Adenylate Deaminase from Aspergillus oryzae . Appl Biochem Biotechnol 180, 1635–1643 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2192-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2192-7