Abstract
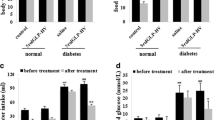
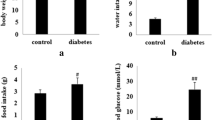
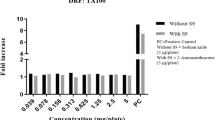
5rolGLP-HV had an ideal therapeutic potential in the prevention of hyperglycemia in type 2 diabetes and delay of the thrombosis. The objective of the study was to investigate the toxicology effects of 5rolGLP-HV and guarantee its safety. In acute toxicity test, the mice were orally receiving 5rolGLP-HV at a single dose of 300 mg/kg or 2000 mg/kg. For sub-chronic toxicity study, the mice received 5rolGLP-HV at doses of 800 mg/kg or 1600 mg/kg for 9 weeks. No significant adverse effects were evident in acute and sub-chronic toxicity tests, indicating that the LD50 value is greater than 2000 mg/kg. Although the liver and kidney exhibited a little abnormal in sub-chronic toxicity study, they could recovery to normal after withdrawal 5rolGLP-HV for 2 weeks. In micronucleus assay, the mice received 5rolGLP-HV at doses of 250, 500, or 1000 mg/kg for two consecutive days. The micronucleus numbers and the polychromatic erythrocytes to normochromatic erythrocytes (PCE/NCE) ratios among 5rolGLP-HV groups were within the normal range. Similarly, sperm aberration test demonstrated that 5rolGLP-HV had no teratogenic effect on the mice sperm. In conclusion, the combined results clearly demonstrated the safety of 5rolGLP-HV and support its use as a drug to treat diabetes and thrombosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
Reference
Ni, Z., Zhang, Y., Wang, H., Wei, Y., Ma, B., Hao, J. et al (2016). Construction of a fusion peptide 5rolGLP-HV and analysis of its therapeutic effect on type 2 diabetes mellitus and thrombosis in mice. Applied Biochemistry and Biotechnology.
Yu, Y., Wang, X., Liu, C., Yao, D., Hu, M., Li, J., et al. (2013). Combined contributions of over-secreted glucagon-like peptide 1 and suppressed insulin secretion to hyperglycemia induced by gatifloxacin in rats. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 266(3), 375–384.
Ranganath, L. R. (2008). Incretins: pathophysiological and therapeutic implications of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1. Journal of Clinical Pathology, 61(4), 401–409.
Doyle, M. E., & Egan, J. M. (2007). Mechanisms of action of glucagon-like peptide 1 in the pancreas. Pharmacology & Therapeutics, 113(3), 546–593.
Campbell, J. E., & Drucker, D. J. (2013). Pharmacology, physiology, and mechanisms of incretin hormone action. Cell Metabolism, 17(6), 819–837.
Henry, R. R., Logan, D., Alessi, T., & Baron, M. A. (2013). A randomized, open-label, multicenter, 4-week study to evaluate the tolerability and pharmacokinetics of ITCA 650 in patients with type 2 diabetes. Clinical Therapeutics, 35(5), 634–645 e631.
Hou, J., Yan, R., Ding, D., Yang, L., Wang, C., Wu, Z., et al. (2007). Oral administration of a fusion protein containing eight GLP-1 analogues produced in Escherichia coli BL21(DE3) in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Biotechnology Letters, 29(10), 1439–1446.
Hou, J., Yan, R., Yang, L., Wu, Z., Wang, C., Ding, D., et al. (2007). High-level expression of fusion protein containing 10 tandem repeated GLP-1 analogs in yeast Pichia Pastoris and its biological activity in a diabetic rat model. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry, 71(6), 1462–1469.
Tu, P., Ma, Z., Wang, H., Ma, B., Li, X., Duan, H., et al. (2015). Expression of CTB-10xrolGLP-1 in E. coli and its therapeutic effect on type 2 diabetes. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology, 16(6), 564–572.
Ma, B., Hu, X., Zhao, X., Zhang, Y., Li, C., Ma, Z., et al. (2014). Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and cytotoxicity of recombinant orally-administrated long-lasting GLP-1 and its therapeutic effect on db/db mice. Experimental and Clinical Endocrinology and Diabetes, 122(4), 215–221.
Zhao, L., Liao, F., Wang, C. Y., Chen, M., Wei, A. M., Du, S. L., et al. (2009). Generation of transgenic cucumbers with expression of a ten-tandem repeat long-acting GLP-1 analogue and their biological function on diabetic rats. Chinese Science Bulletin, 54(24), 4658–4663.
Ou, Y., Liao, G. Y., & Wu, W. T. (2008). Potential use of hirudin in diabetic cataract: a study of galactose mediated human lens epithelial cells injury. Chemico-Biological Interactions, 173(2), 141–147.
Cen, X., Ni, J., Tan, T., Liu, X., Li, C., Chen, J., et al. (2006). Investigation on recombinant hirudin via oral route. Peptides, 27(4), 836–840.
Warkentin, T. E. (2004). Bivalent direct thrombin inhibitors: hirudin and bivalirudin. Best Practice & Research. Clinical Haematology, 17(1), 105–125.
Wang, X. D., Hu, J. J., Pan, D. T., Teng, H., & Xiu, Z. L. (2014). PEGylation kinetics of recombinant hirudin and its application for the production of PEGylated HV2 species. Biochemical Engineering Journal, 8538–8548.
Donges, R., & Brazel, D. (2002). Determination of recombinant hirudin structural deviants by capillary zone electrophoresis augmented with buffer additives. Journal of Chromatography. A, 979(1–2), 217–226.
Kochanowski, R., Kotlowski, R., & Szweda, P. (2006). Novel method of expression and purification of hirudin based on pBAD TOPO, pTYB12 vectors and gene synthesis. Protein Expression and Purification, 50(1), 25–30.
Liu, Y., Lu, W. L., Zhang, X., Wang, X. Q., Zhang, H., & Zhang, Q. (2005). Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics of recombinant hirudin via four non-parenteral routes. Peptides, 26(3), 423–430.
Rouse, R., Xu, L., Stewart, S., & Zhang, J. (2014). High fat diet and GLP-1 drugs induce pancreatic injury in mice. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 276(2), 104–114.
Zhang, L. W., Tobin, G. A. M., & Rouse, R. L. (2012). Oleic acid and glucose regulate glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor expression in a rat pancreatic ductal cell line. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology, 264(2), 274–283.
Nachnani, J. S., Bulchandani, D. G., Nookala, A., Herndon, B., Molteni, A., Pandya, P., et al. (2010). Biochemical and histological effects of exendin-4 (exenatide) on the rat pancreas. Diabetologia, 53(1), 153–159.
Butler, A. E., Campbell-Thompson, M., Gurlo, T., Dawson, D. W., Atkinson, M., & Butler, P. C. (2013). Marked expansion of exocrine and endocrine pancreas with incretin therapy in humans with increased exocrine pancreas dysplasia and the potential for glucagon-producing neuroendocrine tumors. Diabetes, 62(7), 2595–2604.
Dore, D. D., Seeger, J. D., & Chan, K. A. (2009). Use of a claims-based active drug safety surveillance system to assess the risk of acute pancreatitis with exenatide or sitagliptin compared to metformin or glyburide. Current Medical Research and Opinion, 25(4), 1019–1027.
Drucker, D. J., Sherman, S. I., Gorelick, F. S., Bergenstal, R. M., Sherwin, R. S., & Buse, J. B. (2010). Incretin-based therapies for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: evaluation of the risks and benefits. Diabetes Care, 33(2), 428–433.
Matveyenko, A. V., Dry, S., Cox, H. I., Moshtaghian, A., Gurlo, T., Galasso, R., et al. (2009). Beneficial endocrine but adverse exocrine effects of sitagliptin in the human islet amyloid polypeptide transgenic rat model of type 2 diabetes interactions with metformin. Diabetes, 58(7), 1604–1615.
Ayoub, W. A., Kumar, A. A., Naguib, H. S., & Taylor, H. C. (2010). Exenatide-induced acute pancreatitis. Endocrine Practice, 16(1), 80–83.
Denker, P. S., & Dimarco, P. E. (2006). Exenatide (exendin-4)-induced pancreatitis: a case report. Diabetes Care, 29(2), 471.
Anderson, S. L., & Trujillo, J. M. (2010). Association of Pancreatitis with glucagon-like peptide-I agonist use. Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 44(5), 904–909.
Elashoff, M., Matveyenko, A. V., Gier, B., Elashoff, R., & Butler, P. C. (2011). Pancreatitis, pancreatic, and thyroid cancer with glucagon-like peptide-1-based therapies. Gastroenterology, 141(1), 150–156.
Li, X. C., Zhang, Z. Y., & Duke, J. (2014). Glucagon-like peptide 1-based therapies and risk of pancreatitis: a self-controlled case series analysis. Pharmacoepidemiology Drug Safety, 23(3), 234–239.
Dager, W. E., & White, R. H. (2002). Treatment of heparin-induced thrombocytopenia. The Annals of Pharmacotherapy, 36(3), 489–503.
Babicek, K., Cechova, I., Simon, R. R., Harwood, M., & Cox, D. J. (2007). Toxicological assessment of a particulate yeast (1,3/1,6)-beta-D-glucan in rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 45(9), 1719–1730.
Yee, S., Burdock, G. A., Kurata, Y., Enomoto, Y., Narumi, K., Hamada, S., et al. (2008). Acute and subchronic toxicity and genotoxicity of SE5-OH, an equol-rich product produced by Lactococcus garvieae. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 46(8), 2713–2720.
Morsy, M. A., Heeba, G. H., & Mahmoud, M. E. (2015). Ameliorative effect of eprosartan on high-fat diet/streptozotocin-induced early diabetic nephropathy in rats. European Journal of Pharmacology, 75090–75097.
Zhang, J., Gao, X., Pan, Y., Xu, N., & Jia, L. (2016). Toxicology and immunology of Ganoderma lucidum polysaccharides in Kunming mice and Wistar rats. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 85302–85310.
Huang, Q., Ihsan, A., Guo, P., Luo, X., Cheng, G., Hao, H., et al. (2016). Evaluation of the safety of primary metabolites of cyadox: acute and sub-chronic toxicology studies and genotoxicity assessment. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 74123–74136.
Zaveri, N. T. (2006). Green tea and its polyphenolic catechins: medicinal uses in cancer and noncancer applications. Life Sciences, 78(18), 2073–2080.
Segersvard, R., Sylvan, M., Herrington, M., Larsson, J., & Permert, J. (2001). Obesity increases the severity of acute experimental pancreatitis in the rat. Scandinavian Journal of Gastroenterology, 36(6), 658–663.
Shin, K. Y., Lee, W. S., Chung, D. W., Heo, J., Jung, M. K., Tak, W. Y., et al. (2011). Influence of obesity on the severity and clinical outcome of acute pancreatitis. Gut Liver, 5(3), 335–339.
Flammang, A. M., Erexson, G. L., Mirwald, J. M., & Henwood, S. M. (2007). Toxicological and cytogenetic assessment of a Salacia oblonga extract in a rat subchronic study. Food and Chemical Toxicology, 45(10), 1954–1962.
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by the Key Technologies R&D Program of Tianjin (14ZCZDSY00013).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The experiments were approved and supervised by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee of Nankai University.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ni, Z., Wang, B., Ma, X. et al. Toxicology Assessment of a Dual-Function Peptide 5rolGLP-HV in Mice. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 180, 1276–1285 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2166-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12010-016-2166-9